Abstract
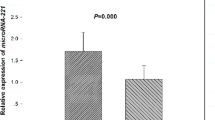
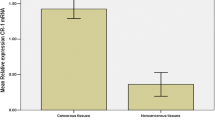
The aim of the present study is to explore the role of annexin II in the development and progression of human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Real-time quantitative reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction was conducted to detect annexin II mRNA expression. Annexin II protein expression was also determined by western blot. In addition, annexin II expression was analyzed by immunohistochemistry in 137 clinicopathologically characterized NSCLC cases. The correlation of annexin II expression with patients’ survival rate was assessed by Kaplan–Meier analysis and Cox regression. Our results showed that the expression levels of annexin II mRNA and protein in NSCLC tissues were significantly higher than those in non-cancerous tissues. Immunohistochemistry analysis showed that annexin II expression was significantly correlated with tumor diameter, pathological grade, pT status, pN status, and pleural invasion. The results of the Kaplan–Meier analysis indicated that a high expression level of annexin II resulted in a significantly poor prognosis of NSCLC patients. Multi-variate Cox regression analysis revealed that annexin II expression level was an independent prognostic parameter for the overall survival rate of NSCLC patients. In conclusion, these results suggested that annexin II up-regulation was associated with poor prognosis in NSCLC; therefore, it might act as a prognostic marker and a new potential target for NSCLC treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:43–66.
Christofori G. New signals from the invasive front. Nature. 2006;441:444–50. doi:10.1038/nature04872.
Seemann J, Weber K, Gerke V. Annexin I targets S100C to early endosomes. FEBS Lett. 1997;413:185–90.
Longerich T, Haller MT, Mogler C, Aulmann S, Lohmann V, Schirmacher P, et al. Annexin A2 as a differential diagnostic marker of hepatocellular tumors. Pathol Res Pract. 2011;207:8–14.
Zhai H, Acharya S, Gravanis I, Mehmood S, Seidman RJ, Shroyer KR, et al. Annexin A2 promotes glioma cell invasion and tumor progression. J Neurosci. 2011;31:14346–60. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3299-11.2011.
Sharma MR, Koltowski L, Ownbey RT, Tuszynski GP, Sharma MC. Angiogenesis-associated protein annexin II in breast cancer: selective expression in invasive breast cancer and contribution to tumor invasion and progression. Exp Mol Pathol. 2006;81:146–56.
Díaz VM, Hurtado M, Thomson TM, Reventós J, Paciucci R. Specific interaction of tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) with annexin II on the membrane of pancreatic cancer cells activates plasminogen and promotes invasion in vitro. Gut. 2004;53:993–1000. doi:10.1136/gut.2003.026831.
Bao H, Jiang M, Zhu M, Sheng F, Ruan J, Ruan C. Overexpression of Annexin II affects the proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and production of proangiogenic factors in multiple myeloma. Int J Hematol. 2009;90:177–85.
Ranson M, Andronicos NM. Plasminogen binding and cancer: promises and pitfalls. Front Biosci. 2003;8:s294–304.
Mussunoor S, Murray GI. The role of annexins in tumour development and progression. J Pathol. 2008;216:131–40. doi:10.1002/path.2400.
Kwaan HC. The plasminogen-plasmin system in malignancy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1992;11:291–311.
Sharma MC, Sharma M. The role of annexin II in angiogenesis and tumor progression: a potential therapeutic target. Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13:3568–75.
Cui JW, Wang YL. Expression and function of Annexin II in lung cancer tissue. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2013;6:150–2. doi:10.1016/S1995-7645(13)60012-7.
Li W, Yu CP, Xia JT, Zhang L, Weng GX, Zheng HQ, et al. Sphingosine kinase 1 is associated with gastric cancer progression and poor survival of patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:1393–9. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1158.
Emoto K, Yamada Y, Sawada H, Fujimoto H, Ueno M, Takayama T, et al. Annexin II overexpression correlates with stromal tenascin-C overexpression: a prognostic marker in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer. 2001;92:1419–26.
Zimmermann U, Woenckhaus C, Pietschmann S, Junker H, Maile S, Schultz K, et al. Expression of annexin II in conventional renal cell carcinoma is correlated with Fuhrman grade and clinical outcome. Virchows Arch. 2004;445:368–74.
Liu JW, Shen JJ, Tanzillo-Swarts A, Bhatia B, Maldonado CM, Person MD, et al. Annexin II expression is reduced or lost in prostate cancer cells and its re-expression inhibits prostate cancer cell migration. Oncogene. 2003;22:1475–85. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206196.
Qi YJ, He QY, Ma YF, Du YW, Liu GC, Li YJ, et al. Proteomic identification of malignant transformation-related proteins in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cell Biochem. 2008;104:1625–35. doi:10.1002/jcb.21727.
Pena-Alonso E, Rodrigo JP, Parra IC, Pedrero JM, Meana MV, Nieto CS, et al. Annexin A2 localizes to the basal epithelial layer and is down-regulated in dysplasia and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2008;263:89–98.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Medicine Scientific Research Projects of Chongqing Municipal Health Bureau, China (grant no.: 2011-2-076).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, JW., Li, KL., Wu, JX. et al. Clinical significance of annexin II expression in human non-small cell lung cancer. Tumor Biol. 34, 1767–1771 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-0715-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-0715-1