Abstract
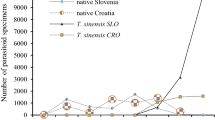
We describe here the parasitoid wasps Torymus sinensis Kamijo and T. beneficus Yasumatsu & Kamijo (early-spring and late-spring strains), which are introduced and indigenous natural enemies of the chestnut gall wasp Dryocosmus kuriphilus Yasumatsu, an invasive chestnut pest in Japan. We recently discovered specimens of T. koreanus Kamijo, endemic in Korea, among Torymus parasitoids collected from D. kuriphilus galls in a Japanese chestnut orchard. In this study we compare the composition of Torymus parasitoids emerging from D. kuriphilus galls before and after the release of T. sinensis. Before the release of T. sinensis, early-spring and late-spring strains of T. beneficus predominated (58.3 and 20.8% of specimens collected). However, a few years after the release, both T. beneficus strains had been almost completely displaced by T. sinensis. In contrast to the rapid decrease in T. beneficus, T. koreanus did not decrease drastically before and even after the release of T. sinensis (approximately 10–20% of specimens collected). These results suggest that not a few T. koreanus were present in the Japanese chestnut orchard investigated at least several years after the release of T. sinensis, although both the T. beneficus strains were rapidly displaced by T. sinensis during this period.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cho DY, Lee SO (1963) Ecological studies on the chestnut gall wasp, Dryocosmus kuriphilus Yasumatsu, and observations on the damages of the chestnut trees by its insect. Korean J Plant Prot 2:47–54 (in Korean with English summary)
Gibbs M, Schönrogge K, Alma A, Melika G, Quacchia A, Stone GN, Aebi A (2011) Torymus sinensis: a viable management option for the biological control of Dryocosmus kuriphilus in Europe? Biocontrol 56:527–538
Grissell EE (1995) Toryminae (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea: Torymidae): a redefinition, generic classification, and annotated world catalog of species. Memoirs on Entomology, International Volume 2. Associated Publishers, Florida
Izawa H, Osakabe Mh, Moriya S (1992) Isozyme discrimination between an imported parasitoid wasp, Torymus sinensis Kamijo and its sibling species, T. beneficus Yasumatsu et Kamijo (Hymenoptera: Torymidae), attacking Dryocosmus kuriphilus Yasumatsu (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae). Jpn J Appl Entomol Zool 36:58–60 (in Japanese with English summary)
Izawa H, Osakabe Mh, Moriya S, Toda S (1996) Use of malic enzyme to detect hybrids between Torymus sinensis and T. beneficus (Hymenoptera: Torymidae) attacking Dryocosmus kuriphilus (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae) and possibility of natural hybridization. Jpn J Appl Entomol Zool 40:205–208 (in Japanese with English summary)
Kamijo K (1982) Two new species of Torymus (Hymenoptera, Torymidae) reared from Dryocosmus kuriphilus (Hymenoptera, Cynipidae) in China and Korea. Kontyû (Tokyo) 50:505–510
Matsuo K, Yara K, Kagoshima K, Tuda M, Moriya S (2011) Finding of Torymus koreanus (Hymenoptera: Torymidae) attacking Dryocosmus kuriphilus (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae) in Japan. Entomol Sci 14:100–102
Moriya S, Inoue K, Mabuchi M (1989) The use of Torymus sinensis to control chestnut gall wasp, Dryocosmus kuriphilus, in Japan. FFTC Tech Bull 118:1–12
Moriya S, Inoue K, Shiga M, Mabuchi M (1992) Interspecific relationship between an introduced parasitoid, Torymus sinensis Kamijo, as a biological control agent of the chestnut gall wasp, Dryocosmus kuriphilus Yasumatsu, and an endemic parasitoid, Torymus beneficus Yasumatsu et Kamijo. Acta Phytopathol Entomol Hung 27:479–483
Moriya S, Shiga M, Adachi I (2003) Classical biological control of the chestnut gall wasp in Japan. In: van Driesche RG (ed) Proceedings of the 1st international symposium on biological control of arthropods, Honolulu, Hawaii, 14–18 January 2002. United States Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Washington, pp 407–415
Murakami Y (1988) Ecotypes of Torymus (Syntomaspis) beneficus Yasumatsu et Kamijo (Hymenoptera: Torymidae) with different seasonal prevalence of adult emergence. Appl Entomol Zool 23:81–87
Murakami Y (1997) Natural enemies of the chestnut gall wasp: approaches to biological control. Kyusyu University Press, Fukuoka (in Japanese)
Noyes JS (2011) Universal Chalcidoidea Database. World Wide Web electronic publication. http://www.nhm.ac.uk/chalcidoids, accessed 27 September 2011
