Abstract
Objectives
To analyze critical steps in the testing algorithm of the National Early Infant Diagnosis (EID) program in India.
Methods
A retrospective analysis of data on cases enrolled in the EID program during 2010–2012 from Tamil Nadu was undertaken.
Results
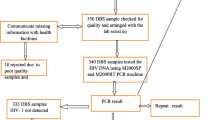
2745 dried blood spots were tested; 9% of these tested positive. Median age of infants at the time of testing was 4 months. Second specimen for confirmation was received from 67% of cases with a turn-around time of 10–270 days.
Discussion
Even with high levels of uptake into the program, huge delays and loss-to-follow-up observed between the first and second sampling, suggests need for revision of the current testing algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
UNICEF. Scaling up Early Infant Diagnosis and Linkages to Care and Treatment. Available from: www.unicef.org/aids/files/EIDWorkingPaperJune02.pdf . Accessed July 3, 2013.
World Health Organization. 2010 Revision. Antiretroviral Therapy for HIV Infection in Infants and Children: Towards Universal Access. Recommendations for a Public Health Approach. Available from: www.who.int/hiv/pub/paediatric/infants2010/en/ . Accessed July 3, 2013.
WHO Antiretroviral Therapy for Infants and Children. Report of the WHO Technical Reference Group, Paediatric HIV/ART Care Guideline Group meeting. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2008. Available from: www.who.int/hiv/pub/paediatricWHO_Paediatric_ART_guideline_rev_mreport2008.pdf . Accessed July 3, 2013.
National AIDS Control Organization. 2006. Guidelines for HIV Care and Treatment in Infants and Children. Available from: nacoonline.org/upload/Policies%20&%20Guidelines/4%20Guidelines%20for%20HIV %20care%20and%20treatment%20in%20Infants%20and%20children.pdf. Accessed July 3, 2013.
Read JS, Committee on Pediatric AIDS. Diagnosis of HIV-1 infection in children younger than 18 months in the United States. Pediatrics. 2007; 120:e1547–62.
World Health Organization. Principles and Recommendations for Infant Feeding in the Context of HIV and a Summary of Evidence. Available from: www.who.int/child_adolescent_health/documents/9789241599535/en/index.html . Accessed July 3, 2013.
World Health Organization. HIV and infant feeding: Revised Principles and Recommendations Rapid Advice. Available from: whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2009/9789241598873_eng.pdf. Accessed July 3, 2013.
World Health Organization. 2010. WHO recommendations on the diagnosis of HIV infection in infants and children. Available from: www.searo.who.int/LinkFiles/HIV-AIDS_paediatric_2.pdf. Accessed July 3, 2013.
Newell M, Coovadia H, Cortina-Borja M, Rollins N, Gaillar P, Dabis F. Mortality of infected and uninfected infants born to HIV-infected mothers in Africa: a pooled analysis. Lancet. 2004;364:1236–41.
Lilian RR, Kalk E, Bhowan K, Berrie L, Carmona S, Technau K, et al. Early diagnosis of in utero and intrapartum HIV infection in infants prior to 6 weeks of age. J Clin Microbiol. 2012;50:2373–7.
Chatterjee A, Tripathi S, Gass R, Hamunime N, Panha S, Kiyaga C, et al. Implementing services for Early Infant Diagnosis (EID): a comparative descriptive analysis of national programs in four countries. BMC Public Health. 2011;11:553.
Jain KK, Mahajan RK, Shevkani M, Kumar P. Early Infant Diagnosis: a new tool of HIV diagnosis in children. Indian J Community Med. 2011;36:139–42.
Dube Q, Dow A, Chirambo C, Lebov J, Tenthani L, Moore M, et al. Implementing early infant diagnosis of HIV infection at the primary care level: experiences and challenges in Malawi. Bull World Health Organ. 2012; 90:699–704.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanna, L.E., Siromany, V.A., Annamalai, M. et al. Challenges in the early diagnosis of HIV infection in infants: Experience from Tamil Nadu, India. Indian Pediatr 52, 307–309 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-015-0629-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-015-0629-7