Abstract
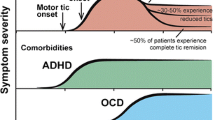
Tourette’s syndrome (TS) consists of chronic motor and phonic tics and characteristically begins in childhood. The tics can be disabling and commonly associated behavioral comorbities such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), can also cause problems in daily functioning. The underlying etiology and neurobiology of TS remain unknown although genetic factors appear to be important, cortical control of basal ganglia motor function appears to be disturbed and neurochemical abnormalities, particularly involving dopamine neurotransmission, are likely present. The treatment of TS involves appropriate education and support. Tics can be treated with habit reversal cognitive behavioral therapy, medications (most commonly alpha agonists and antipsychotics), local intramuscular injections of botulinum toxin and some severe, refractory cases have responded to deep brain stimulation surgery (DBS). It is important to appropriately diagnose and treat comorbid behavioral disorders that are disrupting function. OCD can be treated with cognitive behavioral therapy, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and atypical antipsychotics. DBS has become a treatment option for patients with disabling OCD despite other therapies. ADHD is treated with appropriate classroom accommodations, behavioral therapy, alpha agonists, atomoxetine or methylphenidate-containing stimulant drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheung M-YC, Shahed J, Jankovic J. Malignant Tourette syndrome. Movement Disord. 2007; 22(12):1743–50.
Jankovic J, Kurlan R. Tourette syndrome: Evolving concepts. Movement Disord. 2011; 26(6):1149–56.
Bronfeld M, Bar-Gad I. Tic Disorders: What Happens in the Basal Ganglia? Neuroscientist. 2013; 19(1):101–8.
Orth M, Münchau A, Rothwell JC. Corticospinal system excitability at rest is associated with tic severity in Tourette syndrome. Biol Psychiat. 2008; 64(3):248–51.
Rajagopal S, Seri and S, Cavanna AE. Premonitory urges and sensorimotor processing in Tourette syndrome. Behav Neurol. 2013; 27(1):65–73
Kataoka Y, Kalanithi PSA, Grantz H, Schwartz ML, Saper C, Leckman JF, et al. Decreased number of parvalbumin and cholinergic interneurons in the striatum of individuals with Tourette syndrome. The J Compar Neurol. 2010; 518(3):277–91.
Kalanithi PSA, Zheng W, Kataoka Y, DiFiglia M, Grantz H, Saper CB, et al. Altered parvalbumin-positive neuron distribution in basal ganglia of individuals with Tourette syndrome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2005; 102(37):13307–12.
Lerner A, Bagic A, Simmons JM, Mari Z, Bonne O, Xu B, et al. Widespread abnormality of the γ-aminobutyric acid-ergic system in Tourette syndrome. Brain. 2012; 135(6):1926–36.
Piacentini J, Woods DW, Scahill L, Wilhelm S, Peterson AL, Chang S, et al. Behavior therapy for children with Tourette disorder. JAMA. 2010; 303(19):1929–37.
Roessner V, Plessen K, Rothenberger A, Ludolph A, Rizzo R, Skov L, et al. European clinical guidelines for Tourette syndrome and other tic disorders. Part II: pharmacological treatment. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiat. 2011; 20(4):173–96.
Scahill L, Erenberg G, Berlin Jr CM, Budman C, Coffey BJ, Jankovic J, et al. Contemporary Assessment and Pharmacotherapy of Tourette Syndrome. NeuroRX. 2006; 3(2):192–206.
Tourette's Syndrome Study Group. Short-term versus longer term pimozide therapy in Tourette's syndrome. Neurology. 1999; 52:874–7.
Müller-Vahl KR, Krueger D. Does Tourette syndrome prevent tardive dyskinesia? Movement Disord. 2011; 26(13):2442–3.
Dion Y, Annabele L, Sandor P, Chouinard G. Risperidone in the treatment of Tourette syndrome: A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Psychopharm. 2002; 22:31–9.
