Abstract
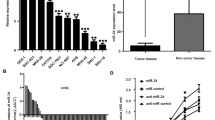
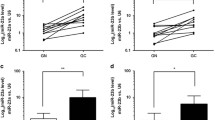
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding RNAs that modulate development, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. The deregulated expression of microRNAs is found in carcinogenesis including gastric cancer (GC). In this study, we showed that the expression levels of miR-488 were downregulated in GC tissues compared to in non-tumor tissues. In addition, the expression of miR-488 was also lower in GC cell lines in contrast with the gastric epithelial cell line (GES). In addition, the expression level of miR-488 was negatively correlated with the TNM stage in GC patients, and lower miR-488 expression was found in tumors with advanced TNM stage. The ectopic expression of miR-488 suppressed the GC cell proliferation, cell cycle, colony information, and migration. PAX6 was identified as a direct target gene of miR-488 in HGC-27. Moreover, we found that the expression level of PAX6 was upregulated in the GC tissues compared with the non-tumor tissues. The PAX6 expression level was correlated with the cancer TNM stage, and higher PAX6 expression was found in tumors with advanced TNM stage. Furthermore, there was an inverse correlation between PAX6 and miR-488 expression levels in GC tissues. Therefore, these studies demonstrated that miR-488 might act as a tumor suppressor miRNA in the development of GC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu A, Xia J, Zuo J, Jin S, Zhou H, Yao L, et al. Microrna-148a is silenced by hypermethylation and interacts with DNA methyltransferase 1 in gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 2012;29:2701–9.
Zheng Y, Cui L, Sun W, Zhou H, Yuan X, Huo M, et al. Microrna-21 is a new marker of circulating tumor cells in gastric cancer patients. Cancer Biomark: Section A Dis Markers. 2011;10:71–7.
Wu Y, Tao Y, Chen Y, Xu W. Rhoc regulates the proliferation of gastric cancer cells through interaction with iqgap1. PLoS One. 2012;7, e48917.
Tsai KW, Hu LY, Wu CW, Li SC, Lai CH, Kao HW, et al. Epigenetic regulation of mir-196b expression in gastric cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2010;49:969–80.
Calcagno DQ, de Arruda Cardoso Smith M, Burbano RR. Cancer type-specific epigenetic changes: gastric cancer. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1238:79–101.
Liang J, Liu X, Xue H, Qiu B, Wei B, Sun K. Microrna-103a inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting c-myb. Cell Prolif. 2015;48:78–85.
Bin Z, Dedong H, Xiangjie F, Hongwei X, Qinghui Y. The microrna-367 inhibits the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by directly repressing rab23. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2015;19:69–74.
Zhang D, Xiao YF, Zhang JW, Xie R, Hu CJ, Tang B, et al. Mir-1182 attenuates gastric cancer proliferation and metastasis by targeting the open reading frame of htert. Cancer Lett. 2015;360:151–9.
Wang GJ, Liu GH, Ye YW, Fu Y, Zhang XF. The role of microrna-1274a in the tumorigenesis of gastric cancer: accelerating cancer cell proliferation and migration via directly targeting foxo4. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2015.
Shen J, Niu W, Zhou M, Zhang H, Ma J, Wang L. Microrna-410 suppresses migration and invasion by targeting mdm2 in gastric cancer. PLoS One. 2014;9, e104510.
Li R, Yuan W, Mei W, Yang K, Chen Z. Microrna 520d-3p inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by downregulating epha2 expression. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;396:295–305.
Fu Z, Qian F, Yang X, Jiang H, Chen Y, Liu S. Circulating mir-222 in plasma and its potential diagnostic and prognostic value in gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 2014;31:164.
Shin VY, Chu KM. Mirna as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:10432–9.
Liu HS, Xiao HS. Micrornas as potential biomarkers for gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:12007–17.
Yu X, Li Z, Yu J, Chan MT, Wu WK. Micrornas predict and modulate responses to chemotherapy in colorectal cancer. Cell Prolif. 2015;48:503–10.
