Abstract
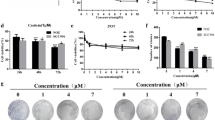
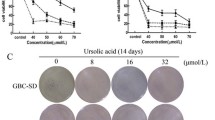
Bufalin, a major digoxin-like immunoreactive component of the Chinese medicine Chan Su, has been shown to exert a potential for anticancer activity against various human cancer cell lines in vitro. However, no detailed studies have so far been reported on its action on human gallbladder carcinoma cells. In this study, bufalin remarkably inhibited growth in human gallbladder cancer cells by decreasing cell proliferation, inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. Bufalin also disrupted the mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) and regulated the expression of cell cycle and apoptosis regulatory molecules. Activation of caspase-9 and the subsequent activation of caspase-3 indicated that bufalin may be inducing mitochondria apoptosis pathways. Intraperitoneal injection of bufalin for 3 weeks significantly inhibited the growth of gallbladder carcinoma (GBC-SD) xenografts in athymic nude mice. Taken together, the results indicate that bufalin may be a potential agent for the treatment of gallbladder cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong P, He XW, Gu J, Wu WG, Li ML, Yang JH, et al. Vimentin significantly promoted gallbladder carcinoma metastasis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011;124:4236–44.
Rifatbegovic Z, Mesic D, Ljuca F, Zildzic M, Morankic M. Incidence and surgical treatment of cancer in gallbladder. Med Arh. 2007;61:30–3.
Wang JW, Peng SY, Li JT, Wang Y, Zhang ZP, Cheng Y, et al. Identification of metastasis-associated proteins involved in gallbladder carcinoma metastasis by proteomic analysis and functional exploration of chloride intracellular channel 1. Cancer Lett. 2009;281:71–81.
Watabe M, Kawazoe N, Masuda Y, Nakajo S, Nakaya K. Bcl-2 protein inhibits bufalin-induced apoptosis through inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in human leukemia u937 cells. Cancer Res. 1997;57:3097–100.
Krenn L, Kopp B. Bufadienolides from animal and plant sources. Phytochemistry. 1998;48:1–29.
Meng Z, Yang P, Shen Y, Bei W, Zhang Y, Ge Y, et al. Pilot study of huachansu in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, nonsmall-cell lung cancer, or pancreatic cancer. Cancer. 2009;115:5309–18.
Takai N, Ueda T, Nishida M, Nasu K, Narahara H. Bufalin induces growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human endometrial and ovarian cancer cells. Int J Mol Med. 2008;21:637–43.
Yu CH, Kan SF, Pu HF, Jea Chien E, Wang PS. Apoptotic signaling in bufalin- and cinobufagin-treated androgen-dependent and -independent human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2008;99:2467–76.
Nasu K, Nishida M, Ueda T, Takai N, Bing S, Narahara H, et al. Bufalin induces apoptosis and the g0/g1 cell cycle arrest of endometriotic stromal cells: a promising agent for the treatment of endometriosis. Mol Hum Reprod. 2005;11:817–23.
Qi F, Inagaki Y, Gao B, Cui X, Xu H, Kokudo N, et al. Bufalin and cinobufagin induce apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via Fas- and mitochondria-mediated pathways. Cancer Sci. 2011;102:951–8.
Wang S, Liu Q, Zhang Y, Liu K, Yu P, Luan J, et al. Suppression of growth, migration and invasion of highly-metastatic human breast cancer cells by berbamine and its molecular mechanisms of action. Mol Cancer. 2009;8:81.
Li D, Qu X, Hou K, Zhang Y, Dong Q, Teng Y, et al. Pi3k/akt is involved in bufalin-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs. 2009;20:59–64.
Xie CM, Chan WY, Yu S, Zhao J, Cheng CH. Bufalin induces autophagy-mediated cell death in human colon cancer cells through reactive oxygen species generation and JNK activation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011;51:1365–75.
Masuda Y, Kawazoe N, Nakajo S, Yoshida T, Kuroiwa Y, Nakaya K. Bufalin induces apoptosis and influences the expression of apoptosis-related genes in human leukemia cells. Leuk Res. 1995;19:549–56.
