Abstract
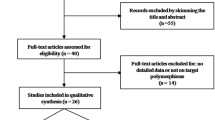
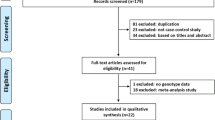
Previous case-control studies on the association of interleukin-17F (IL-17F) T7488C polymorphism and cancer risk have yielded conflicting and inconclusive findings. We performed a meta-analysis by pooling all currently available data to acquire a more precise estimation of the association. A comprehensive literature screening from the PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Wanfang databases was performed for eligible publications without language restrictions. The pooled odds ratios (ORs) with corresponding 95 % confidence intervals (95 % CIs) were calculated. According to the inclusion criteria, a total of nine case-control studies with 3,034 cases and 3,694 controls were included. Overall, the pooled ORs showed that IL-17F T7488C polymorphism was associated with neither increased nor decreased risk of cancer. However, the IL-17F T7488C polymorphism exerted risk effect on cancer in population-based case-control studies when stratifying analysis by source of controls (C vs T OR = 1.24, 95 % CI, 1.10–1.40, pooled OR (POR) < 0.001; TC vs TT OR = 1.28, 95 % CI, 1.11–1.48, POR = 0.001; CC + TC vs TT OR = 1.29, 95 % CI, 1.12–1.48, POR < 0.001). Additionally, the variant genotypes of IL-17F T7488C could alter the risk of gastric cancer under the following comparisons (C vs T OR = 1.29, 95 % CI, 1.13–1.47, POR < 0.001; TC vs TT OR = 1.35, 95 % CI, 1.14–1.60, POR < 0.001; CC + TC vs TT OR = 1.35, 95 % CI, 1.15–1.58, POR < 0.001). Sensitivity analysis by sequential omission of single study did not materially alter the pooled findings. The present meta-analysis suggests that the IL-17F T7488C polymorphism may modify the risk of cancer, particularly gastric cancer. However, the precise association needs to be elucidated by more individual studies with sufficient statistical power.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. 2001;357:539–45.
Wang K, Grivennikov SI, Karin M. Implications of anti-cytokine therapy in colorectal cancer and autoimmune diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72 Suppl 2:ii100–3.
Grivennikov SI, Wang K, Mucida D, Stewart CA, Schnabl B, Jauch D, et al. Adenoma-linked barrier defects and microbial products drive IL-23/IL-17-mediated tumour growth. Nature. 2012;491:254–8.
Amedei A, Munari F, Bella CD, Niccolai E, Benagiano M, Bencini L, et al. Helicobacter pylori secreted peptidyl prolyl cis, trans-isomerase drives Th17 inflammation in gastric adenocarcinoma. Intern Emerg Med. 2014;9:303–9.
Straus DS. TNFalpha and IL-17 cooperatively stimulate glucose metabolism and growth factor production in human colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2013;12:78.
Liao R, Sun J, Wu H, Yi Y, Wang JX, He HW, et al. High expression of IL-17 and IL-17RE associate with poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2013;32:3.
Zarogoulidis P, Katsikogianni F, Tsiouda T, Sakkas A, Katsikogiannis N, Zarogoulidis K. Interleukin-8 and interleukin-17 for cancer. Cancer Invest. 2014.
Hizawa N, Kawaguchi M, Huang SK, Nishimura M. Role of interleukin-17F in chronic inflammatory and allergic lung disease. Clin Exp Allergy. 2006;36:1109–14.
Song X, Qian Y. IL-17 family cytokines mediated signaling in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. Cell Signal. 2013;25:2335–47.
Qinghai Z, Yanying W, Yunfang C, Xukui Z, Xiaoqiao Z. Effect of interleukin-17A and interleukin-17F gene polymorphisms on the risk of gastric cancer in a Chinese population. Gene. 2014;537:328–32.
Wu X, Zeng Z, Chen B, Yu J, Xue L, Hao Y, et al. Association between polymorphisms in interleukin-17A and interleukin-17F genes and risks of gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:86–92.
