Abstract
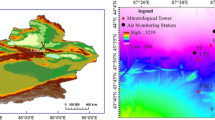
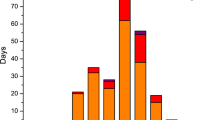
Both surface environmental monitoring and satellite remote sensing show that North China is one of the regions that are heavily polluted by NO2. Using the NO2 monitoring data from 18 major cities in the region, the tropospheric NO2 column density data from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) on the Aura satellite, and the observations from the China Meteorological Administration network, this paper analyzes a regional NO2 pollution event in February 2007 over North China, examines the convergence of the pollutant, and identies its correlation with the atmospheric background conditions. The results show that daily mean NO2 concentrations derived from surface observations are consistent with the mean values of the OMI measurements, with their correlation coeficient reaching 0.81. The correlations of NO2 concentration with general weather patterns and sequential changes of temperature structure from 925 hPa down to the surface indicate that the weather fronts, high pressure and low pressure systems in the atmosphere play a role in changing the temporal and spatial evolutions of NO2 through removing, accumulating or converging of the pollutant, respectively. It is also found that the eastern Taihang Mountains is most heavily polluted by NO2 in North China. Based on a model that correlates NO2 column density with surface wind vector, the relation of the NO2 concentrations in six major cities in North China to the surrounding wind field is analyzed. The results show that the maximum wind field is associated with the highest frequency of pollution events, and under certain large-scale atmospheric conditions together with the topographic effect, small- and meso-scale wind fields often act to transport and converge pollutants, and become a major factor in forming the heaviest NO2 pollution event in North China. Analysis of the causes for the severe NO2 pollution event in this study may shed light on understanding, forecasting, and mitigating occurrences of heavy NO2 pollution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, Z. H., S. Y. Cheng, J. B. Li, et al., 2008: Relationship between atmospheric pollution processes and synoptic pressure patterns in northern China. Atmos. Environ., 24(42), 6078–6087.
Ding Yihui, 2005: Advanced Synoptic Meteorology (Second Edition). China Meteorological Press, 83 pp. (in Chinese)
Kang Na, Gao Qingxian, Wang Yuesi, Su Fuqing, et al., 2009b: Analysis of regional pollution process and application of system cluster method. Res. Environ. Sci., 22(10), 1120–1127. (in Chinese)
—, Xin Jinyuan, Lin Yongyao, et al., 2009a: Meteorological condition analysis of a typical fine particle pollution event in the piedmont region of Beijing. Res. Environ. Sci., 22(9), 1014–1020. (in Chinese)
Kim, S. W., A. Heckel, S. A. McKeen, et al., 2006: Satellite-observed US power plant NOx emission reductions and their impact on air quality. Geophys. Res. Lett., 33(L22), 812–817.
Lamsal, L. N., R. V. Martin, A. van Donkelaar, et al., 2008: Ground-level nitrogen dioxide concentrations inferred from the satellite-borne ozone monitoring instrument. J. Geophys. Res., 113(D16), 308–323.
Ordónez, C., A. Richter, M. Steinbacher, et al., 2006: Comparison of 7 years of satellite-borne and ground-based tropospheric NO2 measurements around Milan, Italy. J. Geophys. Res., 111(D05), 310–322.
Petritoli, A., P. Bonasoni, G. Giovanelli, et al., 2004: First comparison between ground-based and satellite-borne measurements of tropospheric nitrogen dioxide in the Po basin. J. Geophys. Res., 109(D15), 307–324.
Van der A., D. H. M. U. Peters, H. Eskes, et al., 2006: Detection of the trend and seasonal variation in tropospheric NO2 over China. J. Geophys. Res., 111(D12317), doi: 10.1029P2005D006594.
Ren Zhenhai, Su Fuqing, Gao Qingxian, et al., 2005: Analysis of the serious atmospheric pollution event caused by emissions in boundary layer. J. Atmos. Sci., 29(1), 57–63. (in Chinese)
Richter, A., J. P. Burrows, H. NÄu, et al., 2005: Increase in tropospheric nitrogen dioxide over China observed from Space. Nature, 7055(437), 129–132.
Sachin, D. G., R. J. Van der A., G. Beig, et al., 2009: Satellite derived trends in NO2 over the major global hotspot regions during the past decade and their inter-comparison. Environ. Poll., 157(6), 1873–1878.
Su Fuqing, Yang Mingzhen, Zhong Jihong, et al., 2004a: The e®ects of synoptic type on regional atmospheric contamination in North China. Res. Environ. Sci., 17(1), 16–20. (in Chinese)
—, Ren Zhenhai, Gao Qingxian, et al., 2004b: Convergence system of air contamination in boundary layer above Beijing and North China: Transportation convergence in boundary layer. Res. Environ. Sci., 17(1), 22–25. (in Chinese)
Wang Yueqi, Jiang Hong, Zhang Xiuying, et al., 2009: Temporal-spatial distribution of tropospheric NO2 in China using OMI satellite remote sensing data. Res. Environ. Sci., 22(8), 932–937. (in Chinese)
Xu Xiangde, Zhou Li, Zhou Xiuji, et al., 2004: Influence domain of the surrounding pollution sources in heavy urban air pollution process. Sci. China (Ser. D), 34(10), 958–966.
—, Zhou Xiuji, Han Xue, et al., 2005: Spatial structure and scale of air pollution sources influencing an urban cluster. Sci. China (Ser. D), 35(1), 1–19.
Yue Jie, Lin Yunping, Deng Zhaoze, et al., 2009: Seasonal variations of tropospheric NO2 over megalopolis in eastern China using satellite remote-sensing data and chemistry-transport model. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 45(3), 431–438. (in Chinese)
Zhang, Q., D. G. Streets, K. He, et al., 2007a: Major components of China’s anthropogenic primary particulate emissions. Environ. Res. Lett., 2(2007), 045027–045034.
—, —, —, et al., 2007b: NOx emission trends for China, 1995–2004: The view from the ground and the view from space. J. Geophys. Res., 112(D22), 1–18.
—, D. G. Streets, G. R. Carmichael, et al., 2009: Asian emissions in 2006 for the NASA INTEX-B mission. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 14(9), 5131–5153.
Zhang, X. Y., Zhang P., Zhang Y., et al., 2007: The trend, seasonal cycle, and sources of tropospheric NO2 over China during 1997–2006 based on satellite measurement. Science China (Ser. D), 37(10), 1409–1416.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Fundamental Research Fund of the Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences (2010KYYW08).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, P., Ren, Z., Su, F. et al. Environmental process and convergence belt of atmospheric NO2 pollution in North China. Acta Meteorol Sin 25, 797–811 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-011-0610-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-011-0610-x