Abstract
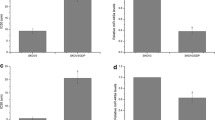
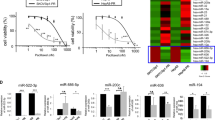
Chemotherapy is the preferred therapeutic approach for the therapy of advanced ovarian cancer, but 5-year survival rate remains low due to the development of drug resistance. Increasing evidence has documented that microRNAs (miRNAs) act important roles in drug resistance in a variety types of cancer. However, the roles of miRNA in regulating Taxol resistance in ovarian cancer and the detailed mechanism are less reported. We used Taqman probe stem loop real-time PCR to accurately measure the levels of miR-197 in normal ovarian cells, ovarian cancer cells, and Taxol-resistant ovarian cancer cells and found that miR-197 was significantly increased in Taxol-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Enforced expression of miR-197 can promote Taxol resistance, cell proliferation, and invasion of ovarian cancer cells. Meanwhile, repression of miR-197 in ovarian cancer cells can sensitize its response to Taxol and also induced attenuated cell proliferation and invasion ability. Furthermore, investigation of the detailed mechanism showed that the promotion of miR-197 on drug resistance in ovarian cancer cells was partially mediated by downregulating NLK, a negative regulator of WNT signaling pathway. Taken together, our work first demonstrated that miR-197 can confer drug resistance to Taxol, by regulating tumor suppressor, NLK expression in ovarian cancer cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vargas-Hernández VM, Moreno-Eutimio MA, Acosta-Altamirano G, Vargas-Aguilar VM. Management of recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer. Gland Surg. 2014;3(3):198–202.
Clarke T, Galaal K, Bryant A, Naik R. Evaluation of follow-up strategies for patients with epithelial ovarian cancer following completion of primary treatment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;9, CD006119.
Aravantinos G, Pectasides D. Bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy for the treatment of advanced ovarian cancer: a systematic review. J Ovarian Res. 2014;7:57.
Mei L, Chen H, Wei DM, Fang F, Liu GJ, Xie HY, et al. Maintenance chemotherapy for ovarian cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;6, CD007414.
Wani MC, Horwitz SB. Nature as a remarkable chemist: a personal story of the discovery and development of Taxol. Anticancer Drugs. 2014;25(5):482–7.
Wu WK, Lee CW, Cho CH, Fan D, Wu K, Yu J, et al. MicroRNA dysregulation in gastric cancer: a new player enters the game. Oncogene. 2010;29:5761–71.
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:7065–70.
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J, Nuovo GJ, Lerner MR, Frankel WL, et al. Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 2007;120:1046–54.
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M, et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell. 2006;9:189–98.
Murakami Y, Yasuda T, Saigo K, Urashima T, Toyoda H, Okanoue T, et al. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene. 2006;25:2537–45.
Yu S, Lu Z, Liu C, Meng Y, Ma Y, Zhao W, et al. miRNA-96 suppresses KRAS and functions as a tumor suppressor gene in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2010;70:6015–25.
Kim YW, Kim EY, Jeon D, Liu JL, Kim HS, Choi JW, et al. Differential microRNA expression signatures and cell type-specific association with Taxol resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014;8:293–314.
Sorrentino A, Liu CG, Addario A, Peschle C, Scambia G, Ferlini C. Role of microRNAs in drug-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;111(3):478–86.
Chen S, Chen X, Xiu YL, Sun KX, Zong ZH, Zhao Y. microRNA 490-3P enhances the drug-resistance of human ovarian cancer cells. J Ovarian Res. 2014;7:84.
Zong C, Wang J, Shi TM. MicroRNA 130b enhances drug resistance in human ovarian cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 2014;35(12):12151–6.
Zhu X, Li Y, Xie C, Yin X, Liu Y, Cao Y, et al. miR-145 sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to paclitaxel by targeting Sp1 and Cdk6. Int J Cancer. 2014;135(6):1286–96.
Huh JH, Kim TH, Kim K, Song JA, Jung YJ, Jeong JY, et al. Dysregulation of miR-106a and miR-591 confers paclitaxel resistance to ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013;109(2):452–61.
Dai W, Wang C, Wang F, Wang Y, Shen M, Chen K, et al. Anti-miR-197 inhibits migration in HCC cells by targeting KAI 1/CD82. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;446(2):541–8.
Hamada S, Satoh K, Miura S, Hirota M, Kanno A, Masamune A, et al. miR-197 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells by targeting p120 catenin. J Cell Physiol. 2013;228(6):1255–63.
Du L, Schageman JJ, Subauste MC, Saber B, Hammond SM, Prudkin L, et al. miR-93, miR-98, and miR-197 regulate expression of tumor suppressor gene FUS1. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7(8):1234–43.
Ishitani T, Ishitani S. Nemo-like kinase, a multifaceted cell signaling regulator. Cell Signal. 2013;25(1):190–7.
Katoh M. Network of WNT and other regulatory signaling cascades in pluripotent stem cells and cancer stem cells. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011;12(2):160–70.
Ishitani T. Protein kinase NLK, that fine-tunes the activity of multiple intracellular signaling pathways. 2012; 84(1):39–42.
Han Y, Kuang Y, Xue X, Guo X, Li P, Wang X, et al. NLK, a novel target of miR-199a-3p, functions as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2014;68(5):497–505.
Lv L, Wan C, Chen B, Li M, Liu Y, Ni T, et al. Nemo-like kinase (NLK) inhibits the progression of NSCLC via negatively modulating WNT signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2014;115(1):81–92.
Wang K, Wang X, Zou J, Zhang A, Wan Y, Pu P, et al. miR-92b controls glioma proliferation and invasion through regulating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling via Nemo-like kinase. Neurol Oncol. 2013;15(5):578–88.
Zhang Y, Peng C, Wu G, Wang Y, Liu R, Yang S, et al. Expression of NLK and its potential effect in ovarian cancer chemotherapy. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2011;21(8):1380–7.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Health Bureau of Chongqing (2013-2-121).
Conflicts of interest
None
Authors’ contributions
Q. Z. conceived the project; D.-L. Z. and L. Y. designed the experiments and carried out the majority of the experiments; X.-T. L. and R. L. helped to collect clinical samples; all authors discussed the results; D. W. and D.-L. Z. wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, D., Wang, D., Li, R. et al. MiR-197 induces Taxol resistance in human ovarian cancer cells by regulating NLK. Tumor Biol. 36, 6725–6732 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3365-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3365-7