Abstract
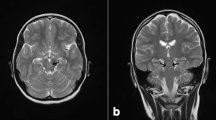
Zellweger syndrome (ZS) is a consequence of a peroxisome biogenesis disorder (PBD) caused by the presence of a pathogenic mutation in one of the 13 genes from the PEX family. ZS is a severe multisystem condition characterized by neonatal appearance of symptoms and a shorter life. Here, we report a case of ZS with a mild phenotype, due to a novel PEX6 gene mutation. The patient presented subtle craniofacial dysmorphic features and slightly slower psychomotor development. At the age of 2 years, he was diagnosed with adrenal insufficiency, hypoacusis, and general deterioration. Magnetic resonance imaging showed a symmetrical hyperintense signal in the frontal and parietal white matter. Biochemical tests showed elevated liver transaminases, elevated serum very long chain fatty acids, and phytanic acid. After the death of the child at the age of 6 years, molecular diagnostics were continued in order to provide genetic counseling for his parents. Next generation sequencing (NGS) analysis with the TruSight One™ Sequencing Panel revealed a novel homozygous PEX6 p.Ala94Pro mutation. In silico prediction of variant severity suggested its possible benign effect. To conclude, in the milder phenotypes, adrenal insufficiency, hypoacusis, and leukodystrophy together seem to be pathognomonic for ZS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barth PG, Gootjes J, Bode H, Vreken P, Majoie CB, Wanders RJ (2001) Late onset white matter disease in peroxisome biogenesis disorder. Neurology 57:1949–1955
Berendse K, Engelen M, Ferdinandusse S, Majoie CB, Waterham HR, Vaz FM, Koelman JH, Barth PG, Wanders RJ, Poll-The BT (2016) Zellweger spectrum disorders: clinical manifestations in patients surviving into adulthood. J Inherit Metab Dis 39:93–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-015-9880-2
Ebberink MS, Csanyi B, Chong WK, Denis S, Sharp P, Mooijer PA, Dekker CJ, Spooner C, Ngu LH, De Sousa C, Wanders RJ, Fietz MJ, Clayton PT, Waterham HR, Ferdinandusse S (2010) Identification of an unusual variant peroxisome biogenesis disorder caused by mutations in the PEX16 gene. J Med Genet 47:608–615. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmg.2009.074302
Ebberink MS, Mooijer PA, Gootjes J, Koster J, Wanders RJ, Waterham HR (2011) Genetic classification and mutational spectrum of more than 600 patients with a Zellweger syndrome spectrum disorder. Hum Mutat 32:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.21388
Grou CP, Carvalho AF, Pinto MP, Alencastre IS, Rodrigues TA, Freitas MO, Francisco T, Sá-Miranda C, Azevedo JE (2009) The peroxisomal protein import machinery—a case report of transient ubiquitination with a new flavor. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:254–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-8415-5
Klouwer FC, Berendse K, Ferdinandusse S, Wanders RJ, Engelen M, Poll-The BT (2015) Zellweger spectrum disorders: clinical overview and management approach. Orphanet J Rare Dis 10:151. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-015-0368-9
Krause C, Rosewich H, Thanos M, Gärtner J (2006) Identification of novel mutations in PEX2, PEX6, PEX10, PEX12, and PEX13 in Zellweger spectrum patients. Hum Mutat 27:1157. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.9462
Krause C, Rosewich H, Woehler A, Gärtner J (2013) Functional analysis of PEX13 mutation in a Zellweger syndrome spectrum patient reveals novel homooligomerization of PEX13 and its role in human peroxisome biogenesis. Hum Mol Genet 22:3844–3857. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddt238
Levesque S, Morin C, Guay SP, Villeneuve J, Marquis P, Yik WY, Jiralerspong S, Bouchard L, Steinberg S, Hacia JG, Dewar K, Braverman NE (2012) A founder mutation in the PEX6 gene is responsible for increased incidence of Zellweger syndrome in a French Canadian population. BMC Med Genet 13:72. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-13-72
Mignarri A, Vinciguerra C, Giorgio A, Ferdinandusse S, Waterham H, Wanders R, Bertini E, Dotti MT, Federico A (2012) Zellweger spectrum disorder with mild phenotype caused by PEX2 gene mutations. JIMD Rep 6:43–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/8904_2011_102
Ploski R, Pollak A, Müller S, Franaszczyk M, Michalak E, Kosinska J, Stawinski P, Spiewak M, Seggewiss H, Bilinska ZT (2014) Does p.Q247X in TRIM63 cause human hypertrophic cardiomyopathy? Circ Res 114:e2–e5. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.302662
