Abstract
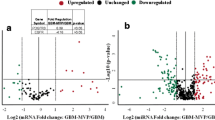
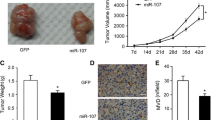
The aberrant expression of microRNAs (miRNAs) is always associated with tumor development and progression. Microvascular proliferation is one of the unique pathologic features of glioblastoma (GBM) . In this study, the microvasculature from GBM or normal brain tissue derived from neurosurgeries was purified and total RNA was isolated from purified microvasculature. The difference of miRNA expression profiles between glioblastoma microvasculature and normal brain capillaries was investigated. It was found that miR-7-5p in GBM microvessels was significantly reduced compared with that in normal brain capillaries. In the in vitro experiments, overexpression of miR-7-5p significantly inhibited human umbilical vein endothelial cell proliferation. Forced expression of miR-7-5p in human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro significantly reduced the protein level of RAF1 and repressed the activity of the luciferase, a reporter vector carrying the 3′-untranslated region of RAF1. These findings indicate that RAF1 is one of the miR-7-5p target genes. Furthermore, a significant inverse correlation between miR-7-5p expression and RAF1 protein level in GBM microvasculature was found. These data suggest that miR-7-5p functions as a tumor suppressor gene to regulate GBM microvascular endothelial cell proliferation potentially by targeting the RAF1 oncogene, implicating an important role for miR-7-5p in the pathogenesis of GBM. It may serve as a guide for the antitumor angiogenesis drug development.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MiRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- GBM:
-
Glioblastoma
- qRT-PCR:
-
Real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR
- 3′-UTR:
-
3′-Untranslated region
- WT:
-
Wild type
- MUT:
-
Mutant type
References
Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431(7006):350–5.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–97.
Pasquinelli AE, Hunter S, Bracht J. MicroRNAs: a developing story. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005;15(2):200–5.
Ahmed FE. Role of miRNA in carcinogenesis and biomarker selection: a methodological view. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2007;7(5):569–603.
Croce CM, Calin GA. miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell 2005; 122 (1) :6–7.
Gregory RI, Shiekhattar R. MicroRNA biogenesis and cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65(9):3509–12.
Croce CM. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10(10):704–14.
Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG, Norden AD, Shu HK, Wen PY, Olson JJ. Exciting new advances in neuro-oncology: the avenue to a cure for malignant glioma. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60(3):166–93.
Kraus JA, Lamszus K, Glesmann N, Beck M, Wolter M, Sabel M, et al. Molecular genetic alterations in glioblastomas with oligodendroglial component. Acta Neuropathol. 2001;101(4):311–20.
Fuller GN, The WHO. Classification of tumours of the central nervous system, 4th edition. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008;132(6):906.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature. 2008;455(7216):1061–8.
Zhang C, Li C, Li J, Han J, Shang D, Zhang Y, et al. Identification of miRNA-mediated core gene module for glioma patient prediction by integrating high-throughput miRNA, mRNA expression and pathway structure. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e96908.
Li JY, Boado RJ, Pardridge WM. Blood–brain barrier genomics. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001;21(1):61–8.
Kefas B, Godlewski J, Comeau L, Li Y, Abounader R, Hawkinson M, Lee J, Fine H, Chiocca EA, Lawler S, Purow B. microRNA-7 inhibits the epidermal growth factor receptor and the Akt pathway and is down-regulated in glioblastoma. Cancer Res 2008; 68 (10) :3566–3572
Kyriakis JM. The integration of signaling by multiprotein complexes containing Raf kinases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1773(8):1238–47.
Leicht DT, Balan V, Kaplun A, Singh-Gupta V, Kaplun L, Dobson M, et al. Raf kinases: function, regulation and role in human cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1773(8):1196–212.
McPhillips F, Mullen P, MacLeod KG, Sewell JM, Monia BP, Cameron DA, et al. Raf-1 is the predominant Raf isoform that mediates growth factor-stimulated growth in ovarian cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27(4):729–39.
Zebisch A, Troppmair J. Back to the roots: the remarkable RAF oncogene story. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006;63(11):1314–30.
