Abstract
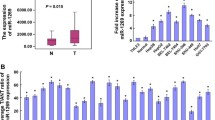
It has been reported that miR-21 is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and overexpressed miR-21 plays a key role in promoting cell cycle progression, reducing cell death and favoring angiogenesis and invasion. Overexpression of hepatocellular carcinoma, downregulated 1 (HEPN1) exhibits an antiproliferative effect on HepG2 cells, suggesting that silencing of HEPN1 may contribute to carcinogenesis of hepatocytes. In silico analysis revealed that HEPN1 may be a potential target of miR-21. Using quantitative reverse transcription PCR and Western blot, we found that HEPN1 was strikingly downregulated in both mRNA (fold change was 33.5, P < 0.0001) and protein levels in human HCC tumor tissues, in comparison with the adjacent non-tumor tissues. More importantly, the expression level of HEPN1 was inversely correlated with the expression of miR-21 in HCC (R 2 = 0.442, P < 0.0001). The combination between the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) of HEPN1 with miR-21 was experimentally verified by a miRNA luciferase reporter approach. The suppressed cell proliferation upon stimulation of miR-21 inhibitor could be partially abolished by knocking down HEPN1, so inhibition of miR-21 expression in HCC cells profoundly suppressed cell proliferation partially by upregulating HEPN1 expression. Taken together, the current study suggested an underlying mechanism that miR-21 directly target HEPN1 and inhibit its expression during the carcinogenesis of HCC. HEPN1 may thus be a candidate as a therapeutic target for patients with HCC.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HEPN1:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma, downregulated 1
- 3′UTR:
-
3′ untranslated region
- miR:
-
microRNA
- HBV:
-
Hepatitis B virus
- HCV:
-
Hepatitis C virus
References
Yang JD, Roberts LR. Hepatocellular carcinoma: a global view. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7:448–58.
Villanueva A, Minguez B, Forner A, Reig M, Llovet JM. Hepatocellular carcinoma: novel molecular approaches for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Annu Rev Med. 2010;61:317–28.
Monto A, Wright TL. The epidemiology and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Oncol. 2001;28:441–9.
Whittaker S, Marais R, Zhu AX. The role of signaling pathways in the development and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 2010;29:4989–5005.
Giordano S, Columbano A. MicroRNAs: new tools for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma? Hepatology. 2013;57:840–7.
Braconi C, Henry JC, Kogure T, Schmittgen T, Patel T. The role of microRNAs in human liver cancers. Semin Oncol. 2011;38:752–63.
Zhou J, Yu L, Gao X, Hu J, Wang J, Dai Z, et al. Plasma microRNA panel to diagnose hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:4781–8.
Tan Y, Ge G, Pan T, Wen D, Chen 2, Yu X, et al. A serum MicroRNA panel as potential biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma related with hepatitis B virus. PLoS One. 2014;9:e107986.
Wang H, Hou L, Li A, Duan Y, Gao H, Song X. Expression of serum exosomal microRNA-21 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:864894.
Wang Y, Gao X, Wei F, Zhang X, Yu J, Zhao H, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating miR-21 for cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gene. 2014;533:389–97.
Turato C, Simonato D, Quarta S, Gatta A, Pontisso P. MicroRNAs and SerpinB3 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Life Sci. 2014;100:9–17.
Gramantieri L, Fornari F, Callegari E, Sabbioni S, Lanza G, Croce CM, et al. MicroRNA involvement in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Mol Med. 2008;12:2189–204.
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST, Patel T. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:647–58.
Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H, Mo YY. MicroRNA-21 targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol Chem. 2007;282:14328–36.
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A, Lindow M, Krogh A, Lund AH. Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:1026–33.
Moh MC, Lee LH, Yang X, Shen S. HEPN1, a novel gene that is frequently down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, suppresses cell growth and induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells. J Hepatol. 2003;39:580–6.
Chung Moh M, Hoon Lee L, Shen S. Cloning and characterization of hepaCAM, a novel Ig-like cell adhesion molecule suppressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2005;42:833–41.
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T, Sander C, Marks DS. Human microRNA targets. PLoS Biol. 2004;2:e363.
Chen S, He Y, Ding J, Jiang Y, Jia S, Xia W, et al. An insertion/deletion polymorphism in the 3′ untranslated region of beta-transducin repeat-containing protein (betaTrCP) is associated with susceptibility for hepatocellular carcinoma in Chinese. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;391:552–6.
Liu Q, Fu H, Sun F, Zhang H, Tie Y, Zhu J, et al. miR-16 family induces cell cycle arrest by regulating multiple cell cycle genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:5391–404.
Liu C, Yu J, Yu S, Lavker RM, Cai L, Liu W, et al. MicroRNA-21 acts as an oncomir through multiple targets in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2010;53:98–107.
Zhou L, Yang ZX, Song WJ, Li QJ, Yang F, Wang DS, et al. MicroRNA-21 regulates the migration and invasion of a stem-like population in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2013;43:661–9.
Bader AG. miR-34—a microRNA replacement therapy is headed to the clinic. Front Genet. 2012;3:120.
Peng H, Fan J, Wu J, Lang J, Wang J, Liu H, et al. Silencing of HEPN1 is responsible for the aggressive biological behavior of pituitary somatotroph adenomas. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;31:379–88.
Vaillant F, Merino D, Lee L, Breslin K, Pal B, Ritchie ME, et al. Targeting BCL-2 with the BH3 mimetic ABT-199 in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2013;24:120–9.
Xin M, Li R, Xie M, Park D, Owonikoko TK, Sica GL, et al. Small-molecule Bax agonists for cancer therapy. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4935.
You S, Li R, Park D, Xie M, Sica GL, Cao Y, et al. Disruption of STAT3 by niclosamide reverses radioresistance of human lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13:606–16.
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81171893, Nos. 81201574 and 81172898) and Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Shuxiang Hu, Ruiyang Tao and Shouyu Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, S., Tao, R., Wang, S. et al. MicroRNA-21 promotes cell proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma partly by targeting HEPN1. Tumor Biol. 36, 5467–5472 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3213-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3213-9