Li Z, Yu X, Shen J, Liu Y, Chan MT, Wu WK. Microrna dysregulation in rhabdomyosarcoma: a new player enters the game. Cell Prolif. 2015;48:511–6.
Yu X, Li Z, Shen J, Wu WK, Liang J, Weng X, et al. Microrna-10b promotes nucleus pulposus cell proliferation through rhoc-akt pathway by targeting hoxd10 in intervetebral disc degeneration. PLoS One. 2013;8, e83080.
Yang Z, Han Y, Cheng K, Zhang G, Wang X. Mir-99a directly targets the mtor signalling pathway in breast cancer side population cells. Cell Prolif. 2014;47:587–95.
Bier A, Giladi N, Kronfeld N, Lee HK, Cazacu S, Finniss S, et al. Microrna-137 is downregulated in glioblastoma and inhibits the stemness of glioma stem cells by targeting rtvp-1. Oncotarget. 2013;4:665–76.
Lee HK, Finniss S, Cazacu S, Bucris E, Ziv-Av A, Xiang C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells deliver synthetic microrna mimics to glioma cells and glioma stem cells and inhibit their cell migration and self-renewal. Oncotarget. 2013;4:346–61.
Wang Z, Wang N, Liu P, Chen Q, Situ H, Xie T, Zhang J, Peng C, Lin Y, Chen J. Microrna-25 regulates chemoresistance-associated autophagy in breast cancer cells, a process modulated by the natural autophagy inducer isoliquiritigenin. Oncotarget. 2014.
Fu LL, Yang Y, Xu HL, Cheng Y, Wen X, Ouyang L, et al. Identification of novel caspase/autophagy-related gene switch to cell fate decisions in breast cancers. Cell Prolif. 2013;46:67–75.
Xiao Z, Li CH, Chan SL, Xu F, Feng L, Wang Y, Jiang JD, Sung JJ, Cheng CH, Chen Y. A small molecule modulator of the tumor suppressor mirna-34a inhibits the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2014.
Song Q, Xu Y, Yang C, Chen Z, Jia C, Chen J, et al. Mir-483-5p promotes invasion and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting rhogdi1 and alcam. Cancer Res. 2014;74:3031–42.
Li Z, Yu X, Shen J, Wu WK, Chan MT. Microrna expression and its clinical implications in Ewing’s sarcoma. Cell Prolif. 2015;48:1–6.
Chow TF, Mankaruos M, Scorilas A, Youssef Y, Girgis A, Mossad S, et al. The mir-17-92 cluster is over expressed in and has an oncogenic effect on renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2010;183:743–51.
Chakravarthi BV, Pathi SS, Goswami MT, Cieslik M, Zheng H, Nallasivam S, et al. The mir-124-prolyl hydroxylase p4ha1-mmp1 axis plays a critical role in prostate cancer progression. Oncotarget. 2014;5:6654–69.
Li Z, Lei H, Luo M, Wang Y, Dong L, Ma Y, et al. DNA methylation downregulated mir-10b acts as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer: Off J Int Gastric Cancer Assoc Jpn Gastric Cancer Assoc. 2015;18:43–54.
Li Z, Yu X, Wang Y, Shen J, Wu WK, Liang J, et al. By downregulating tiam1 expression, microrna-329 suppresses gastric cancer invasion and growth. Oncotarget. 2015;6:17559–69.
Perilli L, Vicentini C, Agostini M, Pizzini S, Pizzi M, D’Angelo E, et al. Circulating mir-182 is a biomarker of colorectal adenocarcinoma progression. Oncotarget. 2014;5:6611–9.
Huang J, Zhang SY, Gao YM, Liu YF, Liu YB, Zhao ZG, et al. Micrornas as oncogenes or tumour suppressors in oesophageal cancer: potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Cell Prolif. 2014;47:277–86.
Li M, Yu M, Liu C, Zhu H, He X, Peng S, et al. Mir-34c works downstream of p53 leading to dairy goat male germline stem-cell (mgscs) apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 2013;46:223–31.
Muinos-Gimeno M, Espinosa-Parrilla Y, Guidi M, Kagerbauer B, Sipila T, Maron E, et al. Human micrornas mir-22, mir-138-2, mir-148a, and mir-488 are associated with panic disorder and regulate several anxiety candidate genes and related pathways. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;69:526–33.
