Abstract
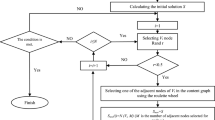
Social networks, which have become so popular today, allow their users to share information. The main challenge the users are facing is the security preservation of their information and privacy. Therefore, structural anonymity techniques were introduced that would hide the identity of users. One of the drawbacks of these techniques, which are based on graph modification, is the lack of attention about the structural semantics of graphs. This paper focuses on the popular notion of a privacy protection method called k-degree anonymization and tries to reduce utility loss on the graph. The new k-degree anonymization method, genetic k-degree edge modification, has two steps. The first step includes partitioning of vertices and community detection in the graph. The result of these two determines the needed increase in edges for every vertex in each society to achieve k-degree anonymization. The second step is graph modification using the genetic algorithm by adding some edges between vertices in each community. Average Path Length (APL), Average Clustering Coefficient, and Transitivity (T) are employed to evaluate the method. The proposed algorithm has been tested on four datasets, and the results have shown the average relative performance demonstrates more stability than the other four well-known algorithms. Also, APL criterion in our algorithm is better preserved than all other algorithms; furthermore, Transitivity parameters are the best result in most cases.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Backstrom L, Cynthia D, Jon K (2007) Wherefore art Thou R3579x? Anonymized social networks, hidden patterns, and structural steganography. In: Proceedings of the 16th international conference on world wide web, pp 181–190
Bhagat S, Cormode G, Krishnamurthy B, Srivastava D (2009) Class-based graph anonymization for social network data. Proc VLDB Endow 2(1):766–777
Blondel VD, Guillaume J-L, Lambiotte R, Lefebvre E (2008) Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J Stat Mech: Theory Exp 2008(10):P10008
Boas PR, Villas FA, Rodrigues G Travieso, Costa LDF (2010) Sensitivity of complex networks measurements. J Stat Mech: Theory Exp 2010(03):P03009
Byun J-W, Ashish K, Elisa B, Ninghui L (2007) Efficient K-anonymization using clustering techniques. In: International conference on database systems for advanced applications, pp 188–200
Campan A, Traian MT (2009) Data and structural K-anonymity in social networks. In: Privacy, security, and trust in KDD. Springer, pp 33–54
Casas-Roma J, Rousseau F (2015) Community-preserving generalization of social networks. In: 2015 IEEE/ACM international conference on advances in social networks analysis and mining (ASONAM), pp 1465–1472
Casas-Roma J, Herrera-Joancomarti J, Torra V (2013) An algorithm for K-degree anonymity on large networks. In: 2013 IEEE/ACM international conference on advances in social networks analysis and mining (ASONAM 2013), pp 671–675
Casas-Roma J, Herrera-Joancomartí J, Torra V (2017) K-Degree anonymity and edge selection: improving data utility in large networks. Knowl Inf Syst 50(2):447–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-016-0947-7
Chbeir R, Al Bouna B (2013) Security and privacy preserving in social networks. Springer, Berlin
Chester S, Kapron B, Ramesh G, Srivastava G, Thomo A, Venkatesh S (2011) K-Anonymization of social networks by vertex addition. ADBIS 2(789):107–116
Chester S, Kapron BM, Ramesh G, Srivastava G, Thomo A, Venkatesh S (2013) Why Waldo befriended the dummy? K-anonymization of social networks with pseudo-nodes. Soc Netw Anal Min 3(3):381–399
Davis L (1991) Handbook of genetic algorithms. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Hao Y, Cao H, Chuan H, Bhattarai K, Misra Satyajayant (2014) K-Anonymity for social networks containing rich structural and textual information. Soc Netw Anal Min 4(1):223
Hay M, Miklau G, Jensen D, Towsley D, Weis P (2008) Resisting structural re-identification in anonymized social networks. Proc VLDB Endow 1(1):102–114. https://doi.org/10.14778/1453856.1453873
