Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the growth pattern of Very Low Birth Weight (VLBW) infants (birthweight <1500g) during hospital stay and to compare the growth of Small for gestational age (SGA) and Appropriate for gestational age (AGA) infants.
Study design
Prospective observational study.
Setting
Level III Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) in Northern India.
Participants
A cohort of 97 VLBW infants, admitted to NICU at Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, from 1 January, 2007 to 31 July, 2008.
Intervention/Measurement
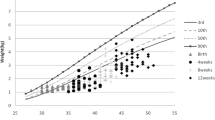
Weight, length and head circumference (HC) were serially measured from birth till discharge and respective Z scores were calculated as per data from Fenton’s references. Growth was also assessed by superimposing these trends on Ehrenkranz’s postnatal growth charts.
Results
The mean Z scores for weight, length and HC at birth were −1.17, −1.09 and −0.54, respectively. These decreased to −2.16, −2.24 and −1.35, respectively by discharge. Both SGA and AGA infants exhibited a decrease of approximately 1 Z score in all parameters. On postnatal charts, growth of infants remained at or above respective reference lines, except in those below 1000g at birth. Average daily weight gain after regaining birth weight was 15.18 ± 1.7 g/kg/d, whereas the increase in HC and length were 0.48 ± 0.2 cm/week and 0.60 ± 0.4 cm/week, respectively. These increments when compared to the intrauterine growth rates, indicated discrepant growth trends.
Conclusions
VLBW infants suffered significant growth lag during NICU stay and exhibited disproportionately slow growth of HC and length.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hack M, Schluchter M, Cartar L, Rahman M, Cuttler L, Borawski E. Growth of very low birth weight infants to age 20 years. Pediatrics 2003; 112: 30–38.
Astbury J, Orgill AA, Bajuk B, Yu VYH. Sequelae of growth failure in appropriate for gestational age, very low birth weight infants. Dev Med Child Neurol 1986; 28: 472–479.
Lundgren EM, Cnattingius S, Jonsson B, Tuvemo T. Intellectual and psychological performance in males born small for gestational age with or without catch-up growth. Pediatr Res 2001; 50: 91–96.
Hajnal BL, Siebenthal KV, Kovari H, Bucher HU, Largo RH. Postnatal growth in VLBW infants: Significant association with neurodevelopmental outcome. J Pediatr 2003; 143: 163–170.
Fenton TR. A new growth chart for preterm babies: Babson and Benda’s chart updated with recent data and a new format. BMC Pediatr 2003; 3: 13–22.
Fenton TR. Preterm Growth Chart 2003 calculations. Available from http://members.shaw.ca/growthchart/FentonGrowthChartcalculations.xls. Accessed on 10 February, 2009.
Ehrenkranz RA, Younes N, Lemons JA, Fanaroff AA, Donovan EF, Wright LL. Longitudinal growth of hospitalized very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 1999; 104: 280–289.
American Academy of Pediatrics, Committee on Nutritional Needs of Low-Birth-Weight Infants. Pediatrics 1977; 60: 519–530.
American Academy of Pediatrics, Committee on Nutritional Needs of Low-Birth-Weight Infants. Pediatrics 1985; 75: 976–986.
Gutbrod T, Wolke D, Soehne B, Ohrt B, Riegel K. Effects of gestation and birth weight on the growth and development of VLBW small for gestational age infants: A matched group comparision. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2000; 82: F 208–214.
Bertino E, Coscia A, Boni L, Rossi C, Martano C, Giuliani F, et al. Weight growth velocity of very low birth weight infants: role of gender, gestational age and major morbidities. Early Hum Dev 2009; 85: 339–347.
Radmacher PG, Looney SW, Rafail ST, Adamkin DH. Prediction of extrauterine growth retardation (EUGR) in VVLBWI. J Perinatol 2003; 23: 392–395.
Powls A, Botting N, Cooke RWI, Pilling D, Marlow N. Growth impairment in very low birthweight children at 12 years: correlation with perinatal and outcome variables. Arch Dis Child 1996; 75: F152–F157.
Hack M, Breslau N, Weissman B, Aram D, Klein N, Borawski E. Effect of very low birth weight and subnormal head size on cognitive abilities at school age. N Engl J Med 1991; 325: 231–237.
Knops NBB, Sneeuw CAK, Brand R, Hille ETM, Ouden AL, Wit JM, et al. Catch-up growth up to ten years of age in children born very preterm or with very low birth weight. BMC Pediatr 2005; 5: 26–34.
Yajnik CS, Fall CHD, Coyaji KJ, Hirve SS, Rao S, Barker DJP, et al. Neonatal anthropometry: the thin-fat indian baby. The Pune Maternal Nutrition Study. Int J Obes 2003; 27: 173–180.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saluja, S., Modi, M., Kaur, A. et al. Growth of very low birth-weight Indian infants during hospital stay. Indian Pediatr 47, 851–856 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-010-0146-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-010-0146-7