Abstract
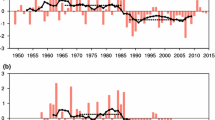
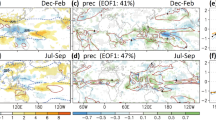
This paper presents a concise summary of the studies on interdecadal variability of the East Asian winter monsoon (EAWM) from three main perspectives. (1) The EAWM has been significantly affected by global climate change. Winter temperature in China has experienced three stages of variations from the beginning of the 1950s: a cold period (from the beginning of the 1950s to the early or mid 1980s), a warm period (from the early or mid 1980s to the early 2000s), and a hiatus period in recent 10 years (starting from 1998). The strength of the EAWM has also varied in three stages: a stronger winter monsoon period (1950 to 1986/87), a weaker period (1986/87 to 2004/05), and a strengthening period (from 2005). (2) Corresponding to the interdecadal variations of the EAWM, the East Asian atmospheric circulation, winter temperature of China, and the occurrence of cold waves over China have all exhibited coherent interdecadal variability. The upper-level zonal circulation was stronger, the mid-tropospheric trough over East Asia was deeper with stronger downdrafts behind the trough, and the Siberian high was stronger during the cold period than during the warm period. (3) The interdecadal variations of the EAWM seem closely related to major modes of variability in the atmospheric circulation and the Pacific sea surface temperature. When the Northern Hemisphere annular mode/Arctic Oscillation and the Pacific decadal oscillation were in negative (positive) phase, the EAWM was stronger (weaker), leading to colder (warmer) temperatures in China. In addition, the negative (positive) phase of the Atlantic multi decadal oscillation coincided with relatively cold (warm) temperatures and stronger (weaker) EAWMs. It is thus inferred that the interdecadal variations in the ocean may be one of the most important natural factors influencing long-term variability in the EAWM. although global warming may have also played a significant role in weakening the EAWM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bueh Cholaw and Ji Liren, 1999: Anomalous activity of East Asian winter monsoon and the tropical Pacific SST. Chin. Sci. Bull., 44, 890–898.
Chan, J. C., and C. Y. Li, 2004: The East Asian winter monsoon. East Asian Monsoon. Chang, C. P., Ed., World Scientific, Singapore, 54–106.
Chang, C. P., and K. M. Lau, 1980: Northeasterly cold surges and near-equatorial disturbances over the winter MONEX area during December 1974. Part II: Planetary-scale aspect. Mon. Wea. Rev., 108, 298–312.
—, and —, 1982: Short term planetary scale interaction over the tropics and the midlatitudes during northern winter. Part I: Contrast between active and inactive periods. Mon. Wea. Rev., 110, 933–946.
Chen, W., M. Takahashi, and H. F. Graf, 2003: Interannual variations of stationary planetary wave activity in the northern winter troposphere and stratosphere and their relations to NAM and SST. J. Geophys. Res., 108, doi: 10.1029/2003JD003834.
Chen Wen, 2002: Impacts of El Nino and La Nina on the cycle of the East Asian winter and summer monsoon. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 26, 595–610. (in Chinese)
—, H. F. Graf, and Huang Ronghui, 2000: The interannual variability of East Asian winter monsoon and its relationship to summer monsoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 17, 48–60.
— and Kang Lihua, 2006: Linkage between the Arctic Oscillation and winter climate over East Asia on the interannual timescale: Roles of quasi-stationary planetary waves. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 30, 863–870. (in Chinese)
Chen Shangfeng, Chen Wen, and Wei Ke, 2013: Recent trends in winter temperature extremes in eastern China and their relationship with the Arctic Oscillation and ENSO. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 30, 1712–1724, doi: 10.1007/s00376-013-2296-8.
Chen, Z., R. G. Wu, and W. Chen, 2014: Distinguishing interannual variations of the northern and southern modes of the East Asian winter monsoon. J. Climate, 27, 835–851, doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00314.1.
Deng Weitao, Sun Zhaobo, Zeng Gang, et al., 2009: Interdecadal variation of summer precipitation pattern over eastern China and its relationship with the North Pacific SST. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 33, 835–846. (in Chinese)
Ding, R., K. Ha, and J. Li, 2010: Interdecadal shift in the relationship between the East Asian summer monsoon and the tropical Indian Ocean. Climate Dyn., 34, 1059–1071.
