Abstract
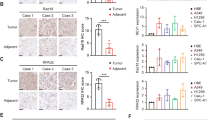
The exact effects of the modulation of Notch signaling pathway on cell growth have been shown to depend on tumor cell type. Recombination signal-binding protein Jκ (RBPJ) is a key transcription factor downstream of receptor activation in Notch signaling pathway. Here, we evaluated the effects of RBPJ inhibition on the growth of lung cancer cells. We found that a short hairpin interfering RNA (shRNA) for RBPJ efficiently inhibited RBPJ expression in lung cancer cells, resulting in a significant decrease in the cell growth. Further analyses showed that RBPJ inhibition altered the levels of its downstream targets, including p21, p27, CDK2, Hes1, Bcl-2, and SKP2, to prevent the cells from growing. Our data thus suggest that shRNA intervention of RBPJ expression could be a promising therapeutic approach for treating human lung cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zarogoulidis K, Zarogoulidis P, Darwiche K, Boutsikou E, Machairiotis N, Tsakiridis K, et al. Treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Thorac Dis. 2013;5:S389–96.
Mitsudomi T, Suda K, Yatabe Y. Surgery for nsclc in the era of personalized medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013;10:235–44.
Pallis AG, Syrigos KN. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of NSCLC. Lung Cancer. 2013;80:120–30.
Jian H, Zhao Y, Liu B, Lu S. SEMA4b inhibits MMP9 to prevent metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:11051–6.
Pei J, Lou Y, Zhong R, Han B. MMP9 activation triggered by epidermal growth factor induced FoxO1 nuclear exclusion in non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:6673–8.
6 Wang W, Wu X, Tian Y: Crosstalk of AP4 and TGFbeta receptor signaling in NSCLC. Tumour Biol 2014.
Hu YY, Zheng MH, Zhang R, Liang YM, Han H. Notch signaling pathway and cancer metastasis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;727:186–98.
Wang Z, Li Y, Banerjee S, Sarkar FH. Exploitation of the notch signaling pathway as a novel target for cancer therapy. Anticancer Res. 2008;28:3621–30.
Hsieh JJ, Hayward SD. Masking of the CBF1/RBPJ kappa transcriptional repression domain by Epstein-Barr virus EBNA2. Science. 1995;268:560–3.
Castel D, Mourikis P, Bartels SJ, Brinkman AB, Tajbakhsh S, Stunnenberg HG. Dynamic binding of RBPJ is determined by notch signaling status. Genes Dev. 2013;27:1059–71.
Hori K, Cholewa-Waclaw J, Nakada Y, Glasgow SM, Masui T, Henke RM, et al. A nonclassical bHLH Rbpj transcription factor complex is required for specification of GABAergic neurons independent of notch signaling. Genes Dev. 2008;22:166–78.
Guo D, Ye J, Dai J, Li L, Chen F, Ma D, et al. Notch-1 regulates Akt signaling pathway and the expression of cell cycle regulatory proteins cyclin D1, CDK2 and p21 in T-ALL cell lines. Leuk Res. 2009;33:678–85.
Gao F, Yao M, Shi Y, Hao J, Ren Y, Liu Q, et al. Notch pathway is involved in high glucose-induced apoptosis in podocytes via Bcl-2 and p53 pathways. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114:1029–38.
Jarriault S, Le Bail O, Hirsinger E, Pourquie O, Logeat F, Strong CF, et al. Delta-1 activation of notch-1 signaling results in HES-1 transactivation. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18:7423–31.
Dohda T, Maljukova A, Liu L, Heyman M, Grander D, Brodin D, et al. Notch signaling induces SKP2 expression and promotes reduction of p27Kip1 in t-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines. Exp Cell Res. 2007;313:3141–52.
Nakamura T, Miyagawa S, Katsu Y, Mizutani T, Sato T, Takeuchi T, et al. P21 and notch signalings in the persistently altered vagina induced by neonatal diethylstilbestrol exposure in mice. J Vet Med Sci. 2012;74:1589–95.
Marcelo KL, Sills TM, Coskun S, Vasavada H, Sanglikar S, Goldie LC, et al. Hemogenic endothelial cell specification requires c-Kit, notch signaling, and p27-mediated cell-cycle control. Dev Cell. 2013;27:504–15.
Harashima H, Dissmeyer N, Schnittger A. Cell cycle control across the eukaryotic kingdom. Trends Cell Biol. 2013;23:345–56.
Teixeira LK, Reed SI. Ubiquitin ligases and cell cycle control. Annu Rev Biochem. 2013;82:387–414.
