Abstract
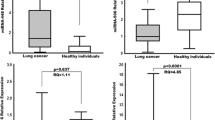
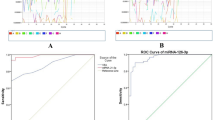
Circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) are potential noninvasive biomarkers for cancer detection. We used preoperative serum samples from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients and healthy controls to investigate whether serum levels of candidate miRNAs could be used as diagnostic biomarkers in patients with resectable NSCLC and whether they were associated with clinicopathologic characteristics. We initially detected expression of 12 miRNAs using quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) in preoperative serum samples of 94 NSCLC patients and 58 healthy controls. We further validated our results using the fluorescence quantum dots liquid bead array for differentially expressed miRNAs in serum samples of 70 NSCLC patients and 54 healthy controls. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed to select the best diagnostic miRNA cutoff value. A predictive model of miRNAs for NSCLC was derived by multivariate logistic regression. We found that five serum miRNAs (miR-16-5p, miR-17b-5p, miR-19-3p, miR-20a-5p, and miR-92-3p) were significantly downregulated in NSCLC, while miR-15b-5p was significantly upregulated (p < 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that miR-15b-5p, miR-16-5p, and miR-20a-5p expression were independent diagnostic factors for the identification of patients with NSCLC after adjustment for patient’s age and sex. In addition, the expression of serum miR-106-5p was higher in stage I than in stages IIa–IIIb, and no significant association was observed between expression of miRNAs and other variables including pathological type, tumor size, and lymph nodes status. Six serum miRNAs could potentially serve as noninvasive diagnostic biomarkers for resectable NSCLC. The predictive model combining miR-15b-5p, miR-16-5p, and miR-20a-5p was the best diagnostic approach.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crino L, Weder W, van Meerbeeck J, Felip E. Early stage and locally advanced (non-metastatic) non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2010;21 Suppl 5:v103–15. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdq207.
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA: A Cancer J Clinicians. 2011;61(2):69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107.
Howlader NN A, Krapcho M, Neyman N, Aminou, R, Waldron W. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2009 (Vintage 2009 Populations) based on November 2011 SEER data submission. Nat Cancer Inst 2012
Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, Black WC, Clapp JD, Fagerstrom RM, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(5):395–409. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1102873.
Yilmaz F, Tastekin G. Sensitivity of (18)F-FDG PET in evaluation of solitary pulmonary nodules. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(1):45–51.
Imdahl A, Jenkner S, Brink I, Nitzsche E, Stoelben E, Moser E, et al. Validation of FDG positron emission tomography for differentiation of unknown pulmonary lesions. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg: Off J Eur Assoc Card-Thorac Surg. 2001;20(2):324–9.
Foa P, Fornier M, Miceli R, Seregni E, Santambrogio L, Nosotti M, et al. Tumour markers CEA, NSE, SCC, TPA and CYFRA 21.1 in resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 1999;19(4C):3613–8.
Blankenburg F, Hatz R, Nagel D, Ankerst D, Reinmiedl J, Gruber C, et al. Preoperative CYFRA 21–1 and CEA as prognostic factors in patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer: external validation of a prognostic score. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med. 2008;29(4):272–7. doi:10.1159/000152945.
Reinmuth N, Brandt B, Semik M, Kunze WP, Achatzy R, Scheld HH, et al. Prognostic impact of Cyfra21-1 and other serum markers in completely resected non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer (Amsterdam, Netherlands). 2002;36(3):265–70.
Grunnet M, Sorensen JB. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) as tumor marker in lung cancer. Lung Cancer (Amsterdam, Netherlands). 2012;76(2):138–43. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2011.11.012.
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K, et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008;18(10):997–1006. doi:10.1038/cr.2008.282.
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(30):10513–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.0804549105.
Turchinovich A, Weiz L, Langheinz A, Burwinkel B. Characterization of extracellular circulating microRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39(16):7223–33. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr254.
Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Hirajima S, Kawaguchi T, Miyamae M, Okajima W, et al. Plasma microRNA profiles: identification of miR-25 as a novel diagnostic and monitoring biomarker in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2014;111(8):1614–24. doi:10.1038/bjc.2014.451.
Joosse SA, Muller V, Steinbach B, Pantel K, Schwarzenbach H. Circulating cell-free cancer-testis MAGE-A RNA, BORIS RNA, let-7b and miR-202 in the blood of patients with breast cancer and benign breast diseases. Br J Cancer. 2014;111(5):909–17. doi:10.1038/bjc.2014.360.
Madhavan D, Cuk K, Burwinkel B, Yang R. Cancer diagnosis and prognosis decoded by blood-based circulating microRNA signatures. Front Genet. 2013;4:116. doi:10.3389/fgene.2013.00116.
