Abstract
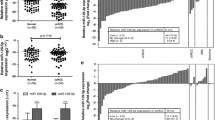
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been proven to be important oncogenes and tumor suppressors in wide range of cancers, including renal cell carcinoma (RCC). In our study, we evaluated miRNA-429 as potential diagnostic/prognostic biomarker in 172 clear cell RCC patients and as a potential regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in vitro. We demonstrated that miR-429 is down-regulated in tumor tissue samples (P < 0.0001) and is significantly associated with cancer metastasis (P < 0.0001), shorter disease-free (P = 0.0105), and overall survival (P = 0.0020). In addition, ectopic expression of miR-429 in 786-0 RCC cells followed by TGF-β treatment led to increase in the levels of E-cadherin expression (P < 0.0001) and suppression of cellular migration (P < 0.0001) in comparison to TGF-β-treated controls. Taken together, our findings suggest that miR-429 may serve as promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in RCC patients. We further suggest that miR-429 has a capacity to inhibit loss of E-cadherin in RCC cells undergoing EMT and consequently attenuate their motility.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of papillary renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:135–45.
Ma X, Gao Y, Fan Y, Ni D, Zhang Y, Chen W, et al. Overexpression of E2F1 promotes tumor malignancy and correlates with TNM stages in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 2013;8:1–12.
KY X, Wu S. Update on the treatment of metastatic clear cell and non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Biomark Res. 2015;3:1–5.
Ohtsuka M, Ling H, Doki Y, Mori M, Calin G. MicroRNA processing and human cancer. J Clin Med. 2015;4:1651–67.
Orom UA, Nielsen FC, Lund AH. MicroRNA-10a binds the 5’UTR of ribosomal protein mRNAs and enhances their translation. Mol Cell. 2008;30:460–71.
Xu J, Yao Q, Hou Y, Xu M, Liu S, Yang L, et al. MiR-223/Ect2/p21 signaling regulates osteosarcoma cell cycle progression and proliferation. Biomed Pharmacother = Biomédecine Pharmacothérapie. 2013;67:381–6.
Huang N, Wu Z, Lin L, Zhou M, Wang L, Ma H, et al. MiR-338-3p inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells by targeting ZEB2 and MACC1/Met/Akt signaling. Oncotarget. 2015;6:15222–34.
Liu YC, Zhang M, Qian J, Bao M, Meng X, Zhang S, et al. miR-134 functions as a tumor suppressor in cell proliferation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting KRAS in renal cell carcinoma cells. DNA Cell Biol. 2015;34:429–36.
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G, Kang Y. The miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:14910–4.
Zhang Y, Yang P, Wang XF. Microenvironmental regulation of cancer metastasis by miRNAs. Trends Cell Biol. 2014;24:153–60.
Sundararajan BS, Gengenbacher N, Stemmler MP, Kleemann JA, Brabletz T. The ZEB1/miR-200c feedback loop regulates invasion via actin interacting proteins MYLK and TKS5. Oncotarget. 2015;6:27083–96.
Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Kolesnikoff N, Bert AG, Wang J, Shannon MF, Goodall GJ. A double-negative feedback loop between ZEB1-SIP1 and the microRNA-200 family regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 2008;68:7846–54.
Ceppi P, Mudduluru P, Kumarswamy R, Rapa I, Scagliotti GV, Papotti M, Allgayer H. Loss of miR-200c expression induces an aggressive, invasive, and chemoresistant phenotype in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2010;8:1207–16.
Xiong H, Hong J, Du W, Lin Y, Ren L, Wang Y, et al. Roles of STAT3 and ZEB1 proteins in E-cadherin down-regulation and human colorectal cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:5819–32.
Paul C. Renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2011;1–6:461–73.
Stewart-Merrill SB, Thompson RH, Boorjian SA, Psutka SP, Lohse CM, Cheville JC, et al. Oncologic surveillance after surgical resection for renal cell carcinoma: a novel risk-based approach. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:4151–7.
Chan SH, Wang LH. Regulation of cancer metastasis by microRNAs. J Biomed Sci. 2015;22:9.
Yoshino H, Enokida H, Itesako T, Tatarano S, Kinoshita T, Fuse M, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related microRNA-200s regulate molecular targets and pathways in renal cell carcinoma. J Hum Genet. 2013;4:1–9.
Sun Y, Shen S, Liu X, Tang H, Wang Z, Yu Z, et al. MiR-429 inhibits cells growth and invasion and regulates EMT-related marker genes by targeting Onecut2 in colorectal carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;390:19–30.
Tang J, Li L, Huang W, Sui C, Yang Y, Lin X, et al. MiR-429 increases the metastatic capability of HCC via regulating classic Wnt pathway rather than epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 2015;364:33–43.
Wang Y, Dong X, Hu B, Wang XJ, Wang Q, Wang WL, et al. The effects of Micro-429 on inhibition of cervical cancer cells through targeting ZEB1 and CRKL. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;80:311–21.
Wang F, Jiang C, Sun Q, Yan F, Wang L, Fu Z, et al. Downregulation of miR-429 and inhibition of cell migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13:3236–42.
Zhu Q, He J, Chen D, Zhang B, Xu L, Ma H, et al. Expression of miR-29c, miR-93, and miR-429 as potential biomarkers for detection of early stage non-small lung cancer. PLoS One. 2014;9:2.
Halvorsen AR, Bjaanæs M, LeBlanc M, Holm AM, Bolstad N, Rubio L, et al. A unique set of 6 circulating microRNAs for early detection of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2016.
Wu CL, Ho JY, Chou SC, Yu DS. MiR-429 reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition by restoring E-cadherin expression in bladder cancer. Oncotarget. 2014.
Chen Y, Xiao Y, Ge W, Zhou K, Wen J, Yan W, et al. miR-200b inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes growth of intestinal epithelial cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e541.
Wu CL, Ho JY, Chou SC, Yu DS. MiR-429 reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition by restoring E-cadherin expression in bladder cancer. Oncotarget. 2016.
Jingushi K, Ueda Y, Kitae K, Hase H, Egawa H, Ohshio I, et al. miR-629 targets TRIM33 to promote TGFβ/Smad signaling and metastatic phenotypes in ccRCC. Mo Cancer Res. 2014;13:565–74.
Huang W, Cen S, Kang X, Wang W, Wang Y, Chen X. TGF-β1-induced Fascin1 promotes cell invasion and metastasis of human 786-0 renal carcinoma cells. Acta Histochem. 2016;118:144–51.
Fu H, Hu Z, Wen J, Wang K, Liu Y. TGF-β promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells by increasing fascin1 expression via ERK and JNK signal pathways. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin Shanghai. 2009;41:648–56.
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by grant no. 15-34678A of the Czech Ministry of Health, by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic under the project CEITEC 2020 (LQ1601), the Project RVO (MOU, 00209805), and The Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports for the Project BBMRI CZ (LM2010004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All patients included in the study signed informed consent forms and the study was approved by the local Ethical Board at the Masaryk Memorial Cancer Institute and University Hospital Brno.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Tana Machackova and Hana Mlcochova contributed equally to the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Machackova, T., Mlcochova, H., Stanik, M. et al. MiR-429 is linked to metastasis and poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma by affecting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Tumor Biol. 37, 14653–14658 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5310-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5310-9