Abstract
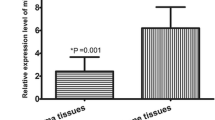
miRNA-22 (miR-22) has been showed to involve in a variety of cancers; however, the association between miR-22 expression level and the prognosis of osteosarcoma is also poorly unknown. Fifty-two patients with surgically resected paired osteosarcoma and non-neoplastic disease between 2008 and 2014 were involved in this study. Real-time PCR was performed to examine the expression level of miR-22 in osteosarcoma tissues and noncancerous bone tissues. Then the association between miR-22 expression and clinical–pathological parameters were further evaluated. Kaplan–Meier analysis and Cox proportional hazards regression models were explored to reveal the correlations of miR-22 expression with survival of patients. The results indicated that miR-22 was downregulated in osteosarcoma tissues in comparison with noncancerous bone tissues. In addition, there is statistically significance between miR-22 expression level and recurrence, metastasis, and chemotherapy response. The patients with lower miR-22 expression level had both poorer overall survival and disease-free survival. The multivariant analysis revealed that the miR-22 expression level and metastasis status are independent prognosis factors for osteosarcoma. In conclusion, miR-22 was downregulated in osteosarcoma and its expression level was correlated with a variety of important clinical–pathological parameters. Moreover, miR-22 may serve as a promising biomarker for predicting the prognosis of osteosarcoma.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fan J, Yang X, Bi Z. 6-Gingerol inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation through apoptosis and AMPK activation. Tumor Biol. 2015;36(2):1135–41.
Miao J, Wu S, Peng Z, Tania M, Zhang C. MicroRNAs in osteosarcoma: diagnostic and therapeutic aspects. Tumour Biol. 2013;34(4):2093–8.
Mishra PJ. MicroRNAs as promising biomarkers in cancer diagnostics. Biomark Res. 2014;2:19.
Namløs HM, Meza-Zepeda LA, Barøy T, Østensen IH, Kresse SH, Kuijjer ML, et al. Modulation of the osteosarcoma expression phenotype by microRNAs. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e48086.
Novello C, Pazzaglia L, Cingolani C, Conti A, Quattrini I, Manara MC, et al. miRNA expression profile in human osteosarcoma: role of miR-1 and miR-133b in proliferation and cell cycle control. Int J Oncol. 2013;42(2):667–75.
Baumhoer D, Zillmer S, Unger K, Rosemann M, Atkinson MJ, Irmler M, et al. MicroRNA profiling with correlation to gene expression revealed the oncogenic miR-17-92 cluster to be up-regulated in osteosarcoma. Cancer Genet. 2012;205(5):212–9.
Choong ML, Yang HH, McNiece I. MicroRNA expression profiling during human cord blood-derived CD34 cell erythropoiesis. Exp Hematol. 2007;35(4):551–64.
Huang ZP, Wang DZ. miR-22 in cardiac remodeling and disease. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2014;24(7):267–72.
Berenguer J, Herrera A, Vuolo L, Torroba B, Llorens F, Sumoy L, et al. MicroRNA 22 regulates cell cycle length in cerebellar granular neuron precursors. Mol Cell Biol. 2013;33(14):2706–17.
Poliseno L, Salmena L, Riccardi L, Fornari A, Song MS, Hobbs RM, et al. Identification of the miR-106b ~ 25 microRNA cluster as a proto-oncogenic PTEN-targeting intron that cooperates with its host gene MCM7 in transformation. Sci Signal. 2010;3(117):ra29.
Wang W, Li F, Zhang Y, Tu Y, Yang Q, Gao X. Reduced expression of miR-22 in gastric cancer is related to clinicopathologic characteristics or patient prognosis. Diagn Pathol. 2013;8(1):102.
Zhang G, Xia S, Tian H, Liu Z, Zhou T. Clinical significance of miR-22 expression in patients with colorectal cancer. Med Oncol. 2012;29(5):3108–12.
Xiong J, Yu D, Wei N, Fu H, Cai T, Huang Y, et al. An estrogen receptor alpha suppressor, microRNA-22, is downregulated in estrogen receptor alpha-positive human breast cancer cell lines and clinical samples. FEBS J. 2010;277(7):1684–94.
Zhang J, Yang Y, Yang T, Liu Y, Li A, Fu S, et al. microRNA-22, downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and correlated with prognosis, suppresses cell proliferation and tumourigenicity. Br J Cancer. 2010;103(8):1215–20.
Wan MN, Zhang YQ, Wang XM, Liu YJ, Zhang YX, Que YH, et al. Down-regulated miR-22 as predictive biomarkers for prognosis of epithelial ovarian cancer. Diagn Pathol. 2014;9(1):178.
Guo S, Bai R, Liu W, Zhao A, Zhao Z, Wang Y, et al. miR-22 inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation and migration by targeting HMGB1 and inhibiting HMGB1-mediated autophagy. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(7):7025–34.
Tian Z, Guo B, Yu M, Wang C, Zhang H, Liang Q, et al. Upregulation of micro-ribonucleic acid-128 cooperating with downregulation of PTEN confers metastatic potential and unfavorable prognosis in patients with primary osteosarcoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2014;7(1):1601–8.
Wang X, Yu H, Lu X, Zhang P, Wang M, Hu Y. MiR-22 suppresses the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting CD151. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;445(1):175–9.
Kong LM, Liao CG, Zhang Y, Xu J, Li Y, Huang W, et al. A regulatory loop involving miR-22, Sp1, and c-Myc modulates CD147 expression in breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2014;74(14):3764–78.
Ling B, Wang GX, Long G, Qiu JH, Hu ZL. Tumor suppressor miR-22 suppresses lung cancer cell progression through post-transcriptional regulation of ErbB3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012;138(8):1355–61.
Li S, Hu R, Wang C, Guo F, Li X, Wang S. miR-22 inhibits proliferation and invasion in estrogen receptor α-positive endometrial endometrioid carcinomas cells. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9(6):2393–9.
Szczyrba J, Löprich E, Wach S, Jung V, Unteregger G, Barth S, et al. The microRNA profile of prostate carcinoma obtained by deep sequencing. Mol Cancer Res. 2010;8(4):529–38.
Ji T, Zheng ZG, Wang FM, Xu LJ, Li LF, Cheng QH, et al. Differential microRNA expression by Solexa sequencing in the sera of ovarian cancer patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(4):1739–43.
Ganepola GA, Rutledge JR, Suman P, Yiengpruksawan A, Chang DH. Novel blood-based microRNA biomarker panel for early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2014;6(1):22–33.
Franchina T, Amodeo V, Bronte G, Savio G, Ricciardi GR, Picciotto M, et al. Circulating miR-22, miR-24 and miR-34a as novel predictive biomarkers to pemetrexed-based chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2014;229(1):97–9.
Liu N, Cui RX, Sun Y, Guo R, Mao YP, Tang LL, et al. A four-miRNA signature identified from genome-wide serum miRNA profiling predicts survival in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2014;134(6):1359–68.
Zhang C, Wang C, Chen X, Yang C, Li K, Wang J, et al. Expression profile of microRNAs in serum: a fingerprint for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Chem. 2010;56(12):1871–9.
Li J, Zhang Y, Zhao J, Kong F, Chen Y. Overexpression of miR-22 reverses paclitaxel-induced chemoresistance through activation of PTEN signaling in p53-mutated colon cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011;357(1):31–8.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G., Shen, N., Cheng, L. et al. Downregulation of miR-22 acts as an unfavorable prognostic biomarker in osteosarcoma. Tumor Biol. 36, 7891–7895 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3379-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3379-1