Ilhan N, Gündüz-Öğüdücü S, Etaner-Uyar AS (2014) Introduction to social networks: analysis and case studies. In: Gündüz-Öğüdücü S, Etaner-Uyar AS (eds) social networks: analysis and case studies. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–18
Liu K, Evimaria T (2008) Towards identity anonymization on graphs. In: Proceedings of the 2008 ACM SIGMOD international conference on management of data, pp 93–106
Liu X, Xie Q, Wang L (2017) Personalized extended ($α$, k)-anonymity model for privacy-preserving data publishing. Concurr Comput Pract Exp 29(6):e3886
Lu X, Yi S, Stéphane B (2012) Fast identity anonymization on graphs. In: Lecture notes in computer science (including subseries lecture notes in artificial intelligence and lecture notes in bioinformatics), vol 7446 LNCS (PART 1), pp 281–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32600-4_21
Ma T, Zhang Y, Cao J, Shen J, Tang M, Tian Y, Al-Dhelaan A, Al-Rodhaan M (2015) $$$\backslash{\$}varvec ${$$\backslash{\$}textit ${$KDVEM$}$$}$ $$ KDVEM: a $$ k $$ k-Degree anonymity with vertex and edge modification algorithm. Computing 97(12):1165–1184
Malekhosseini R, Hosseinzadeh M, Navi K (2018) An investigation into the requirements of privacy in social networks and factors contributing to users’ concerns about violation of their privacy. Soc Netw Anal Min 8(1):41
Memon N, Alhajj R (2010) From sociology to computing in social networks: theory, foundations and applications. Springer, Berlin
Musiał K, Kazienko P (2013) Social networks on the internet. World Wide Web. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11280-011-0155-z
Ragozini G (2020) Challenges in social network research: methods and applications. Springer, Berlin
Rohe K, Tai Q (2013) The blessing of transitivity in sparse and stochastic networks. ArXiv Preprint arXiv:1307.2302
Ros-Martin M, Salas J, Casas-Roma J (2019) Scalable non-deterministic clustering-based k-anonymization for rich networks. Int J Inf Secur 18(2):219–238
Sharma S, Gupta P, Bhatnagar V (2012) Anonymisation in social network: a literature survey and classification. Int J Soc Netw Min 1(1):51–66
Sihag VK (2012) A clustering approach for structural K-anonymity in social networks using genetic algorithm. In: Proceedings of the CUBE international information technology conference, pp 701–706
Sun Y, Yuan Y, Wang G, Cheng Y (2016) Splitting anonymization: a novel privacy-preserving approach of social network. Knowl Inf Syst 47(3):595–623
Talbi E-G (2009) Metaheuristics: from design to implementation, vol 74. Wiley, New York
Tripathy BK, Panda GK (2010) A new approach to manage security against neighborhood attacks in social networks. In: 2010 International conference on advances in social networks analysis and mining (ASONAM), pp 264–269
Wang S-L, Tsai Z-Z, Hong T-P, Ting I-H (2011) Anonymizing shortest paths on social network graphs. In: Asian conference on intelligent information and database systems, pp 129–136
Wang S-L, Tsai Y-C, Kao H-Y, Ting I-H, Hong T-P (2013) Shortest paths anonymization on weighted graphs. International Journal of Software Engineering and Knowledge Engineering 23(1) 65–79
Yazdanjue N, Fathian M, Amiri B (2019) Evolutionary algorithms for k-anonymity in social networks based on clustering approach. Computer J. https://doi.org/10.1093/comjnl/bxz069
Zheleva E, Lise G (2007) Preserving the privacy of sensitive relationships in graph data. In: International workshop on privacy, security, and trust in KDD, pp 153–171
Zheng W, Zhongyue W, Tongtong L, Yong M, Chunfu J (2018) K-anonymity algorithm based on improved clustering. In: International conference on algorithms and architectures for parallel processing, pp 462–476
Zhou B, Pei J, Luk WS (2008) A brief survey on anonymization techniques for privacy preserving publishing of social network data. ACM Sigkdd Explor Newsl 10(2):12–22
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajabzadeh, S., Shahsafi, P. & Khoramnejadi, M. A graph modification approach for k-anonymity in social networks using the genetic algorithm. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 10, 38 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-020-00655-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-020-00655-6