Maraver A, Fernandez-Marcos PJ, Herranz D, Canamero M, Munoz-Martin M, Gomez-Lopez G, et al. Therapeutic effect of gamma-secretase inhibition in KrasG12V-driven non-small cell lung carcinoma by derepression of DUSP1 and inhibition of ERK. Cancer Cell. 2012;22:222–34.
Wang YC, He F, Feng F, Liu XW, Dong GY, Qin HY, et al. Notch signaling determines the M1 versus M2 polarization of macrophages in antitumor immune responses. Cancer Res. 2010;70:4840–9.
Hu XB, Feng F, Wang YC, Wang L, He F, Dou GR, et al. Blockade of notch signaling in tumor-bearing mice may lead to tumor regression, progression, or metastasis, depending on tumor cell types. Neoplasia. 2009;11:32–8.
Dou GR, Wang YC, Hu XB, Hou LH, Wang CM, Xu JF, et al. RBP-J, the transcription factor downstream of notch receptors, is essential for the maintenance of vascular homeostasis in adult mice. FASEB J. 2008;22:1606–17.
Nagao H, Setoguchi T, Kitamoto S, Ishidou Y, Nagano S, Yokouchi M, et al. RBPJ is a novel target for rhabdomyosarcoma therapy. PLoS One. 2012;7:e39268.
Reynolds A, Leake D, Boese Q, Scaringe S, Marshall WS, Khvorova A. Rational sirna design for rna interference. Nat Biotechnol. 2004;22:326–30.
Xiao X, Gaffar I, Guo P, Wiersch J, Fischbach S, Peirish L, et al. M2 macrophages promote beta-cell proliferation by up-regulation of SMAD7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:E1211–1220.
Paternot S, Bockstaele L, Bisteau X, Kooken H, Coulonval K, Roger PP. Rb inactivation in cell cycle and cancer: the puzzle of highly regulated activating phosphorylation of CDK4 versus constitutively active CDK-activating kinase. Cell Cycle. 2010;9:689–99.
Maddika S, Ande SR, Panigrahi S, Paranjothy T, Weglarczyk K, Zuse A, et al. Cell survival, cell death and cell cycle pathways are interconnected: implications for cancer therapy. Drug Resist Updat. 2007;10:13–29.
Coqueret O. New roles for p21 and p27 cell-cycle inhibitors: a function for each cell compartment? Trends Cell Biol. 2003;13:65–70.
Tang Y, Hu C, Yang H, Cao L, Li Y, Deng P, et al. Rnd3 regulates lung cancer cell proliferation through notch signaling. PLoS One. 2014;9:e111897.
Theys J, Yahyanejad S, Habets R, Span P, Dubois L, Paesmans K, et al. High notch activity induces radiation resistance in non small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2013;108:440–5.
Hassan KA, Wang L, Korkaya H, Chen G, Maillard I, Beer DG, et al. Notch pathway activity identifies cells with cancer stem cell-like properties and correlates with worse survival in lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:1972–80.
Xie M, Liu M, He CS. Sirt1 regulates endothelial notch signaling in lung cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7:e45331.
Xie M, Zhang L, He CS, Xu F, Liu JL, Hu ZH, et al. Activation of Notch-1 enhances epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gefitinib-acquired resistant lung cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113:1501–13.
Ji X, Wang Z, Geamanu A, Sarkar FH, Gupta SV. Inhibition of cell growth and induction of apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by delta-tocotrienol is associated with notch-1 down-regulation. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112:2773–83.
Galluzzo P, Bocchetta M. Notch signaling in lung cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011;11:533–40.
Garcia Campelo MR, Alonso Curbera G, Aparicio Gallego G, Grande Pulido E, Anton Aparicio LM. Stem cell and lung cancer development: blaming the Wnt, Hh and Notch signalling pathway. Clin Transl Oncol. 2011;13:77–83.
Westhoff B, Colaluca IN, D’Ario G, Donzelli M, Tosoni D, Volorio S, et al. Alterations of the notch pathway in lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:22293–8.
Sriuranpong V, Borges MW, Ravi RK, Arnold DR, Nelkin BD, Baylin SB, et al. Notch signaling induces cell cycle arrest in small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2001;61:3200–5.
Tilesi F, Fradiani P, Socci V, Willems D, Ascenzioni F. Design and validation of siRNAs and shRNAs. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2009;11:156–64.
Paddison PJ, Hannon GJ. siRNAs and shRNAs: skeleton keys to the human genome. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2003;5:217–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Qun Lv and Ronglin Shen contribute equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, Q., Shen, R. & Wang, J. RBPJ inhibition impairs the growth of lung cancer. Tumor Biol. 36, 3751–3756 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-3015-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-3015-5