Ding, Y. H., 1994: Monsoons over China. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht/Boston/London, 419 pp.
—, 2007: The variability of the Asian summer monsoon. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 85B, 21–54.
—, and T. N. Krishnamurti, 1987: Heat budget of the Siberian high and the winter monsoon. Mon. Wea. Rev., 115, 2428–2449.
—, and D. R. Sikka, 2006: Synoptic systems and weather. The Asian Monsoon. Wang, B., Ed., Praxis Publishing, Hong Kong, 131–201.
Ding Yihui, 2013: China Climate. China Science Press, Beijing, 557 pp. (in Chinese)
—, Sun Ying, Liu Yunyun, et al., 2013: Interdecadal and interannual variabilities of the Asian summer monsoon and its projection of future change. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 37, 253–280. (in Chinese)
Easterling, D. R., and M. F. Wehner, 2009: Is the climate warming or cooling? Geophys. Res. Lett., 36, L08706, doi: 10.1029/2009GL037810.
Gong, D. Y., S. W. Wang, and J. H. Zhu, 2001: East Asian winter monsoon and Arctic oscillation. Geophys. Res. Lett., 28, 2073–2076.
Gong Daoyi, Zhu Jinhong, and Wang Shaowu, 2002: The influence of the Siberian high on large-scale climate over continental Asia. Plateau Meteor., 21, 8–14. (in Chinese)
Gu Lei, Wei Ke, and Huang Ronghui, 2008: Severe disaster of blizzard, freezing rain and low temperature in January 2008 in China and its association with the anomalies of East Asian monsoon system. Climatic Environ. Res., 13, 405–418. (in Chinese)
Guo Qiyun, 1994: Relationship between the variations of East Asian winter monsoon and temperature anomalies in China. J. Appl. Meteor. Sci., 5, 218–224. (in Chinese)
He Shengping and Wang Huijun, 2012: An integrated East Asian winter monsoon index and its inter-annual variability. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 36, 523–538. (in Chinese)
—, 2013: Reduction of the East Asian winter monsoon interannual variability after the mid 1980s and possible cause. Chin. Sci. Bull., 58, 1331–1338.
He Xicheng, Ding Yihui, and He Jinhai, 2008: Response characteristics of the East Asian winter monsoon to ENSO events. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 32, 335–344. (in Chinese)
Huang Ronghui, Chen Wen, Ding Yihui, et al., 2003: Studies on the monsoon dynamics and the interaction between monsoon and ENSO cycle. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 27, 484–502. (in Chinese)
—, Chen Jilong, and Huang Gang, 2007a: Characteristics and variations of the East Asian monsoon system and its impacts on climate disasters in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 24, 993–1023.
—, Wei Ke, Chen Jilong, et al., 2007b: The East Asian winter monsoon anomalies in the winters of 2005/2006 and their relations to the quasi-stationary planetary wave activity in the Northern Hemisphere. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 31, 1033–1048. (in Chinese)
—, Chen Jilong, Wang Lin, et al., 2012: Characteristic, processes, and causes of the spatiotemporal variabilities of the East Asian monsoon system. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 29, 910–942.
Jhun, J. G., and E. J. Lee, 2004: A new East Asian winter monsoon index and associated characteristics of the winter monsoon. J. Climate, 17, 711–726.
Ji Liren, Sun Shuqing, K. Arpe, et al., 1997: Model study on the interannual variability of Asian winter monsoon and its influence. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 14, 1–22.
Jin Zuhui and Sun Shuqing, 1996: Characteristics of low frequency oscillation of the East Asian winter monsoon. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 20, 101–111. (in Chinese)
Kang Lihua, Chen Wen, and Wei Ke, 2006: The interdecadal variation of winter temperature in China and its relation to the anomalies in atmospheric general circulation. Climatic Environ. Res., 11, 330–339. (in Chinese)
Kerr, R. A., 2009: What happened to global warming? Scientists say just wait a bit. Science, 326, 28–29.
Knight, J., J. J. Kennedy, C. Folland, et al., 2009: Do global temperature trends over the last decade falsify climate prediction? Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 90, S22–23.
