Abstract
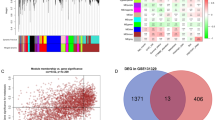
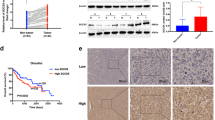
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common cause of cancer-related death worldwide, and its incidence continues to increase. However, the mechanism underlying the development and progression of HCC remains unknown. The suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (SOCS2) is a member of the SOCS family and influences the carcinogenesis of multiple types of tumors, but the biological roles of SOCS2 in HCC remain unclear. In this study, we found that SOCS2 expression was reduced in HCC tissues compared with matched noncancerous liver tissues. Moreover, decreased SOCS2 expression was significantly associated with the presence of intrahepatic metastasis and high histological grade in HCC patients. Colony formation assays and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assays demonstrated that overexpression of SOCS2 or knockdown of endogenous SOCS2 did not significantly affect cell proliferation and tumorigenicity in HCC cells in vitro and in vivo. However, SOCS2 overexpression significantly inhibited the migration and invasion of HCC cells in vitro and inhibited metastasis in vivo. Consistent with these findings, the knockdown of endogenous SOCS2 enhanced migration and invasion in HCC cells in vitro. Our study demonstrated that SOCS2 inhibited human HCC metastasis, and SOCS2 might provide a new potential therapeutic strategy for treating HCC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shiraha H, Yamamoto K, Namba M. Human hepatocyte carcinogenesis (review). Int J Oncol. 2013;42(4):1133–8. doi:10.3892/ijo.2013.1829.
Torre LA, Siegel RL, Ward EM, Jemal A. Global cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends—an update. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2016;25(1):16–27. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.epi-15-0578.
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. doi:10.3322/caac.21262.
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016. doi:10.3322/caac.21338.
Li H, Ge C, Zhao F, Yan M, Hu C, Jia D, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha-activated angiopoietin-like protein 4 contributes to tumor metastasis via vascular cell adhesion molecule-1/integrin beta1 signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2011;54(3):910–9. doi:10.1002/hep.24479.
Fang T, Cui M, Sun J, Ge C, Zhao F, Zhang L, et al. Orosomucoid 2 inhibits tumor metastasis and is upregulated by CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta in hepatocellular carcinomas. Oncotarget. 2015;6(18):16106–19. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.3867.
Yoshimura A, Naka T, M. K. SOCS proteins, cytokine signalling and immune regulation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(6):454–65. doi:10.1038/nri2093.
Hilton DJ, Richardson RT, Alexander WS, Viney EM, Willson TA, Sprigg NS, et al. Twenty proteins containing a C-terminal SOCS box form five structural classes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(1):114–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.1.114.
Wormald S, Hilton DJ. Inhibitors of cytokine signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(2):821–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.R300030200.
Qiu X, Zheng J, Guo X, Gao X, Liu H, Tu Y, et al. Reduced expression of SOCS2 and SOCS6 in hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with aggressive tumor progression and poor prognosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;378(1–2):99–106. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1599-5.
Okochi O, Hibi K, Sakai M, Inoue S, Takeda S, Kaneko T, et al. Methylation-mediated silencing of SOCS-1 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma derived from cirrhosis. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9(14):5295–8.
WY W, Kim H, Zhang CL, Meng XL, Wu ZS. Loss of suppressors of cytokine signaling 3 promotes aggressiveness in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Investig Surg. 2014;27(4):197–204. doi:10.3109/08941939.2013.873098.
Yoshikawa H, Matsubara K, Qian GS, Jackson P, Groopman JD, Manning JE, et al. SOCS-1, a negative regulator of the JAK/STAT pathway, is silenced by methylation in human hepatocellular carcinoma and shows growth-suppression activity. Nat Genet. 2001;28(1):29–35. doi:10.1038/88225.
Chu PY, Yeh CM, Hsu NC, Chang YS, Chang JG, Yeh KT. Epigenetic alteration of the SOCS1 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma. Swiss Med Wkly. 2010;140:w13065. doi:10.4414/smw.2010.13065.
Ko E, Kim SJ, Joh JW, Park CK, Park J, Kim DH. CpG island hypermethylation of SOCS-1 gene is inversely associated with HBV infection in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2008;271(2):240–50. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.06.009.
Niwa Y, Kanda H, Shikauchi Y, Saiura A, Matsubara K, Kitagawa T, et al. Methylation silencing of SOCS-3 promotes cell growth and migration by enhancing JAK/STAT and FAK signalings in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2005;24(42):6406–17. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208788.
