Abstract
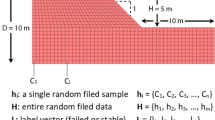
This paper presents an artificial neural network (ANN)-based response surface method that can be used to predict the failure probability of c-φ slopes with spatially variable soil. In this method, the Latin hypercube sampling technique is adopted to generate input datasets for establishing an ANN model; the random finite element method is then utilized to calculate the corresponding output datasets considering the spatial variability of soil properties; and finally, an ANN model is trained to construct the response surface of failure probability and obtain an approximate function that incorporates the relevant variables. The results of the illustrated example indicate that the proposed method provides credible and accurate estimations of failure probability. As a result, the obtained approximate function can be used as an alternative to the specific analysis process in c-φ slope reliability analyses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng, J., Li, Q. S. and Xiao, R. C., 2008. A new artificial neural network-based response surface method for structural reliability analysis, Probabilist. Eng. Mech., 23(1): 51–63.
Cho, S. E., 2007. Effects of spatial variability of soil properties on slope stability, Eng. Geol., 92(3-4): 97–109.
Cho, S. E., 2009. Probabilistic assessment of slope stability that considers the spatial variability of soil properties, J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng., 136(7): 975–984.
Chok, Y. H., 2009. Modelling the Effects of Soil Variability and Vegetation on the Stability of Natural Slopes, Ph. D. Thesis, University of Adelaide.
EI-Ramly, H., Morgenstern, N. R. and Cruden, D. M., 2002. Probabilistic slope stability analysis for practice, Can. Geotech. J., 39(3): 665–683.
Fenton, G. A. and Vanmarcke, E. H., 1990. Simulation of random fields via local average subdivision, J. Eng. Mech., ASCE, 116(8): 1733–1749.
Griffiths, D. V. and Fenton, G. A., 2004. Probabilistic slope stability by finite elements, J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng., 130(5): 507–518.
Griffiths, D. V. and Fenton, G. A., 2007. The random finite element method (RFEM) in slope stability analysis, Probabilistic Methods in Geotechnical Engineering, Springer Vienna, 317–346.
Griffiths, D. V., Huang, J. and Fenton, G. A., 2010. Probabilistic infinite slope analysis, Comput. Geotech., 38(4): 577–584.
Haldar, S. and Basu, D., 2013. Response of Euler-Bernouli beam on spatially random elastic soil, Comput. Geotech., 50, 110–128.
Hicks, M. A. and Onisiphorou, C., 2005. Stochastic evaluation of static liquefaction in a predominantly dilative sand fill, Geotechnique, 55, 123–133.
Hicks, M. A. and Samy, K., 2002. Influence of heterogeneity on undrained clay slope stability, Quart. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol., 35, 41–49.
Ji, J., Liao, H. J. and Low, B. K., 2012. Modeling 2-D spatial variation in slope reliability analysis using interpolated autocorrelations, Comput. Geotech., 40, 135–146.
Khajehzadeh, M., Taha, M. R. and Eslami, M., 2014. Opposition-based firefly algorithm for earth slope stability evaluation, China Ocean Eng., 28(5): 713–725.
Li, K. S. and Lumb, P., 1987. Probabilistic design of slopes, Can. Geotech. J., 24(4): 520–535.
Li, L. and Chu, X. S., 2011. An improved particle swarm optimization algorithm with harmony strategy for the location of critical slip surface of slopes, China Ocean Eng., 25(2): 357–364.
Li, L., Cheng, Y. M. and Chu, X. S., 2013a. A new approach to the determination of the critical slip surfaces of slopes, China Ocean Eng., 27(1): 51–64.
Li, L., Wang, Y., Cao, Z. J. and Chu, X. S., 2013b. Risk de-aggregation and system reliability analysis of slope stability using representative slip surfaces, Comput. Geotech., 53, 95–105.
Luo, X. F., Li, X., Zhou, J. and Cheng, T., 2012. A kriging-based hybrid optimization algorithm for slope reliability analysis, Struct. Saf., 34(1): 401–406.
Luo, Z., Atamturktur, S., Juang, C. H., Huang, H. W. and Lin, P. S., 2011. Probability of serviceability failure in a braced excavation in a spatially random filed: Fuzzy finite element approach, Comput. Geotech., 38(8): 1031–1040.
McKay, M. D., Beckman, R. J. and Conover, W. J., 1979. Comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code, Technometrics, 21(2): 239–245.
Phoon, K. K. and Kulhawy, F. H., 1999. Characterization of geotechnical variability, Can. Geotech. J., 36, 612–624.
Srivastava, A. and Babu, G. L., 2009. Effect of soil variability on the bearing capacity of clay and in slope stability problems, Eng. Geol., 108(1): 142–152.
Vanmarcke, E. H., 1983. Random Fields: Analysis and Synthesis, Cambridge, MIT Press.
Wang, Y., Cao, Z. J. and Au, S. K., 2010. Efficient Monte Carlo simulation of parameter sensitivity in probabilistic slope stability analysis, Comput. Geotech., 37(7): 1015–1022.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51278217).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shu, Sx., Gong, Wh. An artificial neural network-based response surface method for reliability analyses of c-φ slopes with spatially variable soil. China Ocean Eng 30, 113–122 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13344-016-0006-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13344-016-0006-x