Abstract
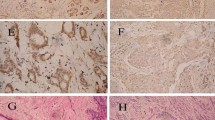
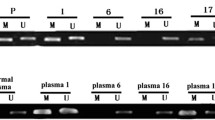
Maspin is a serine protease inhibitor with tumor-suppressor activity. Maspin can suppress tumor growth and metastasis in vivo and tumor cell motility and invasion in vitro. Previous studies indicate that the loss of Maspin expression is closely linked to aberrant methylation of the Maspin promoter. We examined the promoter methylation status of Maspin in tumor and corresponding serum of breast cancer patients. In addition, protein expression of this gene was also assessed to determine possible correlation between promoter hypermethylation and gene silencing. Further, we investigated the correlation of Maspin expression with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A) and MTA1 expression. Maspin methylation was analyzed by methylation-specific PCR in 100 invasive ductal breast carcinoma patients’ tumors and circulating DNA in a prospective study. Promoter hypermethylation was correlated with expression of the encoded protein in tumors by immunohistochemistry. Significant correlation was observed between promoter hypermethylation of Maspin (r = +0.88; p ≤ 0.0001) in tumors and paired sera. Significant association was found between Maspin promoter hypermethylation and loss of its protein expression (p = 0.01, OR = 3.1, 95% CI = 1.3–7.4). The expression of VEGF-A and MTA1 was lower in tumors with high Maspin expression compared to tumors with loss of Maspin expression. Our results indicate that aberrant promoter methylation is associated with loss of Maspin immunoreactivity in breast cancer tissues. Further, loss of Maspin expression is significantly correlated with increased expression of VEGF-A and MTA1.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sheng S, Carey J, Seftor EA, Dias L, Hendrix MJ, Sager R. Maspin acts at the cell membrane to inhibit invasion and motility of mammary and prostatic cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:11669–74.
Liu J, Yin S, Reddy N, Spencer C, Sheng S. Bax mediates the apoptosis-sensitizing effect of maspin. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1703–11.
Jiang N, Meng Y, Zhang S, Mensah-Osman E, Sheng S. Maspin sensitizes breast carcinoma cells to induced apoptosis. Oncogene. 2002;21:4089–98.
Zhang M, Volpert O, Shi YH, Bouck N. Maspin is an angiogenesis inhibitor. Nat Med. 2000;6:196–9.
Domann FE, Rice JC, Hendrix MJ, Futscher BW. Epigenetic silencing of maspin gene expression in human breast cancers. Int J Cancer. 2000;85:805–10.
Maass N, Biallek M, Rosel F, Schem C, Ohike N, Zhang M, et al. Hypermethylation and histone deacetylation lead to silencing of the maspin gene in human breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;297:125–8.
Primeau M, Gagnon J, Momparler RL. Synergistic antineoplastic action of DNA methylation inhibitor 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine and histone deacetylase inhibitor depsipeptide on human breast carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 2003;103:177–84.
Khalkhali-Ellis Z. Maspin: the new frontier. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:7279–83.
Akiyama Y, Maesawa C, Ogasawara S, Terashima M, Masuda T. Cell-type-specific repression of the maspin gene is disrupted frequently by demethylation at the promoter region in gastric intestinal metaplasia and cancer cells. Am J Pathol. 2003;163:1911–9.
Bettstetter M, Woenckhaus M, Wild PJ, Rummele P, Blaszyk H, Hartmann A, et al. Elevated nuclear maspin expression is associated with microsatellite instability and high tumour grade in colorectal cancer. J Pathol. 2005;205:606–14.
Boltze C, Schneider-Stock R, Quednow C, Hinze R, Mawrin C, Hribaschek A, et al. Silencing of the maspin gene by promoter hypermethylation in thyroid cancer. Int J Mol Med. 2003;12:479–84.
Goelz SE, Vogelstein B, Hamilton SR, Feinberg AP. Hypomethylation of DNA from benign and malignant human colon neoplasms. Science. 1985;228:187–90.
Reis-Filho JS, Torio B, Albergaria A, Schmitt FC. Maspin expression in normal skin and usual cutaneous carcinomas. Virchows Arch. 2002;441:551–8.
