Abstract
Objectives
To test the efficacy of oral sucrose in reducing pain/ stress during echocardiography as estimated by Premature Infant Pain Profile score.
Design
Double-blind, parallel-group, randomized control trial.
Setting
Tertiary-care neonatal care unit located in Western India.
Participants
Neonates with established enteral feeding, not on any respiratory support and with gestational age between 32 and 42 weeks requiring echocardiography.
Interventions
Neonates in intervention group received oral sucrose prior to echocardiography.
Main outcome measures
Assessment was done using Premature Infant Pain Profile score.
Results
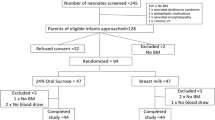
There were 104 examinations; 52 in each group. Baseline characteristics like mean gestational age (37.6 vs. 37.1), birth weight (2.20 vs. 2.08), and feeding status (Breastfeeding- 59.6% vs. 44.2%, paladai feeding- 13.5% vs. 13.5%, and gavage feeding- 26.9% vs. 42.3%) were comparable. The mean (SD) premature infant pain profile score was significantly higher in control group [(7.4 (3.78) vs. 5.2 (1.92), P <0.001].
Conclusion
Oral sucrose significantly reduces pain, and is safe to administer to neonates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taddio A, Shah V, Gilbert-MacLeod C, Katz J. Conditioning and hyperalgesia in new-borns exposed to repeated heel lances. JAMA. 2002;288:857–61.
Grunau RE. Neonatal pain in very preterm infants: longterm effects on brain, neurodevelopment and pain reactivity. Rambam Maimonides Med J. 2013;4:e0025.
Walter-Nicolet E, Annequin D, Biran V, Mitanchez D, Tourniaire B. Pain management in newborns: from prevention to treatment. Paediatr Drugs. 2010;12:353–65.
Nimbalkar AS, Dongara AR, Ganjiwale JD, Nimbalkar SM. Pain in children: knowledge and perceptions of the nursing staff at a rural tertiary care teaching hospital in India. Indian J Pediatr. 2013;80:470–5.
Ou-Yang MC, Chen IL, Chen CC, Chung MY, Chen FS, Huang HC. Expressed breast milk for procedural pain in preterm neonates: a randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled trial. Acta Paediatr. 2013;102:15–21.
Shah PS, Herbozo C, Aliwalas LL, Shah VS. Breastfeeding or breast milk for procedural pain in neonates. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;12:CD004950.
Nimbalkar S, Sinojia A, and Dongara A. Reduction of neonatal pain following administration of 25% lingual dextrose: a randomized control trial. J Trop Pediatr. 2013;59:223–5.
Stevens B, Yamada J, Lee GY, Ohlsson A. Sucrose for analgesia in newborn infants undergoing painful procedures. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;1: CD001069.
Nimbalkar SM, Chaudhary NS, Gadhavi KV, Phatak AG. Kangaroo Mother Care in reducing pain in preterm neonates on heel prick. Indian J Pediatr. 2013;80:6–10.
Hartling L, Shaik MS, Tjosvold L, Leicht R, Liang Y, Kumar M. Music for medical indications in the neonatal period: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2009;94:349–54.
Pillai Riddell RR, Racine NM, Turcotte K, Uman LS, Horton RE, Din Osmun L, et al. Non-pharmacological management of infant and young child procedural pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;10:CD006275.
Jain A, McNamara PJ, Ng E, El-Khuffash A. The use of targeted neonatal echocardiography to confirm placement of peripherally inserted central catheters in neonates. Am J Perinatol. 2012;29:101–6.
Cignacco E, Hamers JP, Stoffel L, van Lingen RA, Schütz N, Müller R, et al. Routine procedures in NICUs: factors influencing pain assessment and ranking by pain intensity. Swiss Med Wkly. 2008 Aug 23;138(33–34):484–91.
Vani SN, Thakre R, Nimbalkar S. Assessment and management of pain in the newborn. NNF Clinical Practice Guidelines. 2010:199–215.
Taddio A, Shah V, Katz J. Reduced infant response to a routine care procedure after sucrose analgesia. Pediatrics. 2009;123:425–9.
Stevens B, Johnston C, Petryshen P, Taddio A. Premature Infant Pain Profile: development and initial validation. Clin J Pain. 1996;12:13–22.
Ballantyne M1, Stevens B, McAllister M, Dionne K, Jack A. Validation of the premature infant pain profile in the clinical setting. Clin J Pain. 1999;15:297–303.
Johnston CC, Filion F, Snider L, Limperopoulos C, Majnemer A, Pelausa E, et al. How much sucrose is too much sucrose? Pediatrics. 2007;119:226.
Johnston CC, Filion F, Snider L, Majnemer A, Limperopoulos C, Walker CD, et al. Routine sucrose analgesia during the first week of life in neonates younger than 31 weeks’ postconceptional age. Pediatrics. 2002;110:523–8
Slater R, Cornelissen L, Fabrizi L, Patten D, Yoxen J, Worley A, et al. Oral sucrose as an analgesic drug for procedural pain in newborn infants: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376:1225–32.
Stevens B, Johnston C, Taddio A, Gibbins S, Yamada J. The premature infant pain profile: evaluation 13 years after development. Clin J Pain. 2010;26:813–30.
Harrison D, Beggs S, Stevens B. Sucrose for procedural pain management in infants. Pediatrics. 2012;130:918–25.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Potana, N.T., Dongara, A.R., Nimbalkar, S.M. et al. Oral sucrose for pain in neonates during echocardiography: A Randomized Controlled Trial . Indian Pediatr 52, 493–497 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-015-0663-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-015-0663-5