Krishnamurti, T. N., 1979: Tropical Meteorology. Translated by Liu Chongjian and Zhu Bocheng. China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 284 pp. (in Chinese)
Lau, N. C., and K. M. Lau, 1984: The structure and energetics of midlatitude disturbances accompanying cold-air outbreaks over East Asia. Mon. Wea. Rev., 112, 1309–1327.
Li Chongyin, 1989a: El Niño events and the temperature anomalies in eastern China. J. Trop. Meteor., 5, 210–219. (in Chinese)
—, 1989b: Warmer winter in eastern China and El Niño. Chinese Sci. Bull., 34, 1801–1805.
—, 1989c: Frequent activities of stronger aerotroughs in East Asia wintertime and the occurrence of the El Niño event. Sci. China (Ser. B), 32, 976–985.
—, Sun Shuqing, and Mu Mingquan, 2001: Origin of the TBO-Interaction between anomalous East Asian winter monsoon and Enso cycle. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 18, 554–566.
—, and Xian Peng, 2003: Atmospheric anomalies related to interdecadal variability of SST in the North Pacific. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 20, 859–874.
—, Wang Liqun, and Gu Wei, 2011: Interannual time-scale relationship between Mongolian high and SST anomaly in the North Pacific in winter. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 35, 193–200. (in Chinese)
Li Fei and Wang Huijun, 2012: Predictability of the East Asian winter monsoon interannual variability as indicated by the DEMETER CGCMS. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 29, 441–454.
Li Shuanglin and G. T. Bates, 2007: Influence of the Atlantic oscillation on the winter climate of East China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 24, 126–135.
—, Wang Yanming, and Gao Yongqi, 2009: A review of the researches on the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO) and its climate influence. Trans. Atmos. Sci., 32, 458–465. (in Chinese)
Liang Biqi, et al., 1990: Tropical Meteorology. Zhongshan University Press, Guangzhou, 383 pp. (in Chinese)
Liang Sujie, Ding Yihui, Zhao Nan, et al., 2014: Analysis of the interdecadal changes of the wintertime surface air temperature over mainland China and regional atmospheric circulation characteristics during 1960–2013. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1401.13234. (in Chinese)
Liu Lihong and Zheng Zuguang, 2003: Analysis on the abrupt change points of Chinese temperature in the last 120 years. J. Nanjing Inst. Meteor., 26, 378–383. (in Chinese)
Lu Mengming, 1994: The relation between East Asia cold surge and low-frequency waves during the winter of 1992/93. Symposium on Weather and Climate across the Taiwan Strait, Taiwan, 49–63. (in Chinese)
Ma Xiaoqing, Ding Yihui, Xu Haiming, et al., 2008: The relation between strong cold waves and low-frequency waves during the winter of 2004/2005. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 32, 380–394. (in Chinese)
Mu Mingquan and Li Chongyin, 1999: ENSO signals in the interannual variability of East-Asian winter monsoon. Part I: Observed data analyses. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 23, 276–285. (in Chinese)
National Climate Center, 2013: Monitoring Bulletin of China’s Climate Change 2013, 61 pp. (in Chinese)
Pan, H. L., and F. X. Zhou, 1985: The 10–20-day tropical-midlatitude interaction during winter monsoon season. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 63, 829–843.
Pei Shunqiang and Li Chongyin, 2007: A further study on the East Asian winter monsoon and its influences. Part I: Features of variation and anomaly. Climatic Environ. Res., 12, 124–136. (in Chinese)
Qu Jinhua, Jiang Zhihong, Tan Guirong, et al., 2006: Relationship of winter North Atlantic SST interannual, interdecadal variation and the China’s temperature. Scientia Geographic Sinica, 26, 5557–5563. (in Chinese)
Shao Pengcheng and Li Dongliang, 2012: Classification and comparison of East Asian winter monsoon indices. Scientia Meteor. Sinica, 32, 226–235. (in Chinese)
Shi Neng, 1996: Features of the East Asian winter monsoon intensity on multiple timescales in recent 40 years and their relation to climate. J. Appl. Meteor. Sci., 7, 175–182. (in Chinese)
Shi Xiaohui, Xu Xianngde, and Xie Li’an, 2007: Interdecadal spatial-temporal change trend of East Asian winter monsoon in the last 40 years. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 31, 747–756. (in Chinese)
Song Yan and Ji Jinjun, 2005: The remarkable test of abrupt climatic warming and spatiotemporal distribution features of temperature and precipitation fields. Climatic Environ. Res., 10, 157–165. (in Chinese)
Sun, J. Q., H. J. Wang, W. Yuan, et al., 2010: Spatial-temporal features of intense snowfall events in China and their possible change. J. Geophys. Res., 115, D16110, doi: 10.1029/2009JD013541.
