Abstract
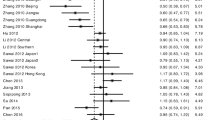
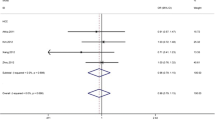
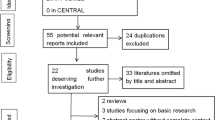
Some publications have evaluated the correlation between KIF1B rs17401966 polymorphism and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with conflicting results. We performed this meta-analysis to clarify the association of KIF1B rs17401966 polymorphism and HCC risk. We searched PubMed, ISI Web of Knowledge, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar. The combined odds ratio (OR) with 95 % confidence interval (CI) was calculated to estimate the strength of the association. Heterogeneity and publication bias were also assessed. In total, 15 case-control studies with 7,596 HCC cases and 9,614 controls were included in the meta-analysis. A significant association between KIF1B rs17401966 polymorphism and HCC risk was detected (OR = 0.81, 95 % CI 0.72–0.91, P < 0.001). We also found a significant association between KIF1B rs17401966 polymorphism and HCC risk in Chinese (OR = 0.77, 95 % CI 0.67–0.89, P < 0.001). In the subgroup analysis by gender, KIF1B rs17401966 polymorphism was significantly associated with HCC risk in man (OR = 0.57, 95 % CI 0.51–0.64, P < 0.001). In the subgroup analyses of age, the similar associations were also observed in young patients (OR = 0.50, 95 % CI 0.39–0.66, P < 0.001) and old patients (OR = 0.66, 95 % CI 0.57–0.77, P < 0.001). However, no association was observed in women subgroup (OR = 0.79, 95 % CI 0.59–1.06, P = 0.11). This meta-analysis showed a significant association between KIF1B rs17401966 polymorphism and HCC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Venook AP, Papandreou C, Furuse J, de Guevara LL. The incidence and epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: a global and regional perspective. Oncologist. 2010;15 Suppl 4:5–13.
Chen QW, Chen H, Cheng JS, Meng ZQ. MDM2 SNP309T>G polymorphism and hepatocellular carcinoma risk: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2013;35(5):4147–51.
Shen YH, Chen S, Peng YF, Shi YH, Huang XW, Yang GH, et al. Quantitative assessment of the effect of glutathione S-transferase genes GSTM1 and GSTT1 on hepatocellular carcinoma risk. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(5):4007–15.
Nangaku M, Sato-Yoshitake R, Okada Y, Noda Y, Takemura R, Yamazaki H, et al. KIF1B, a novel microtubule plus end-directed monomeric motor protein for transport of mitochondria. Cell. 1994;79:1209–20.
Zhang H, Zhai Y, Hu Z, Wu C, Qian J, Jia W, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 1p36.22 as a new susceptibility locus for hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B virus carriers. Nat Genet. 2010;42:755–8.
Hu L, Zhai X, Liu J, Chu M, Pan S, Jiang J, et al. Genetic variants in human leukocyte antigen/DP-DQ influence both hepatitis B virus clearance and hepatocellular carcinoma development. Hepatology. 2012;55:1426–31.
Li S, Qian J, Yang Y, Zhao W, Dai J, Bei JX, et al. GWAS identifies novel susceptibility loci on 6p21.32 and 21q21.3 for hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B virus carriers. PLoS Genet. 2012;8:e1002791.
Sawai H, Nishida N, Mbarek H, Matsuda K, Mawatari Y, Yamaoka M, et al. No association for Chinese HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma susceptibility SNP in other East Asian populations. BMC Med Genet. 2012;13:47.
Chen K, Shi W, Xin Z, Wang H, Zhu X, Wu X, et al. Replication of genome wide association studies on hepatocellular carcinoma susceptibility loci in a Chinese population. PLoS One. 2013;8:e77315.
Jiang DK, Sun J, Cao G, Liu Y, Lin D, Gao YZ, et al. Genetic variants in STAT4 and HLA-DQ genes confer risk of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2013;45:72–5.
Sopipong W, Tangkijvanich P, Payungporn S, Posuwan N, Poovorawan Y. The KIF1B (rs17401966) single nucleotide polymorphism is not associated with the development of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma in Thai patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14:2865–9.
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315:629–34.
Munirajan AK, Ando K, Mukai A, Takahashi M, Suenaga Y, Ohira M, et al. KIF1Bbeta functions as a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor gene mapped to chromosome 1p36.2 by inducing apoptotic cell death. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:24426–34.
Schlisio S, Kenchappa RS, Vredeveld LC, George RE, Stewart R, Greulich H, et al. The kinesin KIF1Bbeta acts downstream from EglN3 to induce apoptosis and is a potential 1p36 tumor suppressor. Genes Dev. 2008;22:884–93.
Yeh IT, Lenci RE, Qin Y, Buddavarapu K, Ligon AH, Leteurtre E, et al. A germline mutation of the KIF1B beta gene on 1p36 in a family with neural and nonneural tumors. Hum Genet. 2008;124:279–85.
Benn DE, Dwight T, Richardson AL, Delbridge L, Bambach CP, Stowasser M, et al. Sporadic and familial pheochromocytomas are associated with loss of at least two discrete intervals on chromosome 1p. Cancer Res. 2000;60:7048–51.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z. Association between KIF1B rs17401966 polymorphism and hepatocellular carcinoma risk: a meta-analysis involving 17,210 subjects. Tumor Biol. 35, 9405–9410 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2192-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2192-6