Abstract
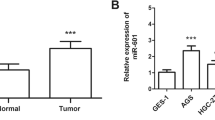
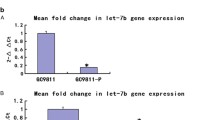
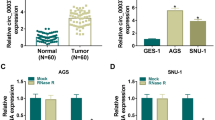
Gastric cancer is the second leading cause of cancer mortality, but the molecular mechanisms underlying its progression and metastasis remain unclear. CCR7 and Dicer 1 protein expression in 80 gastric adenocarcinomas and 40 peritumoral tissues were measured by immunohistochemical staining. The expression of let-7a miRNA in serum, tumor tissues, and peritumoral tissues was measured by real-time PCR. The role of let-7a in CCR7 protein expression, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells was tested in vitro. Dicer 1 protein expression was found to be significantly reduced, whereas CCR7 protein expression was significantly increased in gastric adenocarcinomas compared to peritumoral tissues. The let-7a miRNA levels in the serum and tumor tissues of gastric adenocarcinoma patients were significantly lower than in the serum of healthy controls and peritumoral tissues, respectively. Dicer 1 protein positively correlated with let-7a miRNA level, but negatively correlated with CCR7 protein level in gastric adenocarcinoma. Negative Dicer 1 protein and let-7a miRNA expression and positive CCR7 protein expression significantly correlated with lymph node metastasis, depth of invasion, high clinical TNM stage, and larger tumor size. Let-7a transfection significantly inhibited CCR7 protein expression, migration, and invasion of MNK-45 cells in vitro. High expression of CCR7 protein and low expression of Dicer 1 protein and let-7a miRNA are significantly associated with the metastasis and progression of gastric cancer. High CCR7 protein expression may be caused by the loss of Dicer 1 protein expression and reduced let-7a miRNA level in gastric cancer. The serum let-7a level might be a marker for the diagnosis of gastric cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mashino K, Sadanaga N, Yamaguchi H, Tanaka F, Ohta M, Shibuta K, et al. Expression of chemokine receptor CCR7 is associated with lymph node metastasis of gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2002;62:2937–41.
Campbell JJ, Butcher EC. Chemokines in tissue-specific and microenvironment-specific lymphocyte homing. Curr Opin Immunol. 2000;12:336–41.
Kodama J, Hasengaowa, Seki N, Kusumoto T, Hiramatsu Y. Expression of the CXCR4 and CCR7 chemokine receptors in human endometrial cancer. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2007;28:370–5.
Arigami T, Natsugoe S, Uenosono Y, Yanagita S, Arima H, Hirata M, et al. CCR7 and CXCR4 expression predicts lymph node status including micrometastasis in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 2009;35:19–24.
Schimanski CC, Schwald S, Simiantonaki N, Jayasinghe C, Gönner U, Wilsberg V, et al. Effect of chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CCR7 on the metastatic behavior of human colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:1743–50.
Walser TC, Fulton AM. The role of chemokines in the biology and therapy of breast cancer. Breast Dis. 2004;20:137–43.
Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ, Parker R. Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Genes Dev. 2006;20:515–24.
Bagga S, Pasquinelli AE. Identification and analysis of microRNAs. Genet Eng (N Y). 2006;27:1–20.
Xiong J, Du Q, Liang Z. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-22 inhibits the transcription of E-box-containing c-Myc target genes by silencing c-Myc binding protein. Oncogene. 2010;29:4980–8.
Song JH, Meltzer SJ. MicroRNAs in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of gastroesophageal cancers. Gastroenterology. 2012;143:35–47.
Song B, Ju J. Impact of miRNAs in gastrointestinal cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2010;12:e33.
Kim SJ, Shin JY, Lee KD, Bae YK, Sung KW, Nam SJ, et al. MicroRNA let-7a suppresses breast cancer cell migration and invasion through downregulation of C-C chemokine receptor type 7. Breast Cancer Res. 2012;14:R14.
Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature. 2001;409:363–6.
Macrae IJ, Zhou K, Li F, Repic A, Brooks AN, Cande WZ, et al. Structural basis for double-stranded RNA processing by Dicer. Science. 2006;311:195–8.
Dedes KJ, Natrajan R, Lambros MB, Geyer FC, Lopez-Garcia MA, Savage K, et al. Down-regulation of the miRNA master regulators Drosha and Dicer is associated with specific subgroups of breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47:138–50.
Yamada T, Sato K, Komachi M, Malchinkhuu E, Tobo M, Kimura T, et al. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) in malignant ascites stimulates motility of human pancreatic cancer cells through LPA1. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:6595–605.
Komachi M, Tomura H, Malchinkhuu E, Tobo M, Mogi C, Yamada T, et al. LPA1 receptors mediate stimulation, whereas LPA2 receptors mediate inhibition, of migration of pancreatic cancer cells in response to lysophosphatidic acid and malignant ascites. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:457–65.
Yang Q, Jie Z, Cao H, Greenlee AR, Yang C, Zou F, et al. Low-level expression of let-7a in gastric cancer and its involvement in tumorigenesis by targeting RAB40C. Carcinogenesis. 2011;32:713–22.
Ishigami S, Natsugoe S, Nakajo A, Tokuda K, Uenosono Y, Arigami T, et al. Prognostic value of CCR7 expression in gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2007;54:1025–8.
Li X, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Ding J, Wu K, Fan D. Survival prediction of gastric cancer by a seven-microRNA signature. Gut. 2010;59:579–85.
Zhu Y, Zhong Z, Liu Z. Lentiviral vector-mediated upregulation of let-7a inhibits gastric carcinoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011;46:53–9.
Kumar MS, Lu J, Mercer KL, Golub TR, Jacks T. Impaired microRNA processing enhances cellular transformation and tumorigenesis. Nat Genet. 2007;39:673–7.
Kumar MS, Pester RE, Chen CY, Lane K, Chin C, Lu J, et al. Dicer1 functions as a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor. Genes Dev. 2009;23:2700–27404.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support of the National Hi-tech Program (863 Project) of China (no. 2007AA021804, 2007AA021809).
Conflict of interest
All authors declared no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Wn., Chen, Y., Zhang, Yd. et al. The regulatory mechanism of CCR7 gene expression and its involvement in the metastasis and progression of gastric cancer. Tumor Biol. 34, 1865–1871 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-0728-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-0728-9