Rose SL, Fitzgerald MP, White NO, Hitchler MJ, Futscher BW, De Geest K, et al. Epigenetic regulation of maspin expression in human ovarian carcinoma cells. Gynecol Oncol. 2006;102:319–24.
Sato N, Maitra A, Fukushima N, van Heek NT, Matsubayashi H, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, et al. Frequent hypomethylation of multiple genes overexpressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003;63:4158–66.
Bolat F, Gumurdulu D, Erkanli S, Kayaselcuk F, Zeren H, Ali Vardar M, et al. Maspin overexpression correlates with increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factors a, c, and d in human ovarian carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 2008;204:379–87.
Chua R, Setzer S, Govindarajan B, Sexton D, Cohen C, Arbiser JL. Maspin expression, angiogenesis, prognostic parameters, and outcome in malignant melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60:758–66.
Zhang H, Stephens LC, Kumar R. Metastasis tumor antigen family proteins during breast cancer progression and metastasis in a reliable mouse model for human breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:1479–86.
Balasenthil S, Broaddus RR, Kumar R. Expression of metastasis-associated protein 1 (mta1) in benign endometrium and endometrial adenocarcinomas. Hum Pathol. 2006;37:656–61.
Hofer MD, Kuefer R, Varambally S, Li H, Ma J, Shapiro GI, et al. The role of metastasis-associated protein 1 in prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2004;64:825–9.
Kumar R, Wang RA, Mazumdar A, Talukder AH, Mandal M, Yang Z, et al. A naturally occurring mta1 variant sequesters oestrogen receptor-alpha in the cytoplasm. Nature. 2002;418:654–7.
Mazumdar A, Wang RA, Mishra SK, Adam L, Bagheri-Yarmand R, Mandal M, et al. Transcriptional repression of oestrogen receptor by metastasis-associated protein 1 corepressor. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:30–7.
Nicolson GL, Nawa A, Toh Y, Taniguchi S, Nishimori K, Moustafa A. Tumor metastasis-associated human mta1 gene and its mta1 protein product: role in epithelial cancer cell invasion, proliferation and nuclear regulation. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2003;20:19–24.
Lewis CM, Cler LR, Bu DW, Zochbauer-Muller S, Milchgrub S, Naftalis EZ, et al. Promoter hypermethylation in benign breast epithelium in relation to predicted breast cancer risk. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:166–72.
Frommer M, McDonald LE, Millar DS, Collis CM, Watt F, Grigg GW, et al. A genomic sequencing protocol that yields a positive display of 5-methylcytosine residues in individual DNA strands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:1827–31.
Murai S, Maesawa C, Masuda T, Sugiyama T. Aberrant maspin expression in human endometrial cancer. Cancer Sci. 2006;97(9):883–8.
Sharma G, Mirza S, Prasad CP, Srivastava A, Gupta SD, Ralhan R. Promoter hypermethylation of p16ink4a, p14arf, cyclind2 and slit2 in serum and tumor DNA from breast cancer patients. Life Sci. 2007;80:1873–81.
Mohsin SK, Zhang M, Clark GM, Craig Allred D. Maspin expression in invasive breast cancer: association with other prognostic factors. J Pathol. 2003;199:432–5.
Jang KS, Paik SS, Chung H, Oh YH, Kong G. Mta1 overexpression correlates significantly with tumor grade and angiogenesis in human breast cancers. Cancer Sci. 2006;97:374–9.
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Gelber RD, Coates AS, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ. Meeting highlights: updated international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:3357–65.
Ryden L, Stendahl M, Jonsson H, Emdin S, Bengtsson NO, Landberg G. Tumor-specific vegf-a and vegfr2 in postmenopausal breast cancer patients with long-term follow-up. Implication of a link between vegf pathway and tamoxifen response. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2005;89:135–43.
Rhodes A, Jasani B, Anderson E, Dodson AR, Balaton AJ. Evaluation of her-2/neu immunohistochemical assay sensitivity and scoring on formalin-fixed and paraffin-processed cell lines and breast tumors: a comparative study involving results from laboratories in 21 countries. Am J Clin Pathol. 2002;118:408–17.
