Abstract
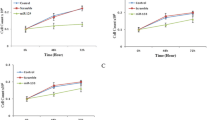
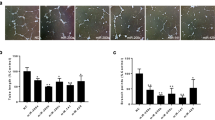
Angiogenesis is essential for a wide variety of physiological and pathological processes. To date, many angiogenic microRNAs (miRNAs) have been identified and several of them were further investigated to elucidate the mechanisms of specific miRNAs in regulating angiogenesis. In recent studies concerning tumor and ischemia, the miRNA-93 had been demonstrated to be able to modulate angiogenesis in different molecular pathways. The miRNA-93 can promote angiogenesis via enhancing endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation. Additionally, miRNA-93-over-expressing cells developed a relationship with the blood vessels allowing tumor cells to survive and to grow well. However, high expression of miRNA-93 can depress the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secretion and its downstream molecular targets in in vivo and vitro experiments. MiRNA-93’s effects on angiogenesis are dependent on the interaction of other multiple genes and signal pathways, such as P21, E2F1, integrin-β8, LATS2, etc. Future investigation should involve mapping the network by which miRNA-93 exerts its functions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siomi H, Siomi MC. Posttranscriptional regulation of microRNA biogenesis in animals. Mol Cell. 2010;38:323–32.
Karreth FA, Tay Y, Perna D, Ala U, Tan SM, Rust AG, et al. In vivo identification of tumor-suppressive PTEN ceRNAs in an oncogenic BRAF-induced mouse model of melanoma. Cell. 2011;147:382–95.
Rehmsmeier M, Steffen P, Hochsmann M, Giegerich R. Fast and effective prediction of microRNA/target duplexes. RNA. 2004;10:1507–17.
Krek A, Grun D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg L, Epstein EJ, et al. Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet. 2005;37:495–500.
Yamakuchi M, Lotterman CD, Bao C, Hruban RH, Karim B, Mendell JT, et al. P53-induced microRNA-107 inhibits HIF-1 and tumor angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:6334–9.
Dao P, Jarray R, Smith N, Lepelletier Y, Coq JL, Lietha D, et al. Inhibition of both focal adhesion kinase and fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 pathways induces anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic activities. Cancer Lett. 2014.
Hong L, Li S, Han Y, Du J, Zhang H, Li J, et al. Angiogenesis-related molecular targets in esophageal cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2011;20:637–44.
Giraldez AJ, Cinalli RM, Glasner ME, Enright AJ, Thomson JM, Baskerville S, et al. MicroRNAs regulate brain morphogenesis in zebrafish. Science. 2005;308:833–8.
Matsuda S, Ichigotani Y, Okuda T, Irimura T, Nakatsugawa S, Hamaguchi M. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel human gene (HERNA) which encodes a putative RNA-helicase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1490:163–9.
Suarez Y, Fernandez-Hernando C, Yu J, Gerber SA, Harrison KD, Pober JS, et al. Dicer-dependent endothelial microRNAs are necessary for postnatal angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:14082–7.
Fish JE, Santoro MM, Morton SU, Yu S, Yeh RF, Wythe JD, et al. MiR-126 regulates angiogenic signaling and vascular integrity. Dev Cell. 2008;15:272–84.
Poliseno L, Tuccoli A, Mariani L, Evangelista M, Citti L, Woods K, et al. MicroRNAs modulate the angiogenic properties of HUVECs. Blood. 2006;108:3068–71.
Dews M, Homayouni A, Yu D, Murphy D, Sevignani C, Wentzel E, et al. Augmentation of tumor angiogenesis by a Myc-activated microRNA cluster. Nat Genet. 2006;38:1060–5.
Bonauer A, Carmona G, Iwasaki M, Mione M, Koyanagi M, Fischer A, et al. MicroRNA-92a controls angiogenesis and functional recovery of ischemic tissues in mice. Science. 2009;324:1710–3.
Dews M, Fox JL, Hultine S, Sundaram P, Wang W, Liu YY, et al. The Myc-miR-17~92 axis blunts TGF{beta} signaling and production of multiple TGF{beta}-dependent antiangiogenic factors. Cancer Res. 2010;70:8233–46.
Li F, Liu J, Li S. MicroRNA 106b approximately 25 cluster and gastric cancer. Surg Oncol. 2013;22:e7–10.
Yeung ML, Yasunaga J, Bennasser Y, Dusetti N, Harris D, Ahmad N, et al. Roles for microRNAs, miR-93 and miR-130b, and tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1 tumor suppressor in cell growth dysregulation by human T-cell lymphotrophic virus 1. Cancer Res. 2008;68:8976–85.
Du L, Schageman JJ, Subauste MC, Saber B, Hammond SM, Prudkin L, et al. MiR-93, miR-98, and miR-197 regulate expression of tumor suppressor gene FUS1. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7:1234–43.
Hazarika S, Farber CR, Dokun AO, Pitsillides AN, Wang T, Lye RJ, et al. MicroRNA-93 controls perfusion recovery after hindlimb ischemia by modulating expression of multiple genes in the cell cycle pathway. Circulation. 2013;127:1818–28.
Savita U, Karunagaran D. MicroRNA-106b-25 cluster targets beta-TRCP2, increases the expression of snail and enhances cell migration and invasion in H1299 (non small cell lung cancer) cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;434:841–7.
Fang L, Deng Z, Shatseva T, Yang J, Peng C, Du WW, et al. MicroRNA miR-93 promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting integrin-beta8. Oncogene. 2011;30:806–21.
Fang L, Du WW, Yang W, Rutnam ZJ, Peng C, Li H, et al. MiR-93 enhances angiogenesis and metastasis by targeting LATS2. Cell Cycle. 2012;11:4352–65.
Dang LT, Lawson ND, Fish JE. MicroRNA control of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling output during vascular development. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33:193–200.
Ling S, Birnbaum Y, Nanhwan MK, Thomas B, Bajaj M, Ye Y. MicroRNA-dependent cross-talk between VEGF and HIF1 alpha in the diabetic retina. Cell Signal. 2013;25:2840–7.
Hua Z, Lv Q, Ye W, Wong CK, Cai G, Gu D, et al. Mirna-directed regulation of VEGF and other angiogenic factors under hypoxia. PLoS One. 2006;1:e116.
Long J, Wang Y, Wang W, Chang BH, Danesh FR. Identification of microRNA-93 as a novel regulator of vascular endothelial growth factor in hyperglycemic conditions. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:23457–65.
Yang IP, Tsai HL, Hou MF, Chen KC, Tsai PC, Huang SW, et al. MicroRNA-93 inhibits tumor growth and early relapse of human colorectal cancer by affecting genes involved in the cell cycle. Carcinogenesis. 2012;33:1522–30.
Liakouli V, Cipriani P, Marrelli A, Alvaro S, Ruscitti P, Giacomelli R. Angiogenic cytokines and growth factors in systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10:590–4.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported partially by the Tianjin Natural Science Funds (13JCYBJC24200) and the National Natural Science Foundation (81302250) of China.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., Liang, X., Chen, Y. et al. Role of microRNA-93 in regulation of angiogenesis. Tumor Biol. 35, 10609–10613 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2605-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2605-6