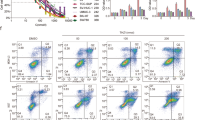
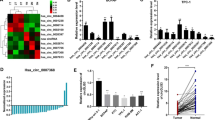
Abstract
Accumulating data suggest that micro RNAs (miRNAs) or double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) can activate gene expression by targeting promoters. The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 CIP1/WAF1 (p21) has also been shown to suppress epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) which plays a crucial role in the early stage of tumor metastases and invasiveness. In a previous study, we have reported that miR-370-5p is low-expressed in bladder cancer (BCa) tissues and cell lines. Here, we identified that miR-370-5p and sequence homology dsRNA (dsP21-555) fully complementary to promoter hold the potent abilities to induce p21 expression. Moreover, transfection of miR-370-5p or dsP21-555 into BCa cells remarkably inverts EMT-associated genes (increases epithelial cell makers E-cadherin and β-catenin, and decreases mesenchymal cell markers ZEB1 and Vimentin) expression mainly via regulating p21 expression. Besides, through manipulating p21, both the candidates can retard BCa cell migration and invasion. In summary, our results provide evidence that both endogenous and exogenous small RNAs may function to induce p21 expression by interacting with the similar promoter region and impede BCa metastasis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer J Int Du cancer. 2010;127:2893–917.
Burger M, Catto JW, Dalbagni G, Grossman HB, Herr H, Karakiewicz P, et al. Epidemiology and risk factors of urothelial bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2013;63:234–41.
Kaufman DS, Shipley WU, Feldman AS. Bladder cancer. Lancet. 2009;374:239–49.
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29.
Warfel NA, El-Deiry WS. p21waf1 and tumourigenesis: 20 years after. Curr Opin Oncol. 2013;25:52–8.
McConkey DJ, Choi W, Marquis L, Martin F, Williams MB, Shah J, et al. Role of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in drug sensitivity and metastasis in bladder cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009;28:335–44.
Gavert N, Ben-Ze'ev A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the invasive potential of tumors. Trends Mol Med. 2008;14:199–209.
Katsuno Y, Lamouille S, Derynck R. Tgf-β signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer progression. Curr Opin Oncol. 2013;25:76–84.
Li LC, Okino ST, Zhao H, Pookot D, Place RF, Urakami S, et al. Small dsRNAs induce transcriptional activation in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:17337–42.
Place RF, Li LC, Pookot D, Noonan EJ, Dahiya R. MicroRNA-373 induces expression of genes with complementary promoter sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:1608–13.
Kang MR, Yang G, Place RF, Charisse K, Epstein-Barash H, Manoharan M, et al. Intravesical delivery of small activating RNA formulated into lipid nanoparticles inhibits orthotopic bladder tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2012;72:5069–79.
Kosaka M, Kang MR, Yang G, Li LC. Targeted p21WAF1/CIP1 activation by RNAa inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2012;22:335–43.
Wei J, Zhao J, Long M, Han Y, Wang X, Lin F, et al. p21WAF1/CIP1 gene transcriptional activation exerts cell growth inhibition and enhances chemosensitivity to cisplatin in lung carcinoma cell. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:632.
Junxia W, Ping G, Yuan H, Lijun Z, Jihong R, Fang L, et al. Double strand RNA-guided endogeneous E-cadherin up-regulation induces the apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of breast carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Sci. 2010;101:1790–6.
Wang C, Chen Z, Ge Q, Hu J, Li F, Hu J, et al. Upregulation of p21 by miRNAs and its implications in bladder cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2014;588:4654–64.
Miyazaki M, Sakaguchi M, Akiyama I, Sakaguchi Y, Nagamori S, Huh NH. Involvement of interferon regulatory factor 1 and S100C/A11 in growth inhibition by transforming growth factor β1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64:4155–61.
Huang V, Qin Y, Wang J, Wang XL, Place RF, Lin GT, et al. RNAa is conserved in mammalian cells. PLoS One. 2010;5.
