Abstract
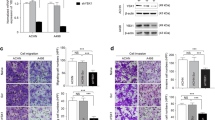
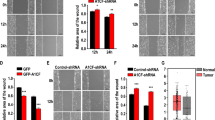
S-phase kinase-associated protein-2 (Skp2) is overexpressed in human cancers and acted as an oncogenic protein associated with poor prognosis by enhancing tumor metastasis. The present study has demonstrated that Skp2 overexpresses stable transfectants from 786-0 human renal cancer cells. We found that these stable transfectants exhibited increased migratory and invasive abilities. In addition, expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and MMP-9 was upregulated and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) was downregulated. In contrast, RNA interference-mediated knockdown Skp2 expression suppressed the ability of ACHN cells to migratory and invasive. Skp2 depletion increased P27 and decreased cyclin E activity, and then induced cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase. Skp2 depletion also downregulated MMP-2 and MMP-9, while upregulated the TIMP-1 activity and expression. The results suggest that Skp2 signaling pathways promoted the ability to metastasize, by stimulating cell proliferation and increasing the ratio of MMP-2 and MMP-9/TIMP-1. So, in conclusion, we provide the first evidence that the imbalance of MMP/TIMP, including upregulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 and downregulation of TIMP-1, is one of the mechanisms by which Skp2 promotes cell invasion.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hung WC, Tseng WL, Shiea J, Chang HC. Skp2 overexpression increases the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 and invasion of lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2010;288:156–61.
Nakayama K, Nagahama H, Minamishima YA, Matsumoto M, Nakamichi I, Kitagawa K, et al. Targeted disruption of Skp2 results in accumulation of cyclin E and p27(Kip1), polyploidy and centrosome overduplication. EMBO J. 2000;19:2069–81.
Wei Z, Jiang X, Liu F, Qiao H, Zhou B, Zhai B, et al. Downregulation of Skp2 inhibits the growth and metastasis of gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Tumour Biol. 2013;34:181–92.
Yang G, Ayala G, De Marzo A, Tian W, Frolov A, Wheeler TM, et al. Elevated Skp2 protein expression in human prostate cancer: association with loss of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 and PTEN and with reduced recurrence-free survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:3419–26.
Abdou AG, Asaad NY, Abd El-Wahed MM, Samaka RM, Allah MS. The prognostic value of Skp2 expression in Egyptian diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2012;20:47–55.
Liu Z, Fu Q, Lv J, Wang F, Ding K. Prognostic implication of p27Kip1, Skp2 and Cks1 expression in renal cell carcinoma: a tissue microarray study. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2008;27:51.
Fisher JF, Mobashery S. Mechanism-based profiling of MMPs. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;622:471–87.
Langner C, von Wasielewski R, Ratschek M, Rehak P, Zigeuner R. Biological significance of p27 and Skp2 expression in renal cell carcinoma. A systematic analysis of primary and metastatic tumour tissues using a tissue microarray technique. Virchows Arch. 2004;445:631–6.
Struckmann K, Mertz K, Steu S, Storz M, Staller P, Krek W, et al. pVHL co-ordinately regulates CXCR4/CXCL12 and MMP2/MMP9 expression in human clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. J Pathol. 2008;214:464–71.
Moore CS, Crocker SJ. An alternate perspective on the roles of TIMPs and MMPs in pathology. Am J Pathol. 2012;180:12–6.
Ramankulov A, Lein M, Johannsen M, Schrader M, Miller K, Jung K. Plasma matrix metalloproteinase-7 as a metastatic marker and survival predictor in patients with renal cell carcinomas. Cancer Sci. 2008;99:1188–94.
Lu H, Yang Z, Zhang H, Gan M, Zhou T, Wang S. The expression and clinical significance of matrix metalloproteinase 7 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases 2 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 2013;5:890–6.
Dong Y, Sui L, Watanabe Y, Sugimoto K, Tokuda M. S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 expression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas and its prognostic implications. Oncol Rep. 2003;10:321–5.
Murphy G, Nagase H. Progress in matrix metalloproteinase research. Mol Asp Med. 2008;29:290–308.
Di Carlo A. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 and -2 in sera and urine of patients with renal carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2014;7:621–6.
Qin H, Sun Y, Benveniste EN. The transcription factors Sp1, Sp3, and AP-2 are required for constitutive matrix metalloproteinase-2 gene expression in astroglioma cells. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:29130–7.
Bergers G, Brekken R, McMahon G, Vu TH, Itoh T, Tamaki K, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during carcinogenesis. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:737–44.
Tapias A, Ciudad CJ, Roninson IB, Noe V. Regulation of Sp1 by cell cycle related proteins. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:2856–67.
Kondapaka SB, Fridman R, Reddy KB. Epidermal growth factor and amphiregulin up-regulate matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in human breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 1997;70:722–6.
Zhang X, Wang Y, Yamamoto G, Tachikawa T. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2, MMP-9 and their tissue inhibitors TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 in the epithelium and stroma of salivary gland pleomorphic adenomas. Histopathology. 2009;55(3):250–60.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the grants from Zhejiang medicine and health science and technology program (2011KYB138) and Taizhou science and technology program (20111ky0704).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, H., Cao, X., Zhang, H. et al. Imbalance between MMP-2, 9 and TIMP-1 promote the invasion and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma via SKP2 signaling pathways. Tumor Biol. 35, 9807–9813 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2256-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2256-7