Chen A, Yu J, Zhang L, Sun Y, Zhang Y, Guo H, et al. Microarray and biochemical analysis of bufalin-induced apoptosis of HL-60 cells. Biotechnol Lett. 2009;31:487–94.
Kawazoe N, Watabe M, Masuda Y, Nakajo S, Nakaya K. Tiam1 is involved in the regulation of bufalin-induced apoptosis in human leukemia cells. Oncogene. 1999;18:2413–21.
Watabe M, Ito K, Masuda Y, Nakajo S, Nakaya K. Activation of AP-1 is required for bufalin-induced apoptosis in human leukemia U937 cells. Oncogene. 1998;16:779–87.
Zhu Z, Sun H, Ma G, Wang Z, Li E, Liu Y, et al. Bufalin induces lung cancer cell apoptosis via the inhibition of PI3k/Akt pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13:2025–35.
Han KQ, Huang G, Gu W, Su YH, Huang XQ, Ling CQ. Anti-tumor activities and apoptosis-regulated mechanisms of bufalin on the orthotopic transplantation tumor model of human hepatocellular carcinoma in nude mice. World J Gastroenterol WJG. 2007;13:3374–9.
Liu TY, Tan ZJ, Jiang L, Gu JF, Wu XS, Cao Y, et al. Curcumin induces apoptosis in gallbladder carcinoma cell line GBC-SD cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2013;13:64.
Belmokhtar CA, Hillion J, Segal-Bendirdjian E. Staurosporine induces apoptosis through both caspase-dependent and caspase-independent mechanisms. Oncogene. 2001;20:3354–62.
Yeh JY, Huang WJ, Kan SF, Wang PS. Effects of bufalin and cinobufagin on the proliferation of androgen dependent and independent prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 2003;54:112–24.
Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Luan J, Duan H, Zhang F, Yagasaki K, et al. Effects of bufalin on the proliferation of human lung cancer cells and its molecular mechanisms of action. Cytotechnology. 2010;62:573–83.
Brenner C, Kroemer G. Apoptosis. Mitochondria—the death signal integrators. Science. 2000;289:1150–1.
Degli Esposti M. Mitochondria in apoptosis: past, present and future. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004;32:493–5.
Earnshaw WC, Martins LM, Kaufmann SH. Mammalian caspases: structure, activation, substrates, and functions during apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68:383–424.
Hengartner MO. The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature. 2000;407:770–6.
Yi CH, Yuan J. The jekyll and hyde functions of caspases. Dev Cell. 2009;16:21–34.
Parsons MJ, Green DR. Mitochondria in cell death. Essays Biochem. 2010;47:99–114.
Murray A. Cyclin ubiquitination: the destructive end of mitosis. Cell. 1995;81:149–52.
Antonsson B, Martinou JC. The BCL-2 protein family. Exp Cell Res. 2000;256:50–7.
Reed JC. Double identity for proteins of the BCL-2 family. Nature. 1997;387:773–6.
Mao WP, Ye JL, Guan ZB, Zhao JM, Zhang C, Zhang NN, et al. Cadmium induces apoptosis in human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells by caspase-dependent and -independent pathways acting on mitochondria. Toxicol In Vitro. 2007;21:343–54.
Potokar M, Milisav I, Kreft M, Stenovec M, Zorec R. Apoptosis triggered redistribution of caspase-9 from cytoplasm to mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 2003;544:153–9.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81172026, 81272402, 81301816, and 81172029), Foundation of Shanghai Outstanding Academic Leaders (No. 11XD1403800), National High Technology Research and Development Program (863 Program) (No. 2012AA022606), Postdoctoral Research Foundation of China (No. 2012 M511107), Foundation for Interdisciplinary Research of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (No. YG2011ZD07), Shanghai Science and Technology Commission intergovernmental international cooperation project (12410705900), Shanghai Science and Technology Commission medical-guiding project (12401905800), and Program for Changjiang Scholars and Postdoctoral Research Program of Shanghai (No. 12R21415300).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Lin Jiang, Ming-Ning Zhao, and Tian-Yu Liu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, L., Zhao, MN., Liu, TY. et al. Bufalin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in gallbladder carcinoma cells. Tumor Biol. 35, 10931–10941 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1911-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1911-3