Li Q, Li J, Wen T, Zeng W, Peng C, Yan S, et al. Overexpression of HMGB1 in melanoma predicts patient survival and suppression of HMGB1 induces cell cycle arrest and senescence in association with p21 (WAF1/CIP1) up-regulation via a p53-independent, Sp1-dependent pathway. Oncotarget. 2014;5:6387–403.
McConkey DJ, Lee S, Choi W, Tran M, Majewski T, Lee S, et al. Molecular genetics of bladder cancer: emerging mechanisms of tumor initiation and progression. Urol Oncol. 2010;28:429–40.
Liu M, Casimiro MC, Wang C, Shirley LA, Jiao X, Katiyar S, et al. P21CIP1 attenuates Ras- and c-myc-dependent breast tumor epithelial mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell-like gene expression in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:19035–9.
Li XL, Hara T, Choi YG, Subramanian M, Francis P, Bilke S, et al. A p21-ZEB1 complex inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the microRNA 183-96-182 cluster. Mol Cell Biol. 2014;34:533–50.
Behnsawy HM, Miyake H, Abdalla MA, Sayed MA, Ahmed AEFI, Fujisawa M. Expression of cell cycle-associated proteins in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: correlation with Intravesical recurrence following transurethral resection. Urol Oncol-Semin Ori. 2011;29:495–501.
Tang K, Wang C, Chen Z, Xu H, Ye Z. Clinicopathologic and prognostic significance of p21 (Cip1/Waf1) expression in bladder cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:4999–5007.
Tiguert R, Lessard A, So A, Fradet Y. Prognostic markers in muscle invasive bladder cancer. World J Urol. 2002;20:190–5.
Stein JP, Ginsberg DA, Grossfeld GD, Chatterjee SJ, Esrig D, Dickinson MG, et al. Effect of p21WAF1/CIP1 expression on tumor progression in bladder cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998;90:1072–9.
Place RF, Wang J, Noonan EJ, Meyers R, Manoharan M, Charisse K, et al. Formulation of small activating RNA into lipidoid nanoparticles inhibits xenograft prostate tumor growth by inducing p21 expression. Mol Ther-Nucl Acids. 2012;1.
Portnoy V, Huang V, Place RF, Li LC. Small RNA and transcriptional upregulation. Wires Rna. 2011;2:748–60.
Janowski BA, Younger ST, Hardy DB, Ram R, Huffman KE, Corey DR. Activating gene expression in mammalian cells with promoter-targeted duplex RNAs. Nat Chem Biol. 2007;3:166–73.
Place RF, Noonan EJ, Foldes-Papp Z, Li LC. Defining features and exploring chemical modifications to manipulate RNAa activity. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2010;11:518–26.
Zheng L, Wang L, Gan J, Zhang H. RNA activation: promise as a new weapon against cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014;355:18–24.
Turunen MP, Lehtola T, Heinonen SE, Assefa GS, Korpisalo P, Girnary R, et al. Efficient regulation of VEGF expression by promoter-targeted lentiviral shRNAs based on epigenetic mechanism: a novel example of epigenetherapy. Circ Res. 2009;105:604–9.
Reynolds A, Leake D, Boese Q, Scaringe S, Marshall WS, Khvorova A. Rational siRNA design for RNA interference. Nat Biotechnol. 2004;22:326–30.
Wang J, Place RF, Huang V, Wang X, Noonan EJ, Magyar CE, et al. Prognostic value and function of KLF4 in prostate cancer: RNAa and vector-mediated overexpression identify KLF4 as an inhibitor of tumor cell growth and migration. Cancer Res. 2010;70:10182–91.
Saito T, Saetrom P. MicroRNAs—targeting and target prediction. New Biotechnol. 2010;27:243–9.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number 81372759, China]. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Chenghe Wang and Qiangqiang Ge contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Ge, Q., Chen, Z. et al. Promoter-associated endogenous and exogenous small RNAs suppress human bladder cancer cell metastasis by activating p21 CIP1/WAF1 expression. Tumor Biol. 37, 6589–6598 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4571-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4571-z