Pal A, Ahmad A, Khan S, Sakabe I, Zhang C, Kasid UN, et al. Systemic delivery of RafsiRNA using cationic cardiolipin liposomes silences Raf-1 expression and inhibits tumor growth in xenograft model of human prostate cancer. Int J Oncol. 2005;26(4):1087–91.
Fushimi K, Nakashima S, You F, Takigawa M, Shimizu K. Prostaglandin E2 downregulates TNF-alpha-induced production of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in HCS-2/8 chondrocytes by inhibiting Raf-1/MEK/ERK cascade through EP4 prostanoid receptor activation. J Cell Biochem. 2007;100(3):783–93.
von Kriegsheim A, Pitt A, Grindlay GJ, Kolch W, Dhillon AS. Regulation of the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway by protein phosphatase 5. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8(9):1011–6.
von B, V, Dubben S, Engelhardt G, Hebel S, Plumakers B, Heine H, Rink L, Haase H. Zinc-dependent suppression of TNF-alpha production is mediated by protein kinase A-induced inhibition of Raf-1 , I kappa B kinase beta, and NF-kappa B. J Immunol 2007; 179 (6) :4180–4186
Li Y, Levesque LO, Anand-Srivastava MB. Epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation by endogenous vasoactive peptides contributes to hyperproliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells of SHR. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010;299(6):H1959–67.
Maretzky T, Evers A, Zhou W, Swendeman SL, Wong PM, Rafii S, et al. Migration of growth factor-stimulated epithelial and endothelial cells depends on EGFR transactivation by ADAM17. Nat Commun. 2011;2:229.
Kyriakakis E, Cavallari M, Pfaff D, Fabbro D, Mestan J, Philippova M, et al. IL-8-mediated angiogenic responses of endothelial cells to lipid antigen activation of iNKT cells depend on EGFR transactivation. J Leukoc Biol. 2011;90(5):929–39.
Guang-Wu H, Sunagawa M, Jie-En L, Shimada S, Gang Z, Tokeshi Y, et al. The relationship between microvessel density, the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and the extension of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 2000;110(12):2066–9.
Goel HL, Mercurio AM. VEGF targets the tumour cell. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13(12):871–82.
Chen Y, Rabson AB, Gorski DH. MEOX2 regulates nuclear factor-kappaB activity in vascular endothelial cells through interactions with p65 and IkappaBbeta. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;87(4):723–31.
Chiplunkar AR, Curtis BC, Eades GL, Kane MS, Fox SJ, Haar JL, et al. The Kruppel-like factor 2 and Kruppel-like factor 4 genes interact to maintain endothelial integrity in mouse embryonic vasculogenesis. BMC Dev Biol. 2013;13:40.
Zhang Y, Chen N, Zhang J, Tong Y. Hsa-let-7 g miRNA targets caspase-3 and inhibits the apoptosis induced by ox-LDL in endothelial cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(11):22708–20.
Lee JW, Soung YH, Kim SY, Nam SW, Park WS, Lee JY, et al. Absence of JAK2 V617F mutation in gastric cancers. Acta Oncol. 2006;45(2):222–3.
Orom UA, Kauppinen S, Lund AH. LNA-modified oligonucleotides mediate specific inhibition of microRNA function. Gene. 2006;372:137–41.
Acknowledgments
We thank Yan Song, Meng Zhang, and Yubao Zhang for the administrative and operational support; Drs. Guiyan Xu, Guangming Qu, Deze Jia, and Donghai Wang for their helpful discussions and critical reading of the manuscript.
Ethics approval
Ethics approval was provided by the National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Research Ethics Committee.
Conflicts of interest
None, there are no conflict of interest.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (NO.81141088) and by the Promotive Research Fund for Excellent Young and Middle-aged Scientists of Shandong Province. (NO. 2004BS02010). JYL was supported by North Shore-LIJ Cancer Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Liu, Y., Li, L. et al. MiR-7-5p is frequently downregulated in glioblastoma microvasculature and inhibits vascular endothelial cell proliferation by targeting RAF1. Tumor Biol. 35, 10177–10184 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2318-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2318-x