Abstract
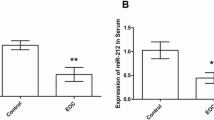
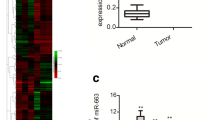
Ovarian cancer is one of the most common human malignancies in women. MiR-214 and semaphorin 4D (sema 4D) were found to be abhorrently expressed and involved in the progress of several kinds of malignant cancers. This study is aimed to investigate the cellular role of miR-214 and demonstrate that miR-214 negatively regulated sema 4D in ovarian cancer cells. The data showed that miR-214 expression was consistently lower in ovarian cancer tissues and cells than those in the normal controls. Over-expression of miR-214 in ovarian cancer SKOV-3 cells inhibited cell proliferation and induced apoptosis. It was suggested that miR-214 functioned as the tumor suppressor in ovarian cancer. Bioinformatic analysis indicated that miR-214 possibly regulated sema 4D by binding the sema 4D messenger RNA (mRNA) 3′-untranslated region (UTR). Sema 4D mRNA and protein levels were up-regulated in ovarian cancer tissues and SKOV-3 cells. Up-regulation of miR-214 in SKOV-3 cell line suppressed the sema 4D expression in both protein and nucleic acid levels. While, down-regulation of miR-214 in SKOV-3 cells would increase sema 4D protein and nucleic acid expression levels. The effects of miR-214 up- and down-regulation on luciferase activities of wild-type (WT) sema 4D 3′-UTR were completely removed upon introduction of mutation in 3′-UTR of WT sema 4D. Therefore, the data also demonstrated that sema 4D was the direct target of miR-214 and was negatively regulated by miR-214 in ovarian cancer cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Sema 4D:
-
Semaphorin 4D
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- 3′-UTR:
-
3′-Untranslated region
- LZTS1:
-
Leucine zipper putative tumor suppressor 1
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- RPMI:
-
Roswell Park Memorial Institute
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene fluoride
References
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–917.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics CA. Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–49.
Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–5.
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120:15–20.
Kloosterman WP, Plasterk RH. The diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease. Dev Cell. 2006;11(e):44150.
Wang F, Liu M, Li X, Tang H. MiR-214 reduces cell survival and enhances cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity via down-regulation of Bcl2l2 in cervical cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2013;587:488–95.
Wang X, Chen J, Li F, Lin Y, Zhang X, Lv Z, et al. MiR-214 inhibits cell growth in hepatocellular carcinoma through suppression of β-catenin. Biochem Biophy Res Commun. 2012;30:525–31.
Zhang XJ, Ye H, Zeng CW, He B, Zhang H, Chen YQ. Dysregulation of miR-15a and miR-214 in human pancreatic cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2010;3:46.
Yang Z, Chen S, Luan X, Li Y, Liu M, Li X, et al. MicroRNA-214 is aberrantly expressed in cervical cancers and inhibits the growth of HeLa cells. IUBMB Life. 2009;61:1075–82.
Peng RQ, Wan HY, Li HF, Liu M, Li X, Tang H. MicroRNA-214 suppresses growth and invasiveness of cervical cancer cells by targeting UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 7. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:14301–9.
Xu Z, Wang T. miR-214 promotes the proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells through direct suppression of LZTS1. Bioch Biophy Res Comm. 2014;449:190–5.
Deng M, Ye Q, Qin Z, Zheng Y, He W, Tang H, et al. MiR-214 promotes tumorigenesis by targeting lactotransferrin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2013;34:1793–800.
Yang TS, Yang XH, Wang XD, Wang YL, Zhou B, Song ZS. MiR-214 regulate gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting PTEN. Cancer Cell Int. 2013;13:68.
Zhang LL, Guo YJ, Zhao CN, Gao JY. Effects and mechanism of miR-214 on hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2015;42:392–8.
Yang H, Kong W, He L, Zhao JJ, O’Donnell JD, Wang J, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling in human ovarian cancer: miR-214 induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN. Cancer Res. 2008;68:425–33.
Negishi M, Oinuma I, Katoh H. Plexins: axon guidance and signal transduction. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005;62:1363–71.
Neufeld G, Kessler O. The semaphorins: versatile regulators of tumour progression and tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:632–45.
Roth L, Koncina E, Satkauskas S, Cremel G, Aunis D, Bagnard D. The many faces of semaphorins: from development to pathology. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009;66:649–66.
Rehman M, Tamagnone L. Semaphorins in cancer: biological mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2013;24:179–89.
Basile JR, Castilho RM, Williams VP, Gutkind JS. Semaphorin 4D provides a link between axon guidance processes and tumor-induced angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:9017–22.
Worzfeld T, Ofermanns S. Semaphorins and plexins as therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Drug DiscoVR. 2014;13:603–21.
Qiang R, Wang F, Shi LY, Liu M, Chen S, Wan HY, et al. Plexin-B1 is a target of miR-214 in cervical cancer and promotes the growth and invasion of HeLa cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011;43:632–41.
Li B, Han Q, Zhu Y, Yu Y, Wang J, Jiang X. Down-regulation of miR-214 contributes to intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma metastasis by targeting Twist. FEBS J. 2012;279:2393–8.
Shih TC, Tien YJ, Wen CJ, Yeh TS, Yu MC, Huang CH, et al. MicroRNA-214 downregulation contributes to tumor angiogenesis by inducing secretion of the hepatoma-derived growth factor in human hepatoma. J Hepatol. 2012;57:584–91.
Chen DL, Wang ZQ, Zeng ZL, Wu WJ, Zhang DS, Luo HY, et al. Identification of miR-214 as a negative regulator of colorectal cancer liver metastasis via regulation of FGFR1 expression. Hepatology. 2014;60:598–609.
Jarvis WD, Fornari Jr FA, Traylor RS, Martin HA, Kramer LB, Erukulla RK, et al. Induction of apoptosis and potentiation of ceramide-mediated cytotoxicity by sphingolipid bases in human myeloid leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:8275–84.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially sponsored by Key Project of Educational Department in Yunnan Province (Nos. 2014Z075 and 2015Z081).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Yang Liu and Honglin Zhou contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Zhou, H., Ma, L. et al. MiR-214 suppressed ovarian cancer and negatively regulated semaphorin 4D. Tumor Biol. 37, 8239–8248 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4708-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4708-0