Abstract
Objective
To develop nomogram of Transcutaneous Bilirubin among healthy term and late-preterm neonates during first 96 hours of age.
Design
Longitudinal observational study.
Setting
Neonatal unit of a tertiary care Hospital of Central Gujarat, India.
Participants
1075 healthy term and late preterm neonates (≥35weeks).
Intervention
Six-hourly transcutaneous bilirubin was obtained from birth to 96 hour of life using Drager JM 103 Transcutaneous Bilirubinometer.
Main outcome measures
Nomogram of Transcutaneous Bilirubin with percentile values was obtained, rate of rise of bilirubin was calculated and predictive ability of normative data was analyzed for subsequent need of phototherapy.
Results
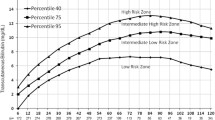
The age-specific percentile curves and nomogram were developed from the transcutaneous bilirubin readings of 1,010 neonates. Rate of rise in first 12 hour was 0.2 mg/dL and was 0.17 mg/dL in 12 to 24 hour of life which decreased on second day of life. Neonates who required phototherapy had consistently higher readings of transcutaneous bilirubin and also higher rate of rise in first 48 hrs.
Conclusion
Neonates whose transcutaneous bilirubin is above the 50th percentile should be monitored for the development of significant hyperbilirubinemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedman MA, Spitzer AR. Discharge criteria for the term newborn. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2004;51:599–618.
Maisels MJ, Kring E. Length of stay, jaundice, and hospital readmission. Pediatrics. 1998;101:995–8.
Management of hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn infant 35 or more weeks of gestation. Pediatrics. 2004;114:297–316.
Thakre R, Murki S, Venkataseshan S. Management of Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia. In: Evidence Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. eds. Kumar P, Jain N, Thakre R, Murki S, Venkatasestan. National Neonatology Forum, New Delhi; 2010: p. 139–54.
Bhutani VK, Johnson L, Sivieri EM. Predictive ability of a predischarge hour-specific serum bilirubin for subsequent significant hyperbilirubinemia in healthy term and near-term newborns. Pediatrics. 1999;103:6–14.
Mahajan G, Kaushal RK, Sankhyan N, Sharma RL, Nakra M. Transcutaneous bilirubinometer in assessment of neonatal jaundice in northern India. Indian Pediatr. 2005;42:41–5.
Maisels MJ, Kring E. Transcutaneous bilirubin levels in the first 96 hours in a normal newborn population of > or = 35 weeks’ gestation. Pediatrics. 2006;117:1169–73.
De Luca D, Romagnoli C, Tiberi E, Zuppa AA, Zecca E. Skin bilirubin nomogram for the first 96 h of life in a European normal healthy newborn population, obtained with multiwavelength transcutaneous bilirubinometry. Acta Paediatrica. 2008;97:146–50.
Sanpavat S, Nuchprayoon I, Smathakanee C, Hansuebsai R. Nomogram for prediction of the risk of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, using transcutaneous bilirubin. J Med Assoc Thai. 2005;88:1187–93.
Mishra S, Chawla D, Agarwal R, Deorari AK, Paul VK. Transcutaneous bilirubin levels in healthy term and late preterm Indian neonates. Indian J Pediatr. 2010;77:45–50.
De Luca D, Jackson GL, Tridente A, Carnielli VP, Engle WD. Transcutaneous bilirubin nomograms: a systematic review of population differences and analysis of bilirubin kinetics. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2009;163:10.
Engle WD, Lai S, Ahmad N, Manning MD, Jackson GL. An hour-specific nomogram for transcutaneous bilirubin values in term and late preterm Hispanic neonates. Am J Perinatol. 2009;26:425–30.
Wainer S, Parmar SM, Allegro D, Rabi Y, Lyon ME. Impact of a transcutaneous bilirubinometry program on resource utilization and severe hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatrics. 2012;129:77–86.
Wainer S, Rabi Y, Parmar SM, Allegro D, Lyon M. Impact of skin tone on the performance of a transcutaneous jaundice meter. Acta Paediatrica. 2009;98:1909–15.
Draque CM, Sanudo A, de Araujo Peres C, de Almeida MF. Transcutaneous bilirubin in exclusively breastfed healthy term newborns upto 12 days of life. Pediatrics. 2011;128:e565–71.
Yu ZB, Dong XY, Han SP, Chen YL, Qiu YF, Sha L, et al. Transcutaneous bilirubin nomogram for predicting neonatal hyperbilirubinemia in healthy term and latepreterm Chinese infants. Eur J Pediatr. 2011;170:185–91.
Bental YA, Shiff Y, Dorsht N, Litig E, Tuval L, Mimouni FB. Bhutani-based nomograms for the prediction of significant hyperbilirubinaemia using transcutaneous measurements of bilirubin. Acta Paediatr. 2009;98:1902–8.
Yu ZB, Han SP, Chen C. Bilirubin nomograms for identification of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia in healthy term and late-preterm infants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Pediatr. 2014;10:211–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thakkar, P., Chavda, H. & Doshi, V. Transcutaneous bilirubin nomogram for healthy term and late preterm neonates in first 96 hours of life. Indian Pediatr 54, 369–372 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-017-1108-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-017-1108-0