Ôtake A (1987) Comparison of some morphological characters among two strains of Torymus beneficus Yasumatsu et Kamijo and T. sinensis Kamijo (Hymenoptera: Torymidae). Appl Entomol Zool 22:600–609
Ôtake A, Moriya S, Shiga M (1984) Colonization of Torymus sinensis Kamijo (Hymenoptera: Torymidae), a parasitoid of chestnut gall wasp, Dryocosmus kuriphilus Yasumatsu (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae), introduced from China. Appl Entomol Zool 19:111–114
Payne JA, Menke AS, Schroeder PM (1975) Dryocosmus kuriphilus Yasumatsu (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae), an oriental chestnut gall wasp in North America. Coop Econ Insect Rep 25:903–905
Piao CS, Moriya S (1992) Longevity and oviposition of Torymus sinensis Kamijo and 2 strains of T. beneficus Yasumatsu et Kamijo (Hymenoptera, Torymidae). Jpn J Appl Entomol Zool 36:113–118 (in Japanese with English summary)
Piao CS, Moriya S (1999) Oviposition of Torymus sinensis Kamijo (Hymenoptera: Torymidae) under natural conditions. Entomol Sci 2:329–334
Quacchia A, Moriya S, Bosio G, Scapin I, Alma A (2008) Rearing, release and settlement prospect in Italy of Torymus sinensis, the biological control agent of the chestnut gall wasp Dryocosmus kuriphilus. Bio Control 53:829–839
Shirai Y, Adachi I, Moriya S (1999) Records of release of Torymus sinensis Kamijo (Hymenoptera: Torymidae), an introduced biological control agent of chestnut gall wasp in Japan. Bull Natl Inst Fruit Tree Sci 33:163–178 (in Japanese with English summary)
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1995) Biometry: the principles and practice of statistics in biological research, 3rd edn. W. H. Freeman and Company, New York
Ueno W (2006) Occurrence and control of chestnut gall wasp in Nepal. Plant Prot 60:510–512 (in Japanese)
Yara K (2004) Relationship between the introduced and indigenous parasitoids Torymus sinensis and T. beneficus (Hymenoptera: Torymidae) as inferred from mt-DNA (COI) sequences. Appl Entomol Zool 39:427–433
Yara K (2006) Identification of Torymus sinensis and T. beneficus (Hymenoptera: Torymidae), introduced and indigenous parasitoids of the chestnut gall wasp Dryocosmus kuriphilus (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae), using the ribosomal ITS2 region. Biol Control 36:15–21
Yara K, Kunimi Y (2009) Discrimination of Torymus sinensis Kamijo (Hymenoptera: Torymidae) and T. beneficus Yasumatsu et Kamijo and their hybrids by allele-specific PCR. Appl Entomol Zool 44:275–280
Yara K, Yano E, Sasawaki T, Shiga M (2000) Detection of hybrids between introduced Torymus sinensis and native T. beneficus (Hymenoptera: Torymidae) in central Japan, using malic enzyme. Appl Entomol Zool 35:201–206
Yara K, Sasawaki T, Kunimi Y (2007) Displacement of Torymus beneficus (Hymenoptera, Torymidae) by T. sinensis, an indigenous and introduced parasitoid of the chestnut gall wasp, Dryocosmus kuriphilus (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae), in Japanese chestnut fields: possible involvement in hybridization. Biol Control 42:148–154
Yara K, Sasawaki T, Kunimi Y (2010) Hybridization between introduced Torymus sinensis (Hymenoptera: Torymidae) and indigenous T. beneficus (late-spring strain), parasitoids of the Asian chestnut gall wasp Dryocosmus kuriphilus (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae). Biol Control 54:14–18
Yasumatsu K, Kamijo K (1979) Chalcidoid parasites of Dryocosmus kuriphilus Yasumatsu (Cynipidae) in Japan, with description of five new species (Hymenoptera). Esakia 14:93–111
Acknowledgments
We wish to express our gratitude to Dr. M. Shiga (National Institute of Fruit Tree Science) and Dr. E. Yano (Kinki University) for providing us with the samples, in addition to their helpful comments and suggestions for the study. We appreciate the two anonymous reviewers’ comments that improved this paper immensely. This research was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (no. 19380037) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yara, K., Matsuo, K., Sasawaki, T. et al. Influence of the introduced parasitoid Torymus sinensis (Hymenoptera: Torymidae) on T. koreanus and T. beneficus as indigenous parasitoids of the chestnut gall wasp Dryocosmus kuriphilus (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae) on chestnut trees in Nagano Prefecture, Japan. Appl Entomol Zool 47, 55–60 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-011-0088-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-011-0088-0