Abstract
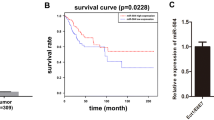
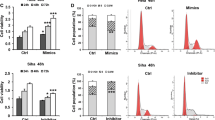
Our previous studies have demonstrated overexpression of Mcl-1 in cervical cancer tumorigenesis. However, the molecular mechanism of its overexpression remains not elucidated. MiR-320 has been reported to be down-regulated in various types of cancer, and bioinformatics prediction indicated that it may regulate the expression of Mcl-1. The aim of this study is to investigate the role of miR-320 and its target gene Mcl-1 in cervical cancer progression and to assess their clinical significance. miR-320 and Mcl-1 expressions in human cervical cancer tissues were investigated by qRT-PCR, in situ hybridization, and immunohistochemical staining, respectively. The clinicopathological implications of these molecules were analyzed. Bioinformatic prediction and luciferase assays were employed to identify the predicted microRNA (miRNA) which regulates Mcl-1. The apoptosis, proliferation, migration, and invasion assays were performed to investigate the effect of miR-320 on the cervical cancer cells. MiR-320 expression is significantly down-regulated versus Mcl-1 expression is up-regulated in cervical cancer tissues compared with normal controls with a negative correlation between them. Luciferase assay showed that miR-320 negatively regulates Mcl-1 expression. In addition, miR-320 induces apoptosis via down-regulation of Mcl-1 and activation of caspase-3 but inhibits cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and tumorigenesis in cervical cancer cells. Our studies show that miR-320 expression is decreased in cervical cancer, and its expression is negatively correlated with Mcl-1 expression in cervical cancer. In addition, miR-320 inhibits cervical cancer progression by down-regulation of Mcl-1. These results indicate that miR-320 may be an important biomarker and target for diagnosis and treatment of cervical cancer patient.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Forouzanfar MH, Foreman KJ, Delossantos AM, et al. Breast and cervical cancer in 187 countries between 1980 and 2010: a systematic analysis. Lancet. 2011;378:1461–84.
Zhou P, Levy NB, Xie H, et al. MCL1 transgenic mice exhibit a high incidence of B-cell lymphoma manifested as a spectrum of histologic subtypes. Blood. 2001;97:3902–9.
Tromp JM, Geest CR, Breij EC, et al. Tipping the Noxa/Mcl-1 balance overcomes ABT-737 resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:487–98.
Zhang H, Guttikonda S, Roberts L, et al. Mcl-1 is critical for survival in a subgroup of non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines. Oncogene. 2011;30:1963–8.
Harrison LR, Micha D, Brandenburg M, et al. Hypoxic human cancer cells are sensitized to BH-3 mimetic-induced apoptosis via downregulation of the Bcl-2 protein Mcl-1. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:1075–87.
Zhang T, Zhao C, Luo L, et al. The expression of Mcl-1 in human cervical cancer and its clinical significance. Med Oncol. 2012;29:1985–91.
Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M, et al. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2000;403:901–6.
Hammond SM, Sharpless NE. HMGA2, microRNAs, and stem cell aging. Cell. 2008;135:1013–6.
Zheng J, Xue H, Wang T, et al. miR-21 downregulates the tumor suppressor P12 (CDK2AP1) and stimulates cell proliferation and invasion. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112:872–80.
Hu X, Schwarz JK, Lewis Jr JS, et al. A microRNA expression signature for cervical cancer prognosis. Cancer Res. 2010;70:1441–8.
Schaar DG, Medina DJ, Moore DF, et al. miR-320 targets transferrin receptor 1 (CD71) and inhibits cell proliferation. Exp Hematol. 2009;37:245–55.
Yan LX, Huang XF, Shao Q, et al. MiR-21 overexpression in human breast cancer is associated with advanced clinical stage, lymph node metastasis and patient poor prognosis. RNA. 2008;14:2348–60.
Bronisz A, Godlewski J, Wallace JA, et al. Reprogramming of the tumour microenvironment by stromal PTEN-regulated miR-320. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;14:159–67.
Khew-Goodall Y, Goodall GJ. Stromal miR-320 keeps an oncogenic secretome in check. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14:124–5.
Kroh EM, Parkin RK, Mitchell PS, et al. Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods. 2010;50:298–301.
Yin Y, Yan ZP, Lu NN, et al. Downregulation of miR-145 associated with cancer progression and VEGF transcriptional activation by targeting N-RAS and IRS1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1829;2013:239–47.
Shi Z, Zhang T, Luo L, et al. Aquaporins in human breast cancer: identification and involvement in carcinogenesis of breast cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2012;106:267–72.
Wang N, Ma Q, Wang Y, et al. CacyBP/SIP expression is involved in the clinical progression of breast cancer. World J Surg. 2010;34:2545–52.
Wan LY, Deng J, Xiang XJ, et al. miR-320 enhances the sensitivity of human colon cancer cells to chemoradiotherapy in vitro by targeting FOXM1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;457:125–32.
Hsieh IS, Chang KC, Tsai YT, et al. MicroRNA-320 suppresses the stem cell-like characteristics of prostate cancer cells by downregulating the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34:530–8.
Schepeler T, Reinert JT, Ostenfeld MS, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic microRNAs in stage II colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68:6416–24.
Kotlabova K, Doucha J, Hromadnikova I. Placental-specific microRNA in maternal circulation-identification of appropriate pregnancy-associated microRNAs with diagnostic potential. J Reprod Immuno. 2011;89:185–91.
Resnick KE, Alder H, Hagan JP, et al. The detection of differentially expressed microRNAs from the serum of ovarian cancer patients using a novel real-time PCR platform. Gynecol Oncol. 2009;112:55–9.
Sun Q, Zou X, Zhang T, et al. The role of miR-200a in vasculogenic mimicry and its clinical significance in ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2014;132:730–8.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81202043 and 81372480), the Postdoctorate Foundation of Jiangsu Province (1401017A), the Postdoctorate Foundation of China (2014M560437 and 2015T80570), the Six Talent Peaks Project Foundation of Jiangsu Province (2014-WSW-059) and the Foundation of Wuxi City Health and Family Planning (MS201501). Authors thank all the women who donated tissues for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Zou, P., Wang, T. et al. Down-regulation of miR-320 associated with cancer progression and cell apoptosis via targeting Mcl-1 in cervical cancer. Tumor Biol. 37, 8931–8940 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4771-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4771-6