Tang Guoli, Luo Yong, Huang Jianbin, et al., 2012: Continuation of the global warming. Progressus Inquisitiones De Mutatione Climatis, 8, 235–242. (in Chinese)
Tollefson, J., 2014: The case of the missing heat. Nature, 505, 276–278.
Tomita, T., and T. Yasunari, 1996: Role of the northeast winter monsoon on the biennial oscillation of the ENSO/monsoon system. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 74, 399–413.
Trenberth, K. E., and J. S. Dennis, 2006: Atlantic hurricanes and natural variability in 2005. Geophys. Res. Lett., 33, L12704, doi: 10.1029/2006GL026894.
Wallace, J. M., 2000: On the Arctic and Antarctic Oscillation. NCAR Summer Colloquium Lecture Notes, http://www.jisao.washington.edu/wallace/ncar.
Wang, B., R. G. Wu, and X. H. Fu, 2000: Pacific-East Asian teleconnection. Part I: How does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J. Climate, 13, 1517–1536.
—, and Q. Zhang, 2002: Pacific-East Asian telecconnection. Part II: How the Philippine sea anomalous anticyclone is established during El Nino development. J. Climate, 15, 3252–3265.
—, R. Wu, and T. Li, 2003: Atmosphere warm ocean interaction and its impacts on Asian Australian monsoon variation. J. Climate, 16, 1195–1211.
—, Z. W. Wu, C. P. Chang, et al., 2010: Another look at interannual-to-interdecadal variations of the East Asian winter monsoon: The northern and southern temperature modes. J. Climate, 23, 1495–1512.
Wang, H. J., E. T. Ye, and S. Yang, 2011: An exceptionally heavy snowfall in Northeast China: Large-scale circulation anomalies and hindcast of the NCAR WRF model. Meteor. Atmos. Phys., 113, 11–25.
Wang Huijun and Fan Ke, 2013: Recent changes in the East Asian monsoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 37, 313–318.
— and He Shengping, 2013: The increase of snowfall in Northeast China after the mid 1980s. Chin. Sci. Bull., 58, 1350–1354.
Wang, L., W. Chen, and R. H. Huang, 2007: Changes in the variability of North Pacific Oscillation around 1975/1976 and its relationship with East Asian winter climate. J. Geophys. Res., 112, D11110, doi: 10.1029/2006JD008054.
—, W. Chen, and R. H. Huang, 2008: Interdecadal modulation of PDO on the impact of ENSO on the East Asian winter monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett., 35, L20702, doi: 10.1029/2008GL035287.
—, R. H. Huang, L. Gu, et al., 2009a: Interdecadal variations of the East Asian winter monsoon and their association with quasi-stationary planetary wave activity. J. Climate, 22, 4860–4872.
Wang Lin, and Chen Wen, 2014: The East Asian winter monsoon: Re-amplification in the mid 2000s. Chin. Sci. Bull., 59, 430–436.
Wang, Y. M., S. L. Li, and D. H. Luo, 2009b: Seasonal response of Asian monsoonal climate to the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation. J. Geophys. Res., 114, D02112, doi: 10.1029/2008JD010929.
Wei Daoming and Li Chongyin, 2009: Regional differences and mutations characteristic of East Asian winter monsoon. Plateau Meteor., 28, 1149–1157. (in Chinese)
Wei Fengying, 2008: Characteristics of the variation of cold wave disasters in China under the background of global warming. Prog. Nat. Sci., 18, 289–295. (in Chinese)
Wei Junhong and Lin Zhaohui, 2009: The leading mode of wintertime cold wave frequency in northern China during the last 42 years and its association with Arctic Oscillation. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett., 2, 130–134.