Shibata T, Tahara T, Hirata I, Arisawa T. Genetic polymorphism of interleukin-17A and -17F genes in gastric carcinogenesis. Hum Immunol. 2009;70:547–51.
Omrane I, Baroudi O, Bougatef K, Mezlini A, Abidi A, Medimegh I, et al. Significant association between IL23R and IL17F polymorphisms and clinical features of colorectal cancer. Immunol Lett. 2014;158:189–94.
Kaabachi W, ben Amor A, Kaabachi S, Rafrafi A, Tizaoui K, Hamzaoui K. Interleukin-17A and -17F genes polymorphisms in lung cancer. Cytokine. 2014;66:23–9.
Zhou B, Zhang P, Wang Y, Shi S, Zhang K, Liao H, et al. Interleukin-17 gene polymorphisms are associated with bladder cancer in a Chinese Han population. Mol Carcinog. 2013;52:871–8.
Wang L, Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Huang S, Wang Z, et al. Association analysis of IL-17A and IL-17F polymorphisms in Chinese Han women with breast cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7:e34400.
Ruan Y, Hu YZ, Tao K, Zhang R. Association analysis of IL-17A and IL-17F gene polymorphism with epithelial ovarian cancer. J Hunan Normal Univ. 2012;9:21–4 [Article in Chinese].
Quan Y, Zhou B, Wang Y, Duan R, Wang K, Gao Q, et al. Association between IL17 polymorphisms and risk of cervical cancer in Chinese women. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:258293.
Cochran WG. The comparison of percentages in matched samples. Biometrika. 1950;37:256–66.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–60.
Mantel N, Haenszel W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959;22:719–48.
DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7:177–88.
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315:629–34.
Stuck AE, Rubenstein LZ, Wieland D. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Asymmetry detected in funnel plot was probably due to true heterogeneity. BMJ. 1998;316:469. author reply 470-461.
Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK. IL-17 and Th17 cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:485–517.
Shime H, Yabu M, Akazawa T, Kodama K, Matsumoto M, Seya T, et al. Tumor-secreted lactic acid promotes IL-23/IL-17 proinflammatory pathway. J Immunol. 2008;180:7175–83.
Lan C, Huang X, Lin S, Huang H, Cai Q, Lu J, et al. High density of IL-17-producing cells is associated with improved prognosis for advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. Cell Tissue Res. 2013;352:351–9.
Li J, Lau G, Chen L, Yuan YF, Huang J, Luk JM, et al. Interleukin 23 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via NF-kappa B induced matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression. PLoS One. 2012;7:e46264.
Arisawa T, Tahara T, Shiroeda H, Matsue Y, Minato T, Nomura T, et al. Genetic polymorphisms of IL17A and pri-microRNA-938, targeting IL17A 3′-UTR, influence susceptibility to gastric cancer. Hum Immunol. 2012;73:747–52.
Siakavellas SI, Bamias G. Role of the IL-23/IL-17 axis in Crohn’s disease. Discov Med. 2012;14:253–62.
Kawaguchi M, Adachi M, Oda N, Kokubu F, Huang SK. IL-17 cytokine family. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114:1265–73. quiz 1274.
Abhimanyu, Bose M, Komal, Varma-Basil M. Lack of association between IL17A and IL17F polymorphisms and related serum levels in north Indians with tuberculosis. Gene. 2013;529:195–8.
Arisawa T, Tahara T, Shibata T, Nagasaka M, Nakamura M, Kamiya Y, et al. Genetic polymorphisms of molecules associated with inflammation and immune response in Japanese subjects with functional dyspepsia. Int J Mol Med. 2007;20:717–23.
Conflicts of interest
None
Funding
This work has no funding to support it.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Fen Yao, Shushan Yan, and Xiaochen Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, F., Yan, S., Wang, X. et al. Role of IL-17F T7488C polymorphism in carcinogenesis: a meta-analysis. Tumor Biol. 35, 9061–9068 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2171-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2171-y