Foss KM, Sima C, Ugolini D, Neri M, Allen KE, Weiss GJ. miR-1254 and miR-574-5p: serum-based microRNA biomarkers for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol: Off Public Int Ass Study Of Lung Cancer. 2011;6(3):482–8. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e318208c785.
Wozniak MB, Scelo G, Muller DC, Mukeria A, Zaridze D, Brennan P. Circulating microRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers for early detection of non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0125026. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0125026.
Shi R, Chiang VL. Facile means for quantifying microRNA expression by real-time PCR. BioTechniques. 2005;39(4):519–25.
Varallyay E, Burgyan J, Havelda Z. MicroRNA detection by northern blotting using locked nucleic acid probes. Nat Protoc. 2008;3(2):190–6. doi:10.1038/nprot.2007.528.
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, Castle J, et al. Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature. 2005;433(7027):769–73. doi:10.1038/nature03315.
Su S, Fan J, Xue B, Yuwen L, Liu X, Pan D, et al. DNA-conjugated quantum dot nanoprobe for high-sensitivity fluorescent detection of DNA and micro-RNA. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(2):1152–7. doi:10.1021/am404811j.
Ruopp MD, Perkins NJ, Whitcomb BW, Schisterman EF. Youden index and optimal cut-point estimated from observations affected by a lower limit of detection. Biom J. 2008;50(3):419–30. doi:10.1002/bimj.200710415.
Chen X, Hu Z, Wang W, Ba Y, Ma L, Zhang C, et al. Identification of ten serum microRNAs from a genome-wide serum microRNA expression profile as novel noninvasive biomarkers for nonsmall cell lung cancer diagnosis. Int J Cancer J Int Du Cancer. 2012;130(7):1620–8. doi:10.1002/ijc.26177.
Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11(9):597–610. doi:10.1038/nrg2843.
Wang S, Xiang J, Li Z, Lu S, Hu J, Gao X, et al. A plasma microRNA panel for early detection of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer J Int Du Cancer. 2015;136(1):152–61. doi:10.1002/ijc.28136.
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(11):857–66. doi:10.1038/nrc1997.
Allegra A, Alonci A, Campo S, Penna G, Petrungaro A, Gerace D, et al. Circulating microRNAs: new biomarkers in diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of cancer (review). Int J Oncol. 2012;41(6):1897–912. doi:10.3892/ijo.2012.1647.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(7):2257–61. doi:10.1073/pnas.0510565103.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435(7043):834–8. doi:10.1038/nature03702.
Bianchi F, Nicassio F, Marzi M, Belloni E, Dall'olio V, Bernard L, et al. A serum circulating miRNA diagnostic test to identify asymptomatic high-risk individuals with early stage lung cancer. EMBO Mol Med. 2011;3(8):495–503. doi:10.1002/emmm.201100154.
Montani F, Marzi MJ, Dezi F, Dama E, Carletti RM, Bonizzi G, et al. miR-test: a blood test for lung cancer early detection. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015;107(6):djv063. doi:10.1093/jnci/djv063.
Boeri M, Verri C, Conte D, Roz L, Modena P, Facchinetti F, et al. MicroRNA signatures in tissues and plasma predict development and prognosis of computed tomography detected lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(9):3713–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.1100048108.
Sun J, Gao B, Zhou M, Wang ZZ, Zhang F, Deng JE, et al. Comparative genomic analysis reveals evolutionary characteristics and patterns of microRNA clusters in vertebrates. Gene. 2013;512(2):383–91. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2012.09.102.
Hayashita Y, Osada H, Tatematsu Y, Yamada H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, et al. A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005;65(21):9628–32. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2352.
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee DH, Nguyen JT, et al. Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33(20):e179. doi:10.1093/nar/gni178.
Bailey VJ, Puleo CM, Ho YP, Yeh HC, Wang TH. Quantum dots in molecular detection of disease. Conf Proc: Ann Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc Ann Conf. 2009;2009:4089–92. doi:10.1109/iembs.2009.5334553.
Hur K, Toiyama Y, Schetter AJ, Okugawa Y, Harris CC, Boland CR et al. Identification of a metastasis-specific MicroRNA signature in human colorectal cancer. J Nat Cancer Inst. 2015;107(3). doi:10.1093/jnci/dju492.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81473469).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital, and written informed consent was obtained from each patient.
Conflicts of interest
None
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81473469).
Additional information
Lihong Fan and Huiwei Qi contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, L., Qi, H., Teng, J. et al. Identification of serum miRNAs by nano-quantum dots microarray as diagnostic biomarkers for early detection of non-small cell lung cancer. Tumor Biol. 37, 7777–7784 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4608-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4608-3