Abstract
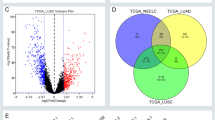
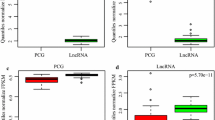
Due to the application of low-dose computed tomography screening, more and more early-stage lung cancers have been diagnosed. Thus, it is essential to characterize the gene expression profile of early-stage lung cancer to develop potential biomarkers for early diagnosis and therapeutic targets. Here, we analyzed microarray data of 181 early-stage lung cancer patients. By comparing gene expression between different tumor and lymph node metastasis stages, we identified various differentially expressed protein-coding genes and long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) in the comparisons of T2 vs. T2 and N1- vs. N0-stage lung cancer. Functional analyses revealed that these differentially expressed genes were enriched in various tumorigenesis or metastasis-related pathways. Survival analysis indicated that two protein-coding genes, C7 and SCN7A, were significantly associated survival of lung cancer. Notably, a novel lncRNA, LINC00313, was highly expressed in both T2- and N1-stage lung cancers. On the other hand, LINC00313 was also upregulated in lung cancer and metastasized lung cancer tissues, compared with adjacent lung tissues and primary lung cancer tissues. Additionally, higher expression level of LINC00313 indicated poor prognosis of lung cancer (hazard ratio = 0.658). Overall, we characterized the expression profiles of protein-coding genes and lncRNA in early-stage lung cancer and found that LINC00313 could be a biomarker for lung cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90.
National Lung Screening Trial Research T, Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, Black WC, Clapp JD, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(5):395–409.
Senthi S, Lagerwaard FJ, Haasbeek CJ, Slotman BJ, Senan S. Patterns of disease recurrence after stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for early stage non-small-cell lung cancer: a retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(8):802–9.
Senan S, Paul MA, Lagerwaard FJ. Treatment of early-stage lung cancer detected by screening: surgery or stereotactic ablative radiotherapy? Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(7):e270–4.
Chang JY, Senan S, Paul MA, Mehran RJ, Louie AV, Balter P, Groen HJ, McRae SE, Widder J, Feng L, van den Borne BE, Munsell MF, Hurkmans C, Berry DA, van Werkhoven E, Kresl JJ, Dingemans AM, Dawood O, Haasbeek CJ, Carpenter LS, De Jaeger K, Komaki R, Slotman BJ, Smit EF, Roth JA. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus lobectomy for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: a pooled analysis of two randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 2015.
Zhu CQ, Pintilie M, John T, Strumpf D, Shepherd FA, Der SD, et al. Understanding prognostic gene expression signatures in lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009;10(5):331–40.
Subramanian J, Simon R. Gene expression-based prognostic signatures in lung cancer: ready for clinical use? J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102(7):464–74.
Zhu CQ, Ding K, Strumpf D, Weir BA, Meyerson M, Pennell N, et al. Prognostic and predictive gene signature for adjuvant chemotherapy in resected non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(29):4417–24.
Der SD, Sykes J, Pintilie M, Zhu CQ, Strumpf D, Liu N, et al. Validation of a histology-independent prognostic gene signature for early-stage, non-small-cell lung cancer including stage IA patients. J Thorac Oncol. 2014;9(1):59–64.
Sandoval J, Mendez-Gonzalez J, Nadal E, Chen G, Carmona FJ, Sayols S, et al. A prognostic DNA methylation signature for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(32):4140–7.
Ponting CP, Oliver PL, Reik W. Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2009;136(4):629–41.
Qiu MT, Hu JW, Yin R, Xu L. Long noncoding RNA: an emerging paradigm of cancer research. Tumour Biol. 2013;34(2):613–20.
Tsai MC, Spitale RC, Chang HY. Long intergenic noncoding RNAs: new links in cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2011;71(1):3–7.