Hu C, Li H, Li J, Zhu Z, Yin S, Hao X, et al. Analysis of ABCG2 expression and side population identifies intrinsic drug efflux in the HCC cell line MHCC-97 L and its modulation by Akt signaling. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29(12):2289–97. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgn223.
Greenhalgh CJ, Miller ME, Hilton DJ, Lund PK. Suppressors of cytokine signaling: relevance to gastrointestinal function and disease. Gastroenterology. 2002;123(6):2064–81. doi:10.1053/gast.2002.37068.
Dey BR, Spence SL, Nissley P, Furlanetto RW. Interaction of human suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS)-2 with the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(37):24095–101. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.37.24095.
Mathews LS, Hammer RE, Behringer RR, D’Ercole AJ, Bell GI, Brinster RL, et al. Growth enhancement of transgenic mice expressing human insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology. 1988;123(6):2827–33. doi:10.1210/endo-123-6-2827.
Greenhalgh CJ, Bertolino P, Asa SL, Metcalf D, Corbin JE, Adams TE, et al. Growth enhancement in suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (SOCS-2)-deficient mice is dependent on signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b (STAT5b). Mol Endocrinol. 2002;16(6):1394–406. doi:10.1210/mend.16.6.0845.
Farabegoli F, Ceccarelli C, Santini D, Taffurelli M. Suppressor of cytokine signalling 2 (SOCS-2) expression in breast carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 2005;58(10):1046–50. doi:10.1136/jcp.2004.024919.
Hoefer J, Kern J, Ofer P, Eder IE, Schafer G, Dietrich D, et al. SOCS2 correlates with malignancy and exerts growth-promoting effects in prostate cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014;21(2):175–87. doi:10.1530/erc-13-0446.
Iglesias-Gato D, Chuan YC, Wikstrom P, Augsten S, Jiang N, Niu Y, et al. SOCS2 mediates the cross talk between androgen and growth hormone signaling in prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35(1):24–33. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgt304.
Newton VA, Ramocki NM, Scull BP, Simmons JG, McNaughton K, Lund PK. Suppressor of cytokine signaling-2 gene disruption promotes Apc(Min/+) tumorigenesis and activator protein-1 activation. Am J Pathol. 2010;176(5):2320–32. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2010.090684.
Sutherland KD, Lindeman GJ, Choong DY, Wittlin S, Brentzell L, Phillips W, et al. Differential hypermethylation of SOCS genes in ovarian and breast carcinomas. Oncogene. 2004;23(46):7726–33. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207787.
Wikman H, Kettunen E, Seppanen JK, Karjalainen A, Hollmen J, Anttila S, et al. Identification of differentially expressed genes in pulmonary adenocarcinoma by using cDNA array. Oncogene. 2002;21(37):5804–13. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205726.
Masuzaki R, Zhao S, Valerius MT, Tsugawa D, Oya Y, Ray KC, et al. SOCS2 balances metabolic and restorative requirements during liver regeneration. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(7):3346–58. doi:10.1074/jbc.M115.703264.
Kazi JU, Ronnstrand L. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (SOCS2) associates with FLT3 and negatively regulates downstream signaling. Mol Oncol. 2013;7(3):693–703. doi:10.1016/j.molonc.2013.02.020.
Letellier E, Haan S. SOCS2: physiological and pathological functions. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2016;8:189–204. doi:10.2741/760.
Tannahill GM, Elliott J, Barry AC, Hibbert L, Cacalano NA, Johnston JA. SOCS2 can enhance interleukin-2 (IL-2) and IL-3 signaling by accelerating SOCS3 degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(20):9115–26. doi:10.1128/mcb.25.20.9115-9126.2005.
Vesterlund M, Zadjali F, Persson T, Nielsen ML, Kessler BM, Norstedt G, et al. The SOCS2 ubiquitin ligase complex regulates growth hormone receptor levels. PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e25358. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025358.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from the National KeySci-Tech Special Project of China (2013ZX10002-011), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81201623, 81372192), Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (13ZZ082), Key Discipline and Specialty Foundation of Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning, and the SKLORG Research foundation (91-12-04, 91-13-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Taoyang Chen, Haiyang Xie and Ying Cui contributed equally to this work.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(247 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, M., Sun, J., Hou, J. et al. The suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 (SOCS2) inhibits tumor metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 37, 13521–13531 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5215-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5215-7