Abstract
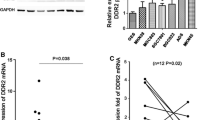
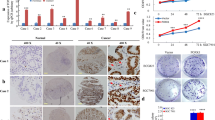
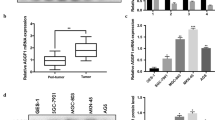
In this study, we investigated the effects of DDR1 on the invasion and metastasis in gastric cancer (GC) via epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Immunohistochemistry analysis was used to detect DDR1, E-cadherin, and Vimentin expression in GC tissues as well as DDR1 expression in GC cell lines and normal gastric epithelial cells. The relationship between DDR1 expression and EMT in GC cell lines was explored by down and upregulating DDR1 and examining corresponding changes in the expression of EMT-related proteins and in biological characteristics. Furthermore, a nude mice model with a transplantation tumor generating from stably transfected GC cells with DDR1 overexpression was established and performed to further reveal the effects of DDR1 expression on cellular morphology and growth of GC. Our results showed that DDR1 was highly expressed in GC tissues and cell lines compared with adjacent tissues and normal cell line, and its expression was significantly higher in GC having poor differentiation (p < 0.01), advanced depth of wall invasion (p = 0.020), lymph node metastasis (p = 0.0001), liver metastasis (p < 0.01), and high TNM stage (p < 0.01). Western blot analyses revealed that DDR1 overexpression resulted in a significant decrease in the expression of E-cadherin (p < 0.01) and an increase in the expression of Vimentin and Snail (p < 0.01), while knockdown of DDR1 led to opposite outcomes. We further demonstrated that DDR1 overexpression promoted GC cell proliferation (p < 0.05), migration (p < 0.01), and invasion (p < 0.01), and accelerated the growth (p < 0.05) as well as the microvessel formation (p < 0.01) of transplantation tumor in nude mice. Our study establishes that DDR1 enhances invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer via EMT.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feng Q, Pei W, Zheng ZX, Bi JJ, Yuan XH. Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognostic factors of 63 gastric cancer patients with metachronous ovarian metastasis. Cancer Biol Med. 2013;10(2):86–91.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Michael J. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–49.
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108.
Alves F, Vogel W, Mossie K, Millauer B, Hofler H, Ullrich A. Distinct structural characteristics of discoidin I subfamily receptor tyrosine kinases and complementary expression in human cancer. Oncogene. 1995;10(3):609–18.
Alves F, Saupe S, Ledwon M, Schaub F, Hiddemann W, Vogel WF. Identification of two novel, kinase-deficient variants of discoidin domain receptor 1: differential expression in human colon cancer cell lines. FASEB J. 2001;15:1321–3.
Miao L, Zhu S, Wang Y, Li Y, Ding J, Dai J, et al. Discoidin domain receptor 1 is associated with poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer and promotes cell invasion via epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Med Oncol. 2013;30(3):626.
Johnson JD, Edman JC, Rutter WJ. A receptor tyrosine kinase found in breast carcinoma cells has an extracellular discoidin I-like domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90(22):10891.
Shimada K, Nakamura M, Ishida E, Higuchi T, Yamamoto H, Tsujikawa K, et al. Prostate cancer antigen-1 contributes to cell survival and invasion though discoidin receptor 1 in human prostate cancer. Cancer Sci. 2008;99(1):39–45.
Jian ZX, Sun J, Chen W, Jin HS, Zheng JH, Wu YL. Involvement of discoidin domain 1 receptor in recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma by genome-wide analysis. Med Oncol. 2012;29:3077–82.
Quan J, Yahata T, Adachi S, Yoshihara K, Tanaka K. Identification of receptor tyrosine kinase, discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1a), as a potential biomarker for serous ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(2):971–82.
Medici D, Nawshad A. Type I collagen promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through ILK-dependent activation of NFkappaB and LEF-1. Matrix Biol. 2010;29(3):161–5.
Ongusaha PP, Kim JI, Fang L, Wong TW, Yancopoulos GD, Aaronson SA, et al. p53 induction and activation of DDR1a kinase counteract p53-mediated apoptosis and influence p53 regulation through a positive feedback loop. EMBO J. 2003;22(6):1289–301.
Ford CE, Lau SK, Zhu CQ, Andersson T, Tsao MS, Vogel WF. Expression and mutation analysis of the discoidin domain receptors 1 and 2 in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2007;96(5):808–14.
Yang SH, Baek HA, Lee HJ, Park HS, Jang KY, Kang MJ, et al. Discoidin domain receptor 1 is associated with poor prognosis of non-small cell lung carcinomas. Oncol Rep. 2010;24:311–9.
Shen Q, Cicinnati VR, Zhang X, Iacob S, Weber F, Sotiropoulos GC, et al. Role of microRNA-199a-5p and discoidin domain receptor 1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma invasion. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:227. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-9-227.