Poll-The BT, Gootjes J, Duran M, de Klerk JB, Maillette de Buy Wenniger‐Prick LJ, Admiraal RJ, Waterham HR, Wanders RJ, Barth PG (2004) Peroxisome biogenesis disorders with prolonged survival: phenotypic expression in a cohort of 31 patients. Am J Med Genet A 126A:333–338. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.20664
Raas-Rothschild A, Wanders RJ, Mooijer PA, Gootjes J, Waterham HR, Gutman A, Suzuki Y, Shimozawa N, Kondo N, Eshel G, Espeel M, Roels F, Korman SH (2002) A PEX6-defective peroxisomal biogenesis disorder with severe phenotype in an infant, versus mild phenotype resembling Usher syndrome in the affected parents. Am J Hum Genet 70:1062–1068. https://doi.org/10.1086/339766
Régal L, Ebberink MS, Goemans N, Wanders RJ, De Meirleir L, Jaeken J, Schrooten M, Van Coster R, Waterham HR (2010) Mutations in PEX10 are a cause of autosomal recessive ataxia. Ann Neurol 68:259–263. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22035
Sevin C, Ferdinandusse S, Waterham HR, Wanders RJ, Aubourg P (2011) Autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia caused by mutations in the PEX2 gene. Orphanet J Rare Dis 6:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1172-6-8
Stradomska TJ, Tylki-Szymańska A (1996) Examination of very long chain fatty acids in diagnosis of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Pediatr Pol 71:197–201
Stradomska TJ, Tylki-Szymańska A (2009) Serum very-long-chain fatty acids levels determined by gas chromatography in the diagnosis of peroxisomal disorders in Poland. Folia Neuropathol 47:306–313
Stradomska TJ, Bachański M, Pawłowska J, Syczewska M, Stolarczyk A, Tylki-Szymańska A (2013) The impact of a ketogenic diet and liver dysfunction on serum very long-chain fatty acids levels. Lipids 48:405–409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-013-3761-y
Takemoto Y, Suzuki Y, Horibe R, Shimozawa N, Wanders RJ, Kondo N (2003) Gas chromatography/mass spectrometry analysis of very long chain fatty acids, docosahexaenoic acid, phytanic acid and plasmalogen for the screening of peroxisomal disorders. Brain Dev 25:481–487
Tran C, Hewson S, Steinberg SJ, Mercimek-Mahmutoglu S (2014) Late-onset Zellweger spectrum disorder caused by PEX6 mutations mimicking X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Pediatr Neurol 51:262–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2014.03.020
Waterham HR, Ebberink MS (2012) Genetics and molecular basis of human peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822:1430–1441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.04.006
Zeharia A, Ebberink MS, Wanders RJ, Waterham HR, Gutman A, Nissenkorn A, Korman SH (2007) A novel PEX12 mutation identified as the cause of a peroxisomal biogenesis disorder with mild clinical phenotype, mild biochemical abnormalities in fibroblasts and a mosaic catalase immunofluorescence pattern, even at 40 degrees C. J Hum Genet 52:599–606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10038-007-0157-y
Zhang Z, Suzuki Y, Shimozawa N, Fukuda S, Imamura A, Tsukamoto T, Osumi T, Fujiki Y, Orii T, Wanders RJ, Barth PG, Moser HW, Paton BC, Besley GT, Kondo N (1999) Genomic structure and identification of 11 novel mutations of the PEX6 (peroxisome assembly factor-2) gene in patients with peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Hum Mutat 13:487–496. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1999)13:6<487::AID-HUMU9>3.0.CO;2-T
Funding
The study was supported by the National Science Centre (NCN) Poland, grant number 2013/11/B/NZ7/04944.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MR and PG performed NGS analysis, TJS performed fatty acid profiling, EJ performed radiological evaluation, EJ performed clinical data collection, GK performed Sanger sequencing for replication study, RP and AT-S conceived and supervised the study, RP, AT-S, and MR drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Bioethical Committee at the Children’s Memorial Health Institute of Warsaw and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent for the genetic analysis was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Written consent was obtained for publication of the patient’s photography.
Additional information
Communicated by: Michal Witt
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rydzanicz, M., Stradomska, T.J., Jurkiewicz, E. et al. Mild Zellweger syndrome due to a novel PEX6 mutation: correlation between clinical phenotype and in silico prediction of variant pathogenicity. J Appl Genetics 58, 475–480 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-017-0414-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-017-0414-5