Dinger ME, Amaral PP, Mercer TR, Pang KC, Bruce SJ, Gardiner BB, et al. Long noncoding RNAs in mouse embryonic stem cell pluripotency and differentiation. Genome Res. 2008;18(9):1433–45.
Ren S, Wang F, Shen J, Sun Y, Xu W, Lu J, et al. Long non-coding RNA metastasis associated in lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 derived miniRNA as a novel plasma-based biomarker for diagnosing prostate cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49(13):2949–59.
Su X, Malouf GG, Chen Y, Zhang J, Yao H, Valero V, et al. Comprehensive analysis of long non-coding RNAs in human breast cancer clinical subtypes. Oncotarget. 2014;5(20):9864–76.
Yang J, Lin J, Liu T, Chen T, Pan S, Huang W, et al. Analysis of lncRNA expression profiles in non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) and their clinical subtypes. Lung Cancer. 2014;85(2):110–5.
Zhang X, Sun S, Pu JK, Tsang AC, Lee D, Man VO, et al. Long non-coding RNA expression profiles predict clinical phenotypes in glioma. Neurobiol Dis. 2012;48(1):1–8.
Wettenhall JM, Smyth GK. limmaGUI: a graphical user interface for linear modeling of microarray data. Bioinformatics. 2004;20(18):3705–6.
The Gene Ontology (GO) project in 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(Database issue):D322-326.
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 2000;25(1):25–9.
Dupuy D, Bertin N, Hidalgo CA, Venkatesan K, Tu D, Lee D, et al. Genome-scale analysis of in vivo spatiotemporal promoter activity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25(6):663–8.
Schlitt T, Palin K, Rung J, Dietmann S, Lappe M, Ukkonen E, et al. From gene networks to gene function. Genome Res. 2003;13(12):2568–76.
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Kawashima S, Okuno Y, Hattori M. The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32(Database issue):D277–80.
Yi M, Horton JD, Cohen JC, Hobbs HH, Stephens RM. WholePathwayScope: a comprehensive pathway-based analysis tool for high-throughput data. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006;7:30.
Draghici S, Khatri P, Tarca AL, Amin K, Done A, Voichita C, et al. A systems biology approach for pathway level analysis. Genome Res. 2007;17(10):1537–45.
Louie AV, Senthi S, Palma DA. Surgery versus SABR for NSCLC. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(12), e491.
Tang H, Xiao G, Behrens C, Schiller J, Allen J, Chow CW, et al. A 12-gene set predicts survival benefits from adjuvant chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(6):1577–86.
Wilusz JE, Sunwoo H, Spector DL. Long noncoding RNAs: functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev. 2009;23(13):1494–504.
Wang KC, Chang HY. Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 2011;43(6):904–14.
Carthew RW, Sontheimer EJ. Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell. 2009;136(4):642–55.
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings HM, Wong DJ, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature. 2010;464(7291):1071–6.
Srikantan V, Zou Z, Petrovics G, Xu L, Augustus M, Davis L, et al. PCGEM1, a prostate-specific gene, is overexpressed in prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(22):12216–21.
Schmidt LH, Spieker T, Koschmieder S, Schaffers S, Humberg J, Jungen D, et al. The long noncoding MALAT-1 RNA indicates a poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer and induces migration and tumor growth. J Thorac Oncol. 2011;6(12):1984–92.
Acknowledgments
This study is founded by the Natural Science Foundation of China (81372321 to Lin Xu; 81201830 and 81472200 to Rong Yin), Natural Science Foundation for High Education of Jiangsu Province (13KJB320010 to Rong Yin), Jiangsu Provincial Special Program of Medical Science (BL2012030 to Lin Xu), and Jiangsu Province Ordinary University Graduate Student Research Innovation Project for 2013 (CXLX13_571 to Mantang Qiu).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Ming Li and Mantang Qiu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Qiu, M., Xu, Y. et al. Differentially expressed protein-coding genes and long noncoding RNA in early-stage lung cancer. Tumor Biol. 36, 9969–9978 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3714-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3714-6