Wen, M., S. Yang, A. Kumar, et al., 2009: An analysis of the large-scale climate anomalies associated with the snowstorms affecting China in January 2008. Mon. Wea. Rev., 137, 1111–1131.
Wu, B. Y., and J. Wang, 2002: Winter Arctic oscillation, Siberian high and East Asian winter monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett., 29, 3-1–3-4, doi: 10.1029/2002GL015373.
Wu Bingyi and Huang Ronghui, 1999: Effects of the extremes in the North Atlantic Oscillation on East Asian winter monsoon. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 23, 641–651. (in Chinese)
—, Bian Lingen, and Zhang Renhe, 2004: Effects of the winter AO and the Arctic sea ice variations on climate change over East Asia. Adv. Polar Sci., 16, 211–220. (in Chinese)
—, Su Jingzhi, and Zhang Renhe, 2011: Effects of autumn-winter Arctic sea ice on winter Siberian high. Chin. Sci. Bull., 56, 3220–3228, doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4696-4.
Wu Shangsen and Liang Jianyin, 2000: Schematic predictive model for extremely severe cold months in south China minter-Physical factors of general circulation, polar sea ice, and perpetual snow. J. Trop. Meteor., 16, 289–296. (in Chinese)
Xu Jianjun, Zhu Qiangen, and Zhou Tiehan, 1999: Sudden and periodic changes of East Asian winter monsoon in the past century. J. Appl. Meteor. Sci., 10, 1–8. (in Chinese)
Yan Hongming, Duan Wei, and Xiao Ziniu, 2003: A study on relation between East Asian winter monsoon and climate change during summer season in China. J. Trop. Meteor., 19, 367–376. (in Chinese)
—, Zhou Wen, Yang Hui, et al., 2009: Definition of a East Asian winter monsoon index and its variation characteristics. Trans. Atmos. Sci., 32, 367–376. (in Chinese)
Yan Li, Wang Panxing, Guan Zhaoyong, et al., 2008: Relationship of sea surface temperatures teleconnection among oceans and China’s winter temperatures. Scientia Meteor. Sinica, 28, 133–138. (in Chinese)
Yang Song and Zhu Qiangen, 1989: The numerical study of cold surge structure and interaction between mid-latitudes and tropics during cold surge. J. Trop. Meteor., 5, 227–234. (in Chinese)
Yang Xiuqun, Zhu Yimin, Xie Qian, et al., 2004: Advances in studies of Pacific Decadal Oscillation. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 28, 979–992. (in Chinese)
Zhang Qingyun, Tao Shiyan, and Peng Jingbei, 2008: The studies of meteorological diseaters over China. Chinese J. Atmos. Sci., 32, 815–825. (in Chinese)
Zhang, R., A. Sumi, and M. Kimoto, 1996: Impact of El Niño on the East Asian monsoon: A diagnostic study of the 86/87 and 91/92 events. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 74, 49–62.
Zhang, Y., K. R. Sperber, and J. S. Boyle, 1997: Climatology and interannual variation of the East Asian winter monsoon: Results from the 1979–95 NCEP/NCAR reanalysis. Mon. Wea. Rev., 125, 2605–2616.
Zhou, W., C. Y. Li, and X. Wang, 2007: Possible connection between Pacific oceanic interdecadal pathway and East Asian winter monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett., 34, L01701, doi: 10.1029/2006GL027809.
Zhu Baozhen, Ding Yihui, and Luo Huibang, 1990: A review of the atmospheric general circulation and monsoon in East Asia. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 48, 4–16. (in Chinese)
Zhu Yanfeng, 2008: An index of East Asian winter monsoon applied to description the Chinese mainland winter temperature changes. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 66, 781–788. (in Chinese)
Zhu Yimin and Yang Xiuqun, 2003: Relationships between Pacific decadal oscillation (PDO) and climate variabilities in China. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 61, 641–654. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National (Key) Basic Research and Development (973) Program of China (2012CB417205 and 2013CB430202), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41130960), China Meteorological Administration Special Public Welfare Research Fund (GYHY201406001), and National Science and Technology Support Program of China (2009BAC51B02).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Y., Liu, Y., Liang, S. et al. Interdecadal variability of the East Asian winter monsoon and its possible links to global climate change. J Meteorol Res 28, 693–713 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-014-4046-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-014-4046-y