Abstract
Objective
To determine early breastfeeding problems using LATCH tool, and analyze the impact of breastfeeding supportive measures in improving LATCH score.
Methods
This prospective study included all inborn term neonates born at our center between September, 2019 and March, 2020. Breastfeeding problems were identified by LATCH score at 6–12h after birth, and were addressed by the study team providing breastfeeding support, education and training to mothers. LATCH scores were reassessed at 24–48h.
Results
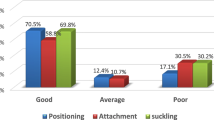
Among 400 mother-infant dyads, 399 (99.7%) required support to position the neonate, 190 (47.5%) had poor latch and 52 (13%) had nipple problems during initial assessment. Breastfeeding supportive measures improved the LATCH score [median (IQR) 7 (5,8) vs 8 (8,8) at 6–12 and 24–48 hours, respectively; P <0.001], and reduced the number of mothers with LATCH score <8 [288 (72%) vs 63 (15.8%); P <0.001].
Conclusion
LATCH is a comprehensive yet simple tool to identify breastfeeding problems. Given the high incidence of breastfeeding problems during early postpartum period, systematic assessment of breastfeeding related problems using LATCH tool can help timely intervention and improvement in the breastfeeding technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sankar MJ, Sinha B, Chowdhury R, et al. Optimal breastfeeding practices and infant and child mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015; 104:3–13.
Azuine RE, Murray J, Alsafi N, Singh GK. Exclusive breast-feeding and under-five mortality, 2006–2014: A cross-national analysis of 57 low-and-middle income countries. Int J MCH AIDS. 2015;4:13–21.
Feenstra MM, Jørgine Kirkeby M, Thygesen M, et al. Early breastfeeding problems: A mixed method study of mothers’ experiences. Sex Reprod Healthc. 2018;16:167–74.
Suresh S, Sharma KK, Saksena M, et al. Predictors of breastfeeding problems in the first postnatal week and its effect on exclusive breastfeeding rate at six months: Experience in a tertiary care centre in Northern India. Indian J Public Health. 2014;58:270–3.
van Dellen SA, Wisse B, Mobach MP, Dijkstra A. The effect of a breastfeeding support programme on breastfeeding duration and exclusivity: a quasi-experiment. BMC Public Health. 2019;19:993.
Fadiloglu E, Karatas E, Tez R, et al. Assessment of factors affecting breastfeeding performance and latch score: A prospective cohort study. Z Geburtshilfe Neonatol. 2021;225:353–60.
Hobbs AJ, Mannion CA, McDonald SW, et al. The impact of caesarean section on breastfeeding initiation, duration and difficulties in the first four months postpartum. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016;16:90.
Sowjanya SVNS, Venugopalan L. LATCH Score as a predictor of exclusive breastfeeding at 6 weeks postpartum: A prospective cohort study. Breastfeed Med. 2018;13:444–9.
Tornese G, Ronfani L, Pavan C, et al. Does the LATCH score assessed in the first 24 hours after delivery predict non-exclusive breastfeeding at hospital discharge? Breastfeed Med. 2012;7:423–30.
Riordan J, Bibb D, Miller M, Rawlins T. Predicting breastfeeding duration using the LATCH breastfeeding assessment tool. J Hum Lact. 2001;17:20–3.
Funding
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SMR, BR: Concept, design, data collection, data analysis, manuscript writing; RJ, TA, SR: Concept, design, data analysis and manuscript review. All authors approved the final manuscript and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the research.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Name of IEC: KMCH Ethics Committee; No. EC/AP/762/08/2019, dated August 24, 2019.
Additional information
Competing interests
None stated.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rapheal, S.M., Rajaiah, B., Karupanan, R. et al. LATCH Score for Identification and Correction of Breastfeeding Problems — A Prospective Observational Study. Indian Pediatr 60, 37–40 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-023-2692-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-023-2692-9