Abstract
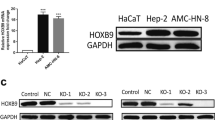
Armc8 (armadillo-repeat-containing protein 8) was proved to promote disruption of E-cadherin complex through regulating α-catenin degradation. In this study, we investigated Armc8 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma using immunohistochemistry (IHC). The positive rate of Armc8 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma was 53.9 % and higher than that in normal hepatic tissues (9.2 %) (p < 0.05). Clinicopathological analysis shows that Armc8 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma was significantly associated with larger tumor size (≥5 cm), multiple tumor numbers, higher pathological grade (media and poor), advanced TNM stages (II/III), and advanced BCLC stages (B/C). Western blot study also detected higher Armc8 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells including HepG2, HCC97L, and SMMC-7721 than in human hepatic cell Bel-7402. We further use specific small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) to knock down Armc8 expression in HepG2 cells and found that knockdown of Armc8 expression significantly inhibited the invasive ability of HepG2 cells. Downregulation of Armc8 expression significantly upregulated α-catenin, β-catenin, and E-cadherin expression in HepG2 cells. Immunofluorescent study shows that knockdown of Armc8 expression restored E-cadherin expression in membrane of HepG2 cells. These results indicate that Armc8 may be a potential cancer marker in hepatocellular carcinoma and may regulate cancer invasion through E-cadherin/catenin complex.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nawrocki B, Polette M, Van Hengel J, et al. Cytoplasmic redistribution of E-cadherin-catenin adhesion complex is associated with down-regulated tyrosine phosphorylation of E-cadherin in human bronchopulmonary carcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1998;153(5):1521–30.
Graziano F, Humar B, Guilford P. The role of the E-cadherin gene (CDH1) in diffuse gastric cancer susceptibility: from the laboratory to clinical practice. Ann Oncol. 2003;14(12):1705–13.
Busche S, Descot A, Julien S, et al. Epithelial cell-cell contacts regulate SRF-mediated transcription via Rac-actin-MAL signalling. J Cell Sci. 2008;121(Pt 7):1025–35.
Alan W, Clayton Y, Christopher R, et al. E-cadherin as an indicator of mesenchymal to epithelial reverting transitions during the metastatic seeding of disseminated carcinomas. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2008;25(6):621–8.
Somesh B, Suresh K. Molecular mechanisms controlling E-cadherin expression in breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;384(1):6–11.
Nobuaki K, Jun Y, Atsuhisa U, et al. RanBPM, muskelin, p48EMLP, p44CTLH, and the armadillo-repeat proteins ARMC8α and ARMC8β are components of the CTLH complex. Gene. 2007;396:236–47.
Suzuki T, Ueda A, Kobayashi N, et al. Proteasome-dependent degradation of alpha-catenin is regulated by interaction with ARMc8alpha. Biochem J. 2008;411(3):581–91.
Koji T, Atsuhisa U, Takeyuki S, et al. Armadillo repeat containing 8α binds to HRS and promotes HRS interaction with ubiquitinated proteins. The Open Biochemistry Journal. 2010;4:1–8.
Solaimani P, Damoiseaux R, Hankinson O. Genome-wide RNAi high-throughput screen identifies proteins necessary for the AHR-dependent induction of CYP1A1 by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Sci. 2013;136(1):107–19.
Francis O, Han F, Adams JC. Molecular phylogeny of a RING E3 ubiquitin ligase, conserved in eukaryotic cells and dominated by homologous components, the muskelin/RanBPM/CTLH complex. PLoS One. 2013;8(10), e75217.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was conducted under the regulations of the Institutional Review Board of the Affiliated Shengjing Hospital, China Medical University. Informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Peng, S., Jia, C. et al. Armc8 regulates the invasive ability of hepatocellular carcinoma through E-cadherin/catenin complex. Tumor Biol. 37, 11219–11224 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5006-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5006-1