Abstract
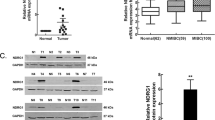
CRKL encodes an adaptor protein that has been recently reported to be overexpressed in various cancers and associate with the malignant behavior of cancer cells. However, the expression pattern of CRKL protein and its clinical significance in human bladder cancer have not been well characterized to date. In the present study, CRKL expression was analyzed in 82 archived bladder cancer specimens using immunohistochemistry, and the correlations between CRKL expression and clinicopathological parameters were evaluated. We found that CRKL was overexpressed in 31 of 82 (37.8 %) bladder cancer specimens. A significant association was observed between CRKL overexpression and tumor status (p = 0.019). To further explore the biological functions of CRKL in bladder cancer, we overexpressed CRKL in BIU-87 and 5637 cell lines. Using CCK8 assay and colony formation assay, we showed that CRKL upregulation increased cell proliferation. In addition, transwell assay showed that CRKL could also facilitate invasion. Further study demonstrated that CRKL upregulation increased cyclin D1 expression and ERK phosphorylation. In conclusion, CRKL is overexpressed in bladder cancer and regulates malignant cell growth and invasion, which makes CRKL a candidate therapeutic target for bladder cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29.
Liang PY, Li HY, Zhou ZY, Jin YX, et al. Overexpression of immunoglobulin G prompts cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis in human urothelial carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2013;34:1783–91.
Tian F, Xu F, Zhang ZY, Ge JP, et al. Expression of CHD1L in bladder cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival. Tumour Biol. 2011;34:3687–90.
Sapre, N, Anderson PD, Costello AJ, Hovens CM, et al., Gene-based urinary biomarkers for bladder cancer: an unfulfilled promise? Urol Oncol. 2013 Oct 17. pii: S1078-1439(13)00289-5. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2013.07.002. [Epub ahead of print]
Sanchez-Carbayo M. Hypermethylation in bladder cancer: biological pathways and translational applications. Tumour Biol. 2012;33:347–61.
Shan GY, Zhang Z, Chen QG, Yu XY, et al. Overexpression of RIN1 associates with tumor grade and progression in patients of bladder urothelial carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2012;33:847–55.
Atkins CD, Wrzesinski SH. Radiotherapy plus chemotherapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;367:380. author reply 380-1.
ten Hoeve J, Arlinghaus RB, Guo JQ, Heisterkamp N, et al. Tyrosine phosphorylation of CRKL in Philadelphia + leukemia. Blood. 1994;84:1731–6.
ten Hoeve J, Morris C, Heisterkamp N, Groffen J. Isolation and chromosomal localization of CRKL, a human crk-like gene. Oncogene. 1993;8:2469–74.
Feller SM. Crk family adaptors-signalling complex formation and biological roles. Oncogene. 2001;20:6348–71.
Zhao T, Miao Z, Wang Z, Xu Y, et al. Overexpression of CRKL correlates with malignant cell proliferation in breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2013;34:2891–7.
Singer CF, Hudelist G, Lamm W, Mueller R, et al. Active (p)CrkL is overexpressed in human malignancies: potential role as a surrogate parameter for therapeutic tyrosine kinase inhibition. Oncol Rep. 2006;15:353–9.
Kim YH, Kwei KA, Girard L, Salari K, et al. Genomic and functional analysis identifies CRKL as an oncogene amplified in lung cancer. Oncogene. 2009;29:1421–30.
Ladanyi M. CRKL as a lung cancer oncogene and mediator of acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors: is it all that it is cracked up to be? Cancer Discov. 2011;1:560–1.
Wang Y, Dong QZ, Fu L, Stoecker M, et al. Overexpression of Crkl correlates with poor prognosis and cell proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Carcinog. 2011;52:890–9.
Tashiro E, Tsuchiya A, Imoto M. Functions of cyclin D1 as an oncogene and regulation of cyclin D1 expression. Cancer Sci. 2007;98:629–35.
Witzel II, Koh LF, Perkins ND. Regulation of cyclin D1 gene expression. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010;38:217–22.
Fristrup N, Birkenkamp-Demtroder K, Reinert T, Sanchez-Carbayo M, et al. Multicenter validation of cyclin D1, MCM7, TRIM29, and UBE2C as prognostic protein markers in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Am J Pathol. 2013;182:339–49.
Sebolt-Leopold JS, Herrera R. Targeting the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade to treat cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:937–47.
Webb CP, Van Aelst L, Wigler MH, Vande Woude GF. Signaling pathways in Ras-mediated tumorigenicity and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:8773–8.
Arai A, Aoki M, Weihua Y, Jin A, et al. CrkL plays a role in SDF-1-induced activation of the Raf-1/MEK/Erk pathway through Ras and Rac to mediate chemotactic signaling in hematopoietic cells. Cell Signal. 2006;18:2162–71.
Xu YY, Mao XY, Song YX, Zhao F, et al. Midkine confers adriamycin resistance in human gastric cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2012;33:1543–8.
Hu L, Xia L, Zhou H, Wu B, et al. TF/FVIIa/PAR2 promotes cell proliferation and migration via PKCalpha and ERK-dependent c-Jun/AP-1 pathway in colon cancer cell line SW620. Tumour Biol. 2002;34:2573–81.
Lee EJ, Lee SJ, Kim S, Cho SC, et al. Interleukin-5 enhances the migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells via ERK1/2-mediated MMP-9/NF-kappaB/AP-1 pathway: involvement of the p21WAF1 expression. Cell Signal. 2013;25:2025–38.
Yang C, Klein EA, Assoian RK, Kazanietz MG. Heregulin beta1 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation through Rac/ERK-dependent induction of cyclin D1 and p21Cip1. Biochem J. 2008;410:167–75.
Dong QZ, Wang Y, Tang ZP, Fu L, et al. Derlin-1 is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and promotes cancer cell invasion via EGFR-ERK-mediated up-regulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Am J Pathol. 2013;182:954–64.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, B., Luan, L., Xu, Z. et al. Clinical significance and biological roles of CRKL in human bladder carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 35, 4101–4106 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1536-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1536-y