Valencia K, Ormazábal C, Zandueta C, Luis-Ravelo D, Antón I, Pajares MJ, et al. Inhibition of collagen receptor discoidin domain receptor-1 (DDR1) reduces cell survival, homing, and colonization in lung cancer bone metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(4):969–80.
Park HS, Kim KR, Lee HJ, Choi HN, Kim DK, Kim BT, et al. Overexpression of discoidin domain receptor 1 increases the migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in association with matrix metalloproteinase. Oncol Rep. 2007;18(6):1435–41.
Yu JJ, Wei LN, Dong C, Fan H, Yu Y, Feng YH, et al. Expression of DDR1a and its clinical significance in gastric carcinoma. Chin J Cancer Prev Treat. 2012;19(14):1074–7.
Kim HP, Han SW, Song SH, Jeong EG, Lee MY, Hwang D, et al. Testican-1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling confers acquired resistance to lapatinib in HER2-positive gastric cancer. Oncogene. 2014;33(25):3334–41.
Bonnomet A, Brysse A, Tachsidis A, Waltham M, Thompson EW, Polette M, et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions and circulating tumor cells. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2010;15:261–73.
Zavadil J, Haley J, Kalluri R, Muthuswamy SK, Thompson E. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 2008;68:9574–7.
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA. Epithelial–mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell. 2009;139871–890.
Katoh M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 2005;27(6):1677–83.
Zheng HX, Cai YD, Wang YD, Cui XB, Xie TT, Li WJ, et al. Fas signaling promotes motility and metastasis through epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastrointestinal cancer. Oncogene. 2013;32(9):1183–92.
Kim MA, Lee HS, Lee HE, Kim JH, Yong HK, Kim WH. Prognostic importance of epithelial–mesenchymal transition-related protein expression in gastric carcinoma. Histopathology. 2009;54:442–51.
Chen D, Li W, Liu S, Su Y, Han G, Xu C, et al. Interleukin-23 promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of oesophageal carcinoma cells via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Sci Rep-UK. 2015;5:8604.
Yamaguchi N, Mimoto R, Yanaihara N, Imawari Y, Hirooka S, Okamoto A, et al. DYRK2 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal- transition and chemosensitivity through Snail degradation in ovarian serous adenocarcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2015;1–11.
Batlle E, Sancho E, Francí C, Domínguez D, Monfar M, Baulida J, et al. (2000). The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2(2):84–9.
Cano A, Pérez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I, Locascio A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, et al. The transcription factor snail controls epithelial–mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2(2):76–83.
Jin H, Yu Y, Zhang T, Zhou X, Zhou J, Jia L, et al. Snail is critical for tumor growth and metastasis of ovarian carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2010;126(9):2102–11.
Blechschmidt K, Sassen S, Schmalfeldt B, Schuster T, Höfler H, Becker KF. The E-cadherin repressor Snail is associated with lower overall survival of ovarian cancer patients. Brit J Cancer. 2008;98(2):489–95.
Shields MA, Krantz SB, Bentrem DJ, Dangi-Garimella S, Munshi HG. Interplay between β1-integrin and Rho signaling regulates differential scattering and motility of pancreatic cancer cells by snail and Slug proteins. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(9):6218–29.
Kudo-Saito C, Shirako H, Takeuchi T, Kawakami Y. Cancer metastasis is accelerated through immunosuppression during Snail-induced EMT of cancer cells. Cancer Cell. 2009;15(3):195–206.
Green D, Ponce DL, Leon-Rodriguez E, Sosa-Sanchez R. Adenocarcinoma of the stomach: univariate and multivariate analysis of factors associated with survival. Am J Clin Oncol. 2002;25:84–9.
Steeg PS. Tumor metastasis: mechanistic insights and clinical challenge. Nat Med. 2006;12:895–904.
Hwang TL, Lee LY, Wang CC, Liang Y, Huang SF, Wu CM. Claudin-4 expression is associated with tumor invasion, MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression in gastric cancer. Exp Ther Med. 2010;1(5):789–97.
Matsuyama W, Hashiguchi T, Umehara F, Matsuura E, Kawabata M, Arimura K, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in tuberculous meningitis. J Neurol Sci. 2001;186:75–9.
Fromowitz FB, Viola MV, Chao S, Oravez S, Mishriki Y, Finkel G, et al. Ras p21 expression in the progression of breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 1987;18(12):1268–75.
Gao M, Duan L, Luo J, Zhang L, Lu X, Zhang Y, et al. Discovery and optimization of 3-(2-(Pyrazolo [1, 5-a] pyrimidin-6-yl) ethynyl) benzamides as novel selective and orally bioavailable discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1a) inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2013;56(8):3281–95.
Kim HG, Tan L, Weisberg EL, Liu F, Canning P, Choi HG, et al. Discovery of a potent and selective DDR1 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. ACS Chem Biol. 2013;8(10):2145–50.
