Abstract
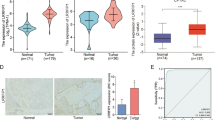
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been shown to play critical roles in the development and progression of diseases. lncRNA activated by transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) (lncRNA-ATB) was discovered as a prognostic factor in hepatocellular carcinoma, gastric cancer, and colorectal cancer. However, little is known about the role of lncRNA-ATB in pancreatic cancer. This study aimed to assess lncRNA-ATB expression in pancreatic cancer and explore its role in pancreatic cancer pathogenesis. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was performed to detect lncRNA-ATB expression in 150 pancreatic cancer tissues and five pancreatic cancer cell lines compared to paired adjacent normal tissues and normal human pancreatic ductal epithelial cell line HPDE6c-7. The correlations between lncRNA-ATB expression and clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis were also analyzed. We found that lncRNA-ATB expression was decreased in pancreatic cancer tissues and pancreatic cancer cell lines. Low lncRNA-ATB expression levels were significantly correlated with lymph node metastases (yes vs. no, P = 0.009), neural invasion (positive vs. negative, P = 0.049), and clinical stage (early stage vs. advanced stage, P = 0.014). Moreover, patients with low lncRNA-ATB expression levels exhibited markedly worse overall survival prognoses (P < 0.001). Multivariate analysis indicated that decreased lncRNA-ATB expression was an independent predictor of poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer patients (P = 0.005). In conclusion, lncRNA-ATB may play a critical role in pancreatic cancer progression and prognosis and may serve as a potential prognostic biomarker in pancreatic cancer patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(1):5–29. doi:10.3322/caac.21254.
Ryan DP, Hong TS, Bardeesy N. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(22):2140–1. doi:10.1056/NEJMc1412266.
Vincent A, Herman J, Schulick R, Hruban RH, Goggins M. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2011;378(9791):607–20. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62307-0.
Hartwig W, Werner J, Jäger D, Debus J, Büchler MW. Improvement of surgical results for pancreatic cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(11):e476–85. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70172-4.
Ponting CP, Oliver PL, Reik W. Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2009;136(4):629–41. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.006.
Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, Yao Y, Song Y. Long non-coding RNAs: a new frontier in the study of human diseases. Cancer Lett. 2013;339(2):159–66. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2013.06.013.
Xu SP, Zhang JF, Sui SY, Bai NX, Gao S, Zhang GW, et al. Down regulation of the long noncoding RNA EGOT correlates with malignant status and poor prognosis in breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3746-y.
Huarte M, Rinn JL. Large non-coding RNAs: missing links in cancer? Hum Mol Genet. 2010;19(R2):R152–61. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddq353.
Li J, Liu D, Hua R, Zhang J, Liu W, Huo Y, et al. Long non-coding RNAs expressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and lncRNA BC008363 an independent prognostic factor in PDAC. Pancreatology. 2014;14(5):385–90. doi:10.1016/j.pan.2014.07.013.
Sun YW, Chen YF, Li J, Huo YM, Liu DJ, Hua R, et al. A novel long non-coding RNA ENST00000480739 suppresses tumour cell invasion by regulating OS-9 and HIF-1α in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2014;111(11):2131–41. doi:10.1038/bjc.2014.520.
Ma C, Nong K, Zhu H, Wang W, Huang X, Yuan Z, et al. H19 promotes pancreatic cancer metastasis by derepressing let-7’s suppression on its target HMGA2-mediated EMT. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(9):9163–9. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2185-5.
Kim K, Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, Johnson G, Frank J, Burghardt R, et al. HOTAIR is a negative prognostic factor and exhibits pro-oncogenic activity in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene. 2013;32(13):1616–25. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.193.
Jiao F, Hu H, Yuan C, Wang L, Jiang W, Jin Z, et al. Elevated expression level of long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 facilitates cell growth, migration and invasion in pancreatic cancer. Oncol Rep. 2014;32(6):2485–92. doi:10.3892/or.2014.3518.