Fitzgerald M, Oshiro M, Holtan N, Krager K, Cullen JJ, Futscher BW, et al. Human pancreatic carcinoma cells activate maspin expression through loss of epigenetic control. Neoplasia. 2003;5:427–36.
Futscher BW, O'Meara MM, Kim CJ, Rennels MA, Lu D, Gruman LM, et al. Aberrant methylation of the maspin promoter is an early event in human breast cancer. Neoplasia. 2004;6:380–9.
Khalkhali-Ellis Z, Hendrix MJ. Elucidating the function of secreted maspin: inhibiting cathepsin d-mediated matrix degradation. Cancer Res. 2007;67:3535–9.
Cho JH, Kim HS, Park CS, Kim JK, Jung KY, Shin BK, et al. Maspin expression in early oral tongue cancer and its relation to expression of mutant-type p53 and vascular endothelial growth factor (vegf). Oral Oncol. 2007;43:272–7.
Frey A, Soubani AO, Adam AK, Sheng S, Pass HI, Lonardo F. Nuclear, compared with combined nuclear and cytoplasmic expression of maspin, is linked in lung adenocarcinoma to reduced vegf-a levels and in stage i, improved survival. Histopathology. 2009;54:590–7.
Solomon LA, Munkarah AR, Schimp VL, Arabi MH, Morris RT, Nassar H, et al. Maspin expression and localization impact on angiogenesis and prognosis in ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2006;101:385–9.
Song SY, Lee SK, Kim DH, Son HJ, Kim HJ, Lim YJ, et al. Expression of maspin in colon cancers: its relationship with p53 expression and microvessel density. Dig Dis Sci. 2002;47:1831–5.
Terashima M, Maesawa C, Oyama K, Ohtani S, Akiyama Y, Ogasawara S, et al. Gene expression profiles in human gastric cancer: expression of maspin correlates with lymph node metastasis. Br J Cancer. 2005;92:1130–6.
Reddy KB, McGowen R, Schuger L, Visscher D, Sheng S. Maspin expression inversely correlates with breast tumor progression in mmtv/tgf-alpha transgenic mouse model. Oncogene. 2001;20:6538–43.
Shi HY, Zhang W, Liang R, Abraham S, Kittrell FS, Medina D, et al. Blocking tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis by maspin in a syngeneic breast cancer model. Cancer Res. 2001;61:6945–51.
Vecchi M, Confalonieri S, Nuciforo P, Vigano MA, Capra M, Bianchi M, et al. Breast cancer metastases are molecularly distinct from their primary tumors. Oncogene. 2008;27:2148–58.
Sheng S. A role of novel serpin maspin in tumor progression: the divergence revealed through efforts to converge. J Cell Physiol. 2006;209:631–5.
Zhang M. Toward re-expressing tumor suppressor gene maspin in breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 2002;3:353–4.
Zou Z, Gao C, Nagaich AK, Connell T, Saito S, Moul JW, et al. P53 regulates the expression of the tumor suppressor gene maspin. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:6051–4.
Maass N, Hojo T, Ueding M, Luttges J, Kloppel G, Jonat W, et al. Expression of the tumor suppressor gene maspin in human pancreatic cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:812–7.
Maass N, Teffner M, Rosel F, Pawaresch R, Jonat W, Nagasaki K, et al. Decline in the expression of the serine proteinase inhibitor maspin is associated with tumour progression in ductal carcinomas of the breast. J Pathol. 2001;195:321–6.
Xia W, Lau YK, Hu MC, Li L, Johnston DA, Sheng S, et al. High tumoral maspin expression is associated with improved survival of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 2000;19:2398–403.
Ferrucci PF, Rabascio C, Gigli F, Corsini C, Giordano G, Bertolini F, et al. A new comprehensive gene expression panel to study tumor micrometastasis in patients with high-risk breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 2007;30:955–62.
Joensuu KM, Leidenius MH, Andersson LC, Heikkila PS. High expression of maspin is associated with early tumor relapse in breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 2009;40:1143–51.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, G., Mirza, S., Parshad, R. et al. Clinical significance of Maspin promoter methylation and loss of its protein expression in invasive ductal breast carcinoma: correlation with VEGF-A and MTA1 expression. Tumor Biol. 32, 23–32 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-010-0087-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-010-0087-8