Abstract
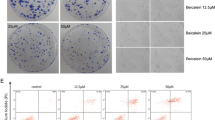
Cinobufacini (Huachansu), a Chinese medicine prepared from the skin of Bufo bufo gargarizans Cantor (Bufonidae), has potent anti-tumor activity in vitro and in vivo. However, the molecular mechanism of cell apoptosis induced by Bufalin remains elusive. Here, we investigated the apoptosis in Bufalin-treated human osteosarcoma MG-63 cells. The results showed that Bufalin could inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Further investigation revealed that a disruption of mitochondrial transmembrane potential (MMP) and an up-regulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in Bufalin-treated cells. By western blot analysis, we found that the up-regulation of Apaf-1, cleaved PARP, cleaved caspase-3, cleaved caspase-9, and Bax/Bcl-2, varies with different concentration of Bufalin. These protein interactions may play a pivotal role in the regulation of apoptosis. Taken together, these results overall indicate that Bufalin could be used as an effective anti-tumor agent in therapy of osteosarcoma targets the mitochondrial-dependent signaling pathway.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thompson Jr RC, Cheng EY, Clohisy DR, Perentesis J, Manivel C, Le CT. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;397:240–347.
Arndt CA, Crist WM. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:342–52.
Bacci G, Longhi A, Bertoni F, Bacchini P, Ruggeri P, Versari M, et al. Primary high-grade osteosarcoma: comparison between preadolescent and older patients. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2005;27:129–34.
Yang C, Choy E, Hornicek FJ, Wood KB, Schwab JH, Liu X, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACI) PCI-24781 potentiates cytotoxic effects of doxorubicin in bone sarcoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011;67:439–46.
Wittenburg LA, Bisson L, Rose BJ, Korch C, Thamm DH. The histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid sensitizes human and canine osteosarcoma to doxorubicin. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011;67:83–92.
Qi F, Li A, Inagaki Y, Kokudo N, Tamura S, Nakata M, et al. Antitumor activity of extracts and compounds from the skin of the toad Bufo bufo gargarizans Cantor. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011;11:342–9.
Qi F, Inagaki Y, Gao B, Cui X, Xu H, Kokudo N, et al. Bufalin and cinobufagin induce apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via Fas- and mitochondria-mediated pathways. Cancer Sci. 2011;102:951–8.
Li H, Wang P, Gao Y, Zhu X, Liu L, Cohen L, et al. Na+/K + −ATPase α3 mediates sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to bufalin. Oncol Rep. 2011;25:825–30.
Xie CM, Chan WY, Yu S, Zhao J, Cheng CH. Bufalin induces autophagy-mediated cell death in human colon cancer cells through reactive oxygen species generation and JNK activation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011;51:1365–75.
Amano Y, Cho Y, Matsunawa M, Komiyama K, Makishima M. Increased nuclear expression and transactivation of vitamin D receptor by the cardiotonic steroid bufalin in human myeloid leukemia cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2009;114:144–51.
Li D, Qu X, Hou K, Zhang Y, Dong Q, Teng Y, et al. PI3K/Akt is involved in bufalin induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs. 2009;20:59–64.
Yu CH, Kan SF, Pu HF, Jea Chien E, Wang PS. Apoptotic signaling in bufalin- and cinobufagin-treated and rogen-dependent and -independent human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2008;99:2467–76.
Hsiao YP, Yu CS, Yu CC, Yang JS, Chiang JH, Lu CC, et al. Triggering apoptotic death of human malignant melanoma A375.S2 cells by bufalin: involvement of caspase cascade-dependent and independent mitochondrial signaling pathways. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:591241.
Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Luan J, Duan H, Zhang F, Yagasaki K, et al. Effects of bufalin on the proliferation of human lung cancer cells and its molecular mechanisms of action. Cytotechnology. 2010;62:573–83.
Zhu Z, Sun H, Ma G, Wang Z, Li E, Liu Y, et al. Bufalin induces lung cancer cell apotosis via the inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13:2025–35.
Ek ET, Choong PF. The role of high-dose therapy and autologous stem cell transplantation for pediatric bone and soft tissue sarcomas. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2006;6:225–37.
Yang C, Hornicek FJ, Wood KB, Schwab JH, Mankin H, Duan Z. RAIDD expression is impaired in multidrug resistant osteosarcoma cell lines. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009;64:607–14.
Sun SY, Hail Jr N, Lotan R. Apoptosis as a novel target for cancer chemoprevention. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96:662–72.
Hirsch T, Marzo I, Kroemer G. Role of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore in apoptosis. Biosci Rep. 1997;17:67–76.
Iannolo G, Conticello C, Memeo L, De Maria R. Apoptosis in normal and cancer stem cells. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2008;66:42–51.
Mohamad N, Gutierrez A, Nunez M, Cocca C, Martín G, Cricco G, et al. Mitochondrial apoptotic pathways. Biocell. 2005;29:149–61.
Orrenius S, Gogvadze V, Zhivotovsky B. Mitochondrial oxidative stress: implications for cell death. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;47:143–83.
Yin XM. Signal transduction mediated by Bid, a pro-death Bcl-2 family proteins, connects the death receptor and mitochondria apoptosis pathways. Cell Res. 2000;10:161–7.
Takahashi A, Masuda A, Sun M, Centonze VE, Herman B. Oxidative stress-induced apoptosis is associated with alterations in mitochondrial caspase activity and Bcl-2-dependent alterations in mitochondrial pH (pHm). Brain Res Bull. 2004;62:497–504.
Li M, Kondo T, Zhao QL, Li FJ, Tanabe K, Arai Y, et al. Apoptosis induced by cadmium in human lymphoma U937 cells through Ca2+-calpain and caspase-mitochondriadependent pathways. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:39702–9.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. Wang (Harbin Medical University) for his technical help.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Bi, Z. Bufalin inhibited the growth of human osteosarcoma MG-63 cells via down-regulation of Bcl-2/Bax and triggering of the mitochondrial pathway. Tumor Biol. 35, 4885–4890 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1640-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1640-7