Abstract
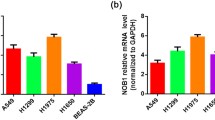
Raf-1 kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) expression was associated with the onset, development, invasion, and metastasis of numerous tumor types including prostate cancer, melanoma, colorectal cancer, liver cancer, and breast cancer. However, RKIP mRNA expression and the clinical significance in non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) remain unresolved. Real-time PCR was performed to detect the expression of RKIP mRNA in 126 pairs of lung tumor tissues (TT) and surrounding normal tissues (sNT). Correlations between RKIP mRNA expression and clinicopathological features were evaluated by statistical analysis. In the 126 patients examined, RKIP mRNA expression was significantly lower in lung TT than the sNT (p < 0.05). Our results indicated that downregulation of RKIP mRNA expression was associated with a poorer N-stage (p = 0.019) and poorer pathological TNM stage (p = 0.015). However, no significant association was observed between the expression status of RKIP mRNA and clinicopathologic factors, such as gender, age, histological type, and the size of the tumor (p > 0.05). The level of RKIP mRNA expression was found to be significantly downregulated in NSCLC, and the lower mRNA levels correlated with poorer differentiation, advanced pathologic TNM stage in patients with NSCLC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63(1):11–30.
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE, Adjei AA. Non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83:584–94.
Alberg AJ, Brock MV, Ford JG, Samet JM, Spivack SD. Epidemiology of lung cancer: diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143(5 Suppl):e1S–e29S.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 2, 2013. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/f_guidelines.asp#nscl
Yeung K, Janosch P, McFerran B, Rose DW, Mischak H, et al. Mechanism of suppression of the Raf/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway by the raf kinase inhibitor protein. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:3079–85.
Granovsky AE, Rosner MR. Raf kinase inhibitory protein: a signal transduction modulator and metastasis suppressor. Cell Res. 2008;18(4):452–7.
Beshir AB, Ren G, Magpusao AN, Barone LM, Yeung KC, Fenteany G. Raf kinase inhibitor protein suppresses nuclear factor-κB-dependent cancer cell invasion through negative regulation of matrix metalloproteinase expression. Cancer Lett. 2010;299(2):137–49.
Zeng L, Imamoto A, Rosner MR. Raf kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP): a physiological regulator and future therapeutic target. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2008;12(10):1275–87. doi:10.1517/14728222.12.10.1275.
Fu Z, Smith PC, Zhang L, Rubin MA, Dunn RL, Yao Z, et al. Effects of Raf kinase inhibitor protein expression on suppression of prostate cancer metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95(12):878–89.
Xu YF, Yi Y, Qiu SJ, Gao Q, Li YW, Dai CX, et al. PEBP1 downregulation is associated to poor prognosis in HCC related to hepatitis B infection. J Hepatol. 2010;53(5):872–9.
Lin K, Baritaki S, Militello L, Malaponte G, Bevelacqua Y, Bonavida B. The role of B-RAF mutations in melanoma and the induction of EMT via dysregulation of the NF-kappaB/Snail/RKIP/PTEN circuit. Genes Cancer. 2010;1(5):409–20.
Al-Mulla F, Hagan S, Al-Ali W, Jacob SP, Behbehani AI, Bitar MS, et al. Raf kinase inhibitor protein: mechanism of loss of expression and association with genomic instability. J Clin Pathol. 2008;61(4):524–9.
Li HZ, Gao Y, Zhao XL, Liu YX, Sun BC, Yang J, et al. Effects of Raf kinase inhibitor protein expression on metastasis and progression of human breast cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7(6):832–40.
Beach S, Tang H, Park S, Dhillon AS, Keller ET, Kolch W, et al. Snail is a repressor of RKIP transcription in metastatic prostate cancer cells. Oncogene. 2008;27(15):2243–8.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant form Nanjing General Hospital Foundation “Cancer associated fibroblasts promote angiogenesis and metastasis by secreting periostin in non-small cell lung cancer” (2013020).
Conflict of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Wu, X., Wu, T. et al. Clinical significance of RKIP mRNA expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Tumor Biol. 35, 4377–4380 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1575-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1575-4