Pang EJ, Yang R, Fu XB, Liu YF. Overexpression of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 is correlated with clinical progression and unfavorable prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(4):2403–7. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2850-8.
Yuan JH, Yang F, Wang F, Ma JZ, Guo YJ, Tao QF, et al. A long noncoding RNA activated by TGF-β promotes the invasion-metastasis cascade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2014;25(5):666–81. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2014.03.010.
Saito T, Kurashige J, Nambara S, Komatsu H, Hirata H, Ueda M, et al. A long non-coding RNA activated by transforming growth factor-β is an independent prognostic marker of gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015. doi:10.1245/s10434-015-4554-8.
Iguchi T, Uchi R, Nambara S, Saito T, Komatsu H, Hirata H, et al. A long noncoding RNA, lncRNA-ATB, is involved in the progression and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2015;35(3):1385–8.
Qu S, Song W, Yang X, Wang J, Zhang R, Zhang Z, et al. Microarray expression profile of circular RNAs in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Genomics Data. 2015;5:385–7.
Esteller M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12(12):861–74. doi:10.1038/nrg3074.
Qu S, Yang X, Li X, Wang J, Gao Y, Shang R, et al. Circular RNA: a new star of noncoding RNAs. Cancer Lett. 2015;365(2):141–8. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2015.06.003.
Kung JT, Colognori D, Lee JT. Long noncoding RNAs: past, present, and future. Genetics. 2013;193(3):651–69. doi:10.1534/genetics.112.146704.
Shi SJ, Wang LJ, Yu B, Li YH, Jin Y, Bai XZ. LncRNA-ATB promotes trastuzumab resistance and invasion-metastasis cascade in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6(13):11652–63.
Yang X, Wang J, Qu S, Zhang H, Ruan B, Gao Y, et al. MicroRNA-200a suppresses metastatic potential of side population cells in human hepatocellular carcinoma by decreasing ZEB2. Oncotarget. 2015;6(10):7918–29.
Lu R, Ji Z, Li X, Qin J, Cui G, Chen J, et al. Tumor suppressive microRNA-200a inhibits renal cell carcinoma development by directly targeting TGFB2. Tumour Biol. 2015 Mar 27. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3355-9.
Xia H, Ng SS, Jiang S, Cheung WK, Sze J, Bian XW, et al. miR-200a-mediated down regulation of ZEB2 and CTNNB1 differentially inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell growth, migration and invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;391(1):535–41. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.11.093.
Liu N, Zhong L, Zeng J, Zhang X, Yang Q, Liao D, et al. Up regulation of microRNA-200a associates with tumor proliferation, CSCs phenotype and chemosensitivity in ovarian cancer. Neoplasma. 2015;62(4):550–9. doi:10.4149/neo_2015_066.
Snowdon J, Zhang X, Childs T, Tron VA, Feilotter H. The microRNA-200 family is upregulated in endometrial carcinoma. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e22828. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022828.
Li A, Omura N, Hong SM, Vincent A, Walter K, Griffith M, et al. Pancreatic cancers epigenetically silence SIP1 and hypomethylate and overexpress miR-200a/200b in association with elevated circulating miR-200a and miR-200b levels. Cancer Res. 2010;70(13):5226–37.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Yan Qiu and Kun Liu (Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery of Xijing Hospital) for collecting the samples and the follow-up information. We thank Xuejun Hu and Zhidong Wang (Fourth Military Medical University) for his help in statistics. We are also grateful for the anonymous reviewers’ constructive comments and suggestions. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81772061) and the Health Public Welfare Industry Special Scientific Research Projects of China (No.201202007).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shibin Qu, Xisheng Yang and Wenjie Song contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, S., Yang, X., Song, W. et al. Downregulation of lncRNA-ATB correlates with clinical progression and unfavorable prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Tumor Biol. 37, 3933–3938 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4252-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4252-y