Abstract
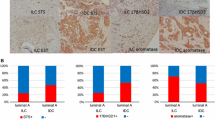
Patients with hormone receptor positive breast cancer who are treated with endocrine therapy generally have a good prognosis. However, resistance to hormonal therapy and progression occurs, and the reasons for this are manifold. It has been proposed that the local estrogenic environment has a role in the process of local invasion and progression. We have determined the expression pattern of estrogen receptor α, estrogen receptor β, and the epithelial and stromal expression of the estrogen-metabolizing enzymes aromatase and sulfotransferase by immunohistochemistry in tissue arrays, containing 50 paraffin-embedded sets of tissues obtained from breast cancer and from corresponding metastatic axillary lymph nodes of the same patients. We have found statistically significant higher estrogen receptors α and β expression in primary tumors than in corresponding lymph node metastases (p = 0.0004 and p = 0.003, respectively). Aromatase was also expressed more frequently in epithelial as well as in stromal cells of the malignant tumor when compared to according lymph node metastases (p = 0.08 and p = 0.12, respectively). While in lymph node metastases only estrogen receptor α and stromal aromatase expression were correlated (p = 0.01), significant associations were seen between the estrogen receptor β and stromal aromatase, and epithelial sulfotransferase (p = 0.0006 and p = 0.03, respectively) in the primary tumor. We hypothesize that the decreased expression of local estrogens by aromatase, in combination with a decreased expression of estrogen receptors α and β in lymphatic metastases, renders these metastases hormone insensitive and could contribute to the poor response to endocrine therapy that is often seen in nodal-positive tumors.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schiff R, Massarweh S, Shou J, et al. Breast cancer endocrine resistance: how growth factor signaling and estrogen receptor coregulators modulate response. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:447–54.
Bedard PL, Freedman OC, Howell A, et al. Overcoming endocrine resistance in breast cancer: are signal transduction inhibitors the answer? Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008;108:307–17.
Hudelist G, Czerwenka K, Keckstein J, et al. Expression of aromatase and estrogen sulfotransferase in eutopic and ectopic endometrium: evidence for unbalanced estradiol production in endometriosis. Reprod Sci. 2007;14:798–805.
Abul-Hajj YJ, Iverson R, Kiang DT. Aromatization of androgens by human breast cancer. Steroids. 1979;33:205–22.
Lipton A, Santner SJ, Santen RJ, et al. Aromatase activity in primary and metastatic human breast cancer. Cancer. 1987;59:779–82.
Suzuki T, Miki Y, Nakamura Y, et al. Sex steroid-producing enzymes in human breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2005;12:701–20.
Zhang H, Varlamova O, Vargas FM, Falany CN, Leyh TS. Sulfuryl transfer: the catalytic mechanism of human estrogen sulfotransferase. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:10888–92.
Geisler J. Breast cancer tissue estrogens and their manipulation with aromatase inhibitors and inactivators. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2003;86:245–53.
Geisler J, Lønning PE. Aromatase inhibition: translation into a successful therapeutic approach. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:2809–21.
Sasano H, Nagura H, Harada N, Goukon Y, Kimura M. Immunolocalization of aromatase and other steroidogenic enzymes in human breast disorders. Hum Pathol. 1994;25:530–5.
Sasano H, Frost AR, Saitoh R, et al. Aromatase and 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in human breast carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 1996;81:4042–6.
Remmele W, Stegner HE. Recommendation for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast cancer tissue. Pathologe. 1987;8:138–40.
Hudelist G, Wülfing P, Kersting C. Expression of aromatase and estrogen sulfotransferase in preinvasive and invasive breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008;134:67–73.
Kristek J, Dmitrović B, Kurbel S, et al. Tumor growth fraction, expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors, p53, bcl-2 and cathepsin D activity in primary ductal invasive breast carcinoma and their axillary lymph node metastases. Coll Antropol. 2007;31:1043–7.
Harrell JC, Dye WW, Harvell DM, et al. Estrogen insensitivity in a model of estrogen receptor positive breast cancer lymph node metastasis. Cancer Res. 2007;67:10582–91.
Speirs V, Parkes AT, Kerin MJ, et al. Coexpression of estrogen receptor alpha and beta: poor prognostic factors in human breast cancer? Cancer Res. 1999;59:525–8.
Rosa FE, Caldeira JR, Felipes J, et al. Evaluation of estrogen receptor alpha and beta and progesterone receptor expression and correlation with clinicopathologic factors and proliferative marker Ki-67 in breast cancers. Hum Pathol. 2008;39:720–30.
Vinayagam R, Sibson DR, Holcombe C, Aachi V, Davies MP. Association of oestrogen receptor beta 2 (ER beta 2/ER beta cx) with outcome of adjuvant endocrine treatment for primary breast cancer- a retrospective study. BMC Cancer. 2007;7:131.
Esslimani-Sahla M, Simony-Lafontaine J, Kramar A, et al. Estrogen receptor beta (ER beta) level but not its ER beta cx variant helps to predict tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:5769–76.
Cappelletti V, Celio L, Bajetta E, et al. Prospective evaluation of estrogen receptor-beta in predicting response to neoadjuvant antiestrogen therapy in elderly breast cancer patients. Endocr-Relat Cancer. 2004;11:761–70.
Silva MC, Rowlands MG, Dowsett M, et al. Intratumoral aromatase as a prognostic factor in human breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1989;49:2588–91.
Miller WR, Anderson TJ, Jack WJ. Relationship between tumor aromatase activity, tumor characteristics and response to therapy. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;37:1055–9.
Miller WR. Aromatase activity in breast tissue. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;39:783–90.
Bolufer P, Ricart E, Lluch A, et al. Aromatase activity and estradiol in human breast cancer: its relationship to estradiol and epidermal growth factor receptors and to tumor-node-metastasis staging. J Clin Oncol. 1992;10:438–46.
Lipton A, Santen RJ, Santner SJ, Harvey HA, Sanders SI, Matthews YL. Prognostic value of breast cancer aromatase. Cancer. 1992;70:1951–5.
Santner SJ, Feil PD, Santen RJ. In situ estrogen production via the estrone sulfatase pathway in breast tumors: relative importance versus the aromatase pathway. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984;59:29–33.
Purohit A, Newman SP, Reed MJ. The role of cytokines in regulating estrogen synthesis: implications for the etiology of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2002;4:65–9.
Esteban JM, Warsi Z, Haniu M, Hall P, Shively JE, Chen S. Detection of intratumoral aromatase in breast carcinomas. An immunohistochemical study with clinicopathologic correlation. Am J Pathol. 1992;140:337–43.
Lu Q, Nakmura J, Savinov A, et al. Expression of aromatase protein and messenger ribonucleic acid in tumor epithelial cells and evidence of functional significance of locally produced estrogen in human breast cancers. Endocrinology. 1996;137:3061–8.
Brodie AM, Lu Q, Long BJ, et al. Aromatase and COX-2 expression in human breast cancers. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2001;79:41–7.
Miki Y, Suzuki T, Tazawa C, et al. Aromatase localization in human breast cancer tissues: possible interactions between intratumoral stromal and parenchymal cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67:3945–54.
Suzuki T, Nakata T, Miki Y, et al. Estrogen sulfotransferase and steroid sulfatase in human breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003;63:2762–70.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of this scientific work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gschwantler-Kaulich, D., Fink-Retter, A., Czerwenka, K. et al. Differential expression pattern of estrogen receptors, aromatase, and sulfotransferase in breast cancer tissue and corresponding lymph node metastases. Tumor Biol. 32, 501–508 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-010-0144-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-010-0144-3