Abstract
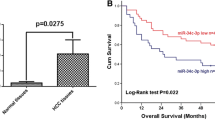
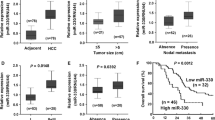
Increasing evidence has suggested that dysregulation of microRNAs (miRNAs) could contribute to tumor progression. Previous miRNA microarray analysis illustrated that miR-335 is downregulated in various cancers; however, the role of miR-335 on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has not been well elucidated. In this study, we investigated the biological functions and molecular mechanisms of miR-335 in human HCC in vitro, discussing whether it could be a therapeutic biomarker of HCC in the future. Four HCC cell lines and samples from 62 patients with HCC were analyzed for the expression of miR-335 by quantitative RT-PCR. Overexpression of miR-335 was established by transfecting mimics into HepG2 and HuH7 cells. Cell proliferation and cell migration were assessed by cell viability assay and transwell assay. Luciferase reporter assay and Western blot were to verify ROCK1 as a novel target gene of miR-335. We observed that miR-335 was downregulated in human HCC tissues and in all four HCC cell lines. The MTT assay revealed that overexpression of miR-335 subsequently inhibited cell growth. Furthermore, the transwell assay also showed significant cell migration inhibition in miR-335 transfectant. The expression of ROCK1 was decreased evidently after overexpression of miR-335, indicating that ROCK1 is a target gene for miR-335. Our data revealed that miR-335 could inhibit the proliferation and migration invasion of HCC cells via regulating ROCK1, suggesting that miR-335 could be a therapeutic biomarker of HCC in the future.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90.
Block TM, Mehta AS, Fimmel CJ, Jordan R. Molecular viral oncology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2003;22:5093–107.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136:215–33.
Zhao Y, Samal E, Srivastava D. Serum response factor regulates a muscle specific microRNA that targets Hand2 during cardiogenesis. Nature. 2005;436:214–20.
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Shimizu M, et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:13944–9.
Giordano S, Columbano A. MicroRNAs: new tools for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma? Hepatology. 2013;57(2):840–7.
He XX, Guo AY, Xu CR, Chang Y, Xiang GY, Gong J, et al. Bioinformatics analysis identifies miR-221 as a core regulator in hepatocellular carcinoma and its silencing suppresses tumor properties. Oncol Rep. 2014;32(3):1200–10.
Yu L, Zhang J, Guo X, Li Z, Zhang P. MicroRNA-224 upregulation and AKT activation synergistically predict poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. 2014;38(4):408–13.
Takaki Y, Saito Y, Takasugi A, Toshimitsu K, Yamada S, Muramatsu T, et al. Silencing of microRNA-122 is an early event during hepatocarcinogenesis from non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Cancer Sci. 2014;105(10):1254–60.
Xu L, Beckebaum S, Iacob S, Wu G, Kaiser GM, Radtke A, et al. MicroRNA-101 inhibits human hepatocellular carcinoma progression through EZH2 downregulation and increased cytostatic drug sensitivity. J Hepatol. 2014;60(3):590–8.
Shi L, Jiang D, Sun G, Wan Y, Zhang S, Zeng Y, et al. miR-335 promotes cell proliferation by directly targeting Rb1 in meningiomas. J Neurooncol. 2012;110:155–16.
Xu Y, Zhao F, Wang Z, Song Y, Luo Y, Zhang X, et al. MicroRNA-335 acts as a metastasis suppressor in gastric cancer by targeting Bcl-wand specificity protein 1. Oncogene. 2012;31(11):1398–407
Schmitz KJ, Helwig J, Bertram S, Sheu SY, Suttorp AC, Seggewiss J, et al. Differential expression of microRNA-675, microRNA-139-3p and microRNA-335 in benign and malignant adrenocortical tumours. J Clin Pathol. 2011;64(6):529–35.
Wang H, Li M, Zhang R, Wang Y, Zang W, Ma Y, et al. Effect of miR-335 upregulation on the apoptosis and invasion of lung cancer cell A549 and H1299. Tumour Biol. 2013;34(5):3101–9.
Png KJ, Yoshida M, Zhang XH, Shu W, Lee H, Rimner A, et al. MicroRNA-335 inhibits tumor reinitiation and is silenced through genetic and epigenetic mechanisms in human breast cancer. Genes Dev. 2011;25(3):226–31.
Wang Y, Zhao W, Fu Q. miR-335 suppresses migration and invasion by targeting ROCK1 in osteosarcoma cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;384(1-2):105–11.
Braconi C, Patel T. Non-coding RNAs as therapeutic targets in hepatocellular cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2012;12(9):1073–80.
Xu Y, Zhao F, Wang Z, Song Y, Luo Y, Zhang X, et al. MicroRNA-335 acts as a metastasis suppressor in gastric cancer by targeting Bcl-w and specificity protein 1. Oncogene. 2012;31(11):1398–407.
Narumiya S, Tanji M, Ishizaki T. Rho signaling, ROCK and mDia1, in transformation, metastasis and invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009;28:65–76.
Liu S. The ROCK signaling and breast cancer metastasis. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38:1363–6.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30900266).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The Publisher and Editor retract this article in accordance with the recommendations of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE). After a thorough investigation we have strong reason to believe that the peer review process was compromised.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13277-017-5487-6.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Li, W., Chen, C. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: MiR-335 acts as a potential tumor suppressor miRNA via downregulating ROCK1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 36, 6313–6319 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3317-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3317-2