Abstract
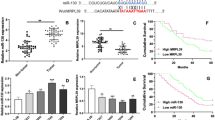
We examined the expression pattern and functional roles of microRNA 15a-5p (miR-15a-5p) in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Possible miR-15a-5p aberrant expression in HCC cell lines or clinical HCC specimens was examined by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). In HCC HepG2 and SNU-182 cells, miR-15a-5p was ectopically overexpressed by lentiviral transduction. Its effect on HCC proliferation, cancer division, and in vivo tumor growth were examined by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, cell cycle assay, and tumorigenicity assay, respectively. The targeting of miR-15a-5p on its downstream gene, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), was examined by dual-luciferase assay, qRT-PCR, and Western blot, respectively. BDNF was then overexpressed in HepG2 and SNU-182 cells to evaluate its selective effect on miR-15a-5p in HCC modulation. MiR-15a-5p is aberrantly downregulated in in vitro HCC cell lines and in vivo HCC clinical specimens. Ectopic overexpression of miR-15a-5p suppressed cancer proliferation, induced cell cycle arrest in HepG2 or SNU-182 cells in vitro, and inhibited HCC tumor growth in vivo. MiR-15a-5p selectively and negatively regulated BDNF at both gene and protein levels in HCC cells. Forced overexpression of BDNF effectively reversed the tumor suppressive functions of miR-15a-5p on HCC proliferation and cell division in vitro. Our study demonstrated that miR-15a-5p is a tumor suppressor in HCC and its regulation is through BDNF in HCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bosetti C, Turati F, La Vecchia C. Hepatocellular carcinoma epidemiology. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2014;28:753–70.
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29.
Germano D, Daniele B. Systemic therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma: current status and future perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:3087–99.
Bronte F, Bronte G, Cusenza S, Fiorentino E, Rolfo C, Cicero G, et al. Targeted therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Med Chem. 2014;21:966–74.
Nilsen TW. Mechanisms of microRNA-mediated gene regulation in animal cells. Trends Genet. 2007;23:243–9.
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP, Anderson TA. MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 2007;302:1–12.
Li Y, Tan W, Neo TW, Aung MO, Wasser S, Lim SG, et al. Role of the miR-106b-25 microRNA cluster in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2009;100:1234–42.
Tsai WC, Hsu PW, Lai TC, Chau GY, Lin CW, Chen CM, et al. MicroRNA-122, a tumor suppressor microRNA that regulates intrahepatic metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2009;49:1571–82.
Zheng F, Liao YJ, Cai MY, Liu YH, Liu TH, Chen SP, et al. The putative tumour suppressor microRNA-124 modulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell aggressiveness by repressing ROCK2 and EZH2. Gut. 2012;61:278–89.
Su H, Yang JR, Xu T, Huang J, Xu L, Yuan Y, et al. MicroRNA-101, down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, promotes apoptosis and suppresses tumorigenicity. Cancer Res. 2009;69:1135–42.
Druz A, Chen YC, Guha R, Betenbaugh M, Martin SE, Shiloach J. Large-scale screening identifies a novel microRNA, miR-15a-3p, which induces apoptosis in human cancer cell lines. RNA Biol. 2013;10:287–300.
Bonci D, Coppola V, Musumeci M, Addario A, Giuffrida R, Memeo L, et al. The miR-15a-miR-16-1 cluster controls prostate cancer by targeting multiple oncogenic activities. Nat Med. 2008;14:1271–7.
McAllister AK. Neurotrophins and neuronal differentiation in the central nervous system. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001;58:1054–60.
Cao L, Liu X, Lin EJ, Wang C, Choi EY, Riban V, et al. Environmental and genetic activation of a brain-adipocyte BDNF/leptin axis causes cancer remission and inhibition. Cell. 2010;142:52–64.
Kaplan DR, Matsumoto K, Lucarelli E, Thiele CJ. Induction of TrkB by retinoic acid mediates biologic responsiveness to BDNF and differentiation of human neuroblastoma cells. Eukaryotic Signal Transduction Group. Neuron. 1993;11:321–31.
Guo D, Hou X, Zhang H, Sun W, Zhu L, Liang J, et al. More expressions of BDNF and TrkB in multiple hepatocellular carcinoma and anti-BDNF or K252a induced apoptosis, supressed invasion of HepG2 and HCCLM3 cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011;30:97.
Yang N, Ekanem NR, Sakyi CA, Ray SD. Hepatocellular carcinoma and microRNA: new perspectives on therapeutics and diagnostics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;81:62–74.
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M, et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:13944–9.
Bandi N, Zbinden S, Gugger M, Arnold M, Kocher V, Hasan L, et al. miR-15a and miR-16 are implicated in cell cycle regulation in a Rb-dependent manner and are frequently deleted or down-regulated in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2009;69:5553–9.
Aqeilan RI, Calin GA, Croce CM. miR-15a and miR-16-1 in cancer: discovery, function and future perspectives. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17:215–20.
Liu X, McMurphy T, Xiao R, Slater A, Huang W, Cao L. Hypothalamic gene transfer of BDNF inhibits breast cancer progression and metastasis in middle age obese mice. Mol Ther. 2014;22:1275–84.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (2013B021800284) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81272312, 81300421).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Jianting Long and Chunlin Jiang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, J., Jiang, C., Liu, B. et al. MicroRNA-15a-5p suppresses cancer proliferation and division in human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting BDNF. Tumor Biol. 37, 5821–5828 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4427-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4427-6