Scahill L, Leckman JF, Schultz RT, Katsovich L, Peterson BS. A placebo-controlled trial of risperidone in Tourette syndrome. Neurology. 2003; 69:1130–5.
Peña MS, Yaltho TC, Jankovic J. Tardive dyskinesia and other movement disorders secondary to aripiprazole. Movement Disord. 2011; 26(1):147–52.
Scahill L, Chappell PB, Kim YS, Schultz RT, Katsovich L, Shepherd E, et al. A placebo-controlled study of guanfacine in the treatment of children with tic disorders and ADHD. Am J Psychiatry. 2001; 158:1067–74.
Leckman JF, Hardin MT, Riddle MA, Stevenson J, Ort SI, Cohen DJ. Clonidine treatment of Gilles de la Tourette syndrome. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1991; 48:324–8.
Porta M, Sassi M, Cavallazzi M, Fornari M, Brambilla A, Servello D. Tourettes Syndrome and Role of Tetrabenazine: Review and Personal Experience. Clin Drug Invest. 2008; 28(7):443–59.
Kenney CJ, Hunter CB, Mejia NI, Jankovic J. Tetrabenazine in the treatment of Tourette syndrome. J Ped Neurol. 2007; 5(1):9–13.
Jimenez-Shahed J, Jankovic J. Tetrabenazine for treatment of chorea associated with Huntington's disease and other potential indications. Expert Opinion on Orphan Drugs. 2013; 1(5):423–36.
Jankovic J, Jimenez-Shahed J, Brown LW. A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of topiramate in the treatment of Tourette syndrome. J Neurol Neurosur Ps. 2010; 81(1):70–3.
Kurlan R, Crespi G, Coffey B, Muller-Vahl K, Koval S, Wunderlich G, Pramipexole for TS Trial Investigators. A multi-center randomized placebo-controlled trial of pramipexole in Tourette's syndrome. Movement Disord. 2012; 27:775–8.
Kwak CH, Hanna PA, Jankovic J. Botulinum toxin in the treatment of tics. Arch Neurol. 2000; 57(8):1190–3.
Simpson DM, Blitzer A, Brashear A, Comella C, Dubinsky R, Hallett M, et al. Assessment: Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of movement disorders (an evidence-based review). Neurology. 2008; 70(19):1699–706.
Maciunas RJ, Maddux BN, Riley DE, Whitney CM, Schoenberg MR, Ogrocki PJ, et al. Prospective randomized double-blind trial of bilateral thalamic deep brain stimulation in adults with Tourette syndrome. J Neurosurg. 2007; 107(5):1004–14.
Servello D, Porta M, Sassi M, Brambilla A, Robertson MM. Deep brain stimulation in 18 patients with severe Gilles de la Tourette syndrome refractory to treatment: the surgery and stimulation. J Neurol Neurosur Ps. 2008; 79(2):136–42.
Viswanathan A, Jimenez-Shahed J, Baizabal Carvallo JF, Jankovic J. Deep brain stimulation for Tourette syndrome: target selection. Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery. 2012; 90(4):213–24.
Tourette's Syndrome Study Group. Treatment of ADHD in children with Tourette's syndrome (TACT Trial). Ann Neurol. 2000; 48:953
Gadow KD, Sverd J, Nolan EE, Sprafkin J, Schneider J. Immediate-release methylphenidate for ADHD in children with comorbid chronic multiple tic disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2007; 46(7):840–8.
Allen AJ, Kurlan RM, Gilbert DL, Coffey BJ, Linder SL, Lewis DW, et al. Atomoxetine treatment in children and adolescents with ADHD and comorbid tic disorders. Neurology. 2005; 65(12):1941–9.
Required Author Forms
Disclosure forms provided by the authors are available with the online version of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Invited Review for Movement Disorders Therapeutics, in NeuroTherapeutics, Jankovic J and Factor S (editors)
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 1224 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurlan, R.M. Treatment of Tourette Syndrome. Neurotherapeutics 11, 161–165 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-013-0215-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-013-0215-4