Yan SB, Peek VL, Ajamie R, Buchanan SG, Graff JR, Heidler SA, et al. LY2801653 is an orally bioavailable multi-kinase inhibitor with potent activity against MET, MST1R, and other oncoproteins, and displays anti-tumor activities in mouse xenograft models. Invest New Drugs. 2013;31(4):833–44.
Wang SH, Li X, Zhou LS, Cao ZW, Shi C, Zhou CZ, et al. microRNA-148a suppresses human gastric cancer cell metastasis by reversing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Tumor Biol. 2013;34(6):3705–12.
Shi Z, Zhang J, Qian X, Han L, Zhang K, Chen L, et al. AC1MMYR2, an inhibitor of dicer-mediated biogenesis of oncomir miR-21, reverses epithelial–mesenchymal transition and suppresses tumor growth and progression. Cancer Res. 2013;73(17):5519–31.
Voon DC, Wang H, Koo JK, Nguyen TA, Hor YT, Chu YS, et al. Runx3 protects gastric epithelial cells against epithelial-mesenchymal transition-induced cellular plasticity and tumorigenicity. Stem Cells. 2012;30(10):2088–99.
Maeyama M, Koga H, Selvendiran K, Yanagimoto C, Hanada S, Taniguchi E, et al. Switching in discoid domain receptor expressions in SLUG-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer. 2008;113(10):2823–31.
Eswaramoorthy R, Wang CK, Chen WC, Tang MJ, Ho ML, Hwang CC, et al. DDR1a regulates the stabilization of cell surface E-cadherin and E-cadherin-mediated cell aggregation. J Cell Physiol. 2010;224(2):387–97.
Yeh YC, Wu CC, Wang YK, Tang MJ. DDR1a triggers epithelial cell differentiation by promoting cell adhesion through stabilization of E-cadherin. Mol Biol Cell. 2011;22(7):940–53.
Wang CZ, Yeh YC, Tang MJ. DDR1a/E-cadherin complex regulates the activation of DDR1a and cell spreading. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009;297(2):C419–29.
Abdulkhalek S, Geen OD, Brodhagen L, Haxho F, Alghamdi F, Allison S, et al. Transcriptional factor snail controls tumor neovascularization, growth and metastasis in mouse model of human ovarian carcinoma. Clin Transl Med. 2014;3(1):1–16.
von Burstin J, Eser S, Paul MC, Seidler B, Brandl M, Messer M, et al. E-cadherin regulates metastasis of pancreatic cancer in vivo and is suppressed by a SNAIL/HDAC1/HDAC2 repressor complex. Gastroenterology. 2009;137(1):361–71.
Zhou BP, Deng J, Xia W, Xu J, Li YM, Gunduz M, et al. Dual regulation of Snail by GSK-3β-mediated phosphorylation in control of epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6(10):931–40.
Bettencourt MC, Bauer JJ, Sesterhenn IA, Connelly RR, Moul JW. CD34 immunohistochemical assessment of angiogenesis as a prognostic marker for prostate cancer recurrence after radical prostatectomy. J Urol. 1998;160(2):459–65.
Erbersdobler A, Isbarn H, Dix K, Steiner I, Schlomm T, Mirlacher M, et al. Prognostic value of microvessel density in prostate cancer: a tissue microarray study. World J Urol. 2010;28(6):687–92.
Miyata Y, Ohba K, Matsuo T, Watanabe SI, Hayashi T, Sakai H, et al. Tumor-associated stromal cells expressing E-prostanoid 2 or 3 receptors in prostate cancer: correlation with tumor aggressiveness and outcome by angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Urology. 2013;81(1):136–42.
Ho JW, Poon RT, Sun CK, Xue WC, Fan ST. Clinicopathological and prognostic implications of endoglin (CD105) expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and its adjacent non-tumorous liver. World J Gastroentero. 2005;11(2):176–81.
Yao Y, Pan Y, Chen J, Sun X, Qiu Y, Ding Y. Endoglin (CD105) expression in angiogenesis of primary hepatocellular carcinomas: analysis using tissue microarrays and comparisons with CD34 and VEGF. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2007;37(1):39–48.
He L, Wang Q, Zhao X. Microvessel density as a prognostic factor in ovarian cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer P. 2015;16(3):869–74.
Bădescu A, Georgescu CV, Vere CC, Crăiţoiu S, Grigore D. Correlations between Her2 oncoprotein, VEGF expression, MVD and clinicopathological parameters in gastric cancer. Rom J Morphol Embryo. 2012;53(4):997–1005.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Health Bureau of Gansu Province (No. GSWST2011-08), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81272661), and the Lanzhou University Second Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Written informed consent was obtained from all patients before sample collection, and the study was approved by the institutional Review Board of Lanzhou University Second Hospital.
The experiments were approved by the Ethics Committee of Lanzhou University Second Hospital.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, R., Wang, X., Qi, G. et al. DDR1 enhances invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer via epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Tumor Biol. 37, 12049–12059 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5070-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5070-6