Patnaik SK, Kannisto E, Knudsen S, Yendamuri S. Evaluation of microrna expression profiles that may predict recurrence of localized stage I non-small cell lung cancer after surgical resection. Cancer Res. 2010;70:36–45.
Tong HX, Zhou YH, Hou YY, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Xie B, et al. Expression profile of micrornas in gastrointestinal stromal tumors revealed by high throughput quantitative rt-pcr microarray. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:5843–55.
Liu Y, Guo R, Hao G, Xiao J, Bao Y, Zhou J, et al. The expression profiling and ontology analysis of noncoding rnas in peritoneal fibrosis induced by peritoneal dialysis fluid. Gene. 2015;564:210–9.
de Cubas AA, Leandro-Garcia LJ, Schiavi F, Mancikova V, Comino-Mendez I, Inglada-Perez L, et al. Integrative analysis of mirna and mrna expression profiles in pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma identifies genotype-specific markers and potentially regulated pathways. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2013;20:477–93.
Sikand K, Slaibi JE, Singh R, Slane SD, Shukla GC. Mir 488* inhibits androgen receptor expression in prostate carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 2011;129:810–9.
Song J, Kim D, Lee CH, Lee MS, Chun CH, Jin EJ. Microrna-488 regulates zinc transporter slc39a8/zip8 during pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. J Biomed Sci. 2013;20:31.
Mishra S, Maurya SK, Srivastava K, Shukla S, Mishra R. Pax6 influences expression patterns of genes involved in neuro- degeneration. Ann Neurosci. 2015;22:226–31.
Thomas MG, Welch C, Stone L, Allan P, Barker RA, White RB. Pax6 expression may be protective against dopaminergic cell loss in Parkinson’s disease. CNS & neurological disorders drug targets. 2015.
Manuel MN, Mi D, Mason JO, Price DJ. Regulation of cerebral cortical neurogenesis by the pax6 transcription factor. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015;9:70.
Huettl RE, Eckstein S, Stahl T, Petricca S, Ninkovic J, Gotz M, Huber AB. Functional dissection of the pax6 paired domain: roles in neural tube patterning and peripheral nervous system development. Dev Biol. 2015.
Lai JP, Mertens RB, Mirocha J, Koo J, Venturina M, Chung F, et al. Comparison of pax6 and pax8 as immunohistochemical markers for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Endocr Pathol. 2015;26:54–62.
Shubham K, Mishra R. Pax6 interacts with sparc and tgf-beta in murine eyes. Mol Vis. 2012;18:951–6.
Bai SW, Li B, Zhang H, Jonas JB, Zhao BW, Shen L, et al. Pax6 regulates proliferation and apoptosis of human retinoblastoma cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:4560–70.
van Bever Y, van Hest L, Wolfs R, Tibboel D, van den Hoonaard TL, Gischler SJ. Exclusion of a pax6, foxc1, pitx2, and mycn mutation in another patient with apple peel intestinal atresia, ocular anomalies and microcephaly and review of the literature. Am J Med Genet A. 2008;146A:500–4.
Meng Y, Zou Q, Liu T, Cai X, Huang Y, Pan J. Microrna-335 inhibits proliferation, cell-cycle progression, colony formation, and invasion via targeting pax6 in breast cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11:379–85.
Shahi MH, Afzal M, Sinha S, Eberhart CG, Rey JA, Fan X, et al. Regulation of sonic hedgehog-gli1 downstream target genes ptch1, cyclin d2, plakoglobin, pax6 and nkx2.2 and their epigenetic status in medulloblastoma and astrocytoma. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:614.
Zhao X, Yue W, Zhang L, Ma L, Jia W, Qian Z, et al. Downregulation of pax6 by shrna inhibits proliferation and cell cycle progression of human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. PLoS One. 2014;9, e85738.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Lu, G., Ke, X. et al. miR-488 acts as a tumor suppressor gene in gastric cancer. Tumor Biol. 37, 8691–8698 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4645-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4645-y