Abstract
Background
Thyroid cancer is one of the most common endocrine malignant tumors. The study has found that microRNA-125-5p (miR-125-5p) is regarded as a key regulator of gene expression and involved in cancer cell growth by affecting the miRNA-mediated signal pathway. It is crucial to understand the potential mechanism of miR-125-5p in regulating thyroid tumor cell proliferation and metastasis.
Objective
To investigate biological functions of miR-125-5p in thyroid cancer growth and metastasis and explored potential mechanism mediated by miR-125-5p in thyroid cancer cells.
Methods
Western blot, gene transfection, flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry were used to analyze the regulatory effects of miR-125-5p in thyroid cancer cells.
Result
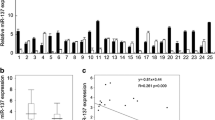
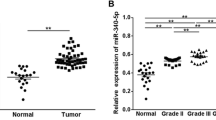
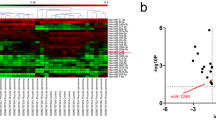
Results observed that miR-125-5p expression was down-regulated in thyroid cancer tissue compared to adjacent normal tissue. miR-125-5p overexpression inhibited thyroid cancer cell growth, migration and invasion. miR-125-5p overexpression arrested thyroid cancer cell cycle at S phase, and significantly induced apoptosis of thyroid cancer cells. miR-125-5p overexpression increased the protein levels of extracellular regulated protein kinase (ERK), phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K) and phosphoinositide dependent kinase (AKT) while it decreased protein expression of phosphorylated ERK, PI3K and AKT in thyroid cancer cells. In vivo assay demonstrated that miR-125-5p transfection inhibited tumor growth and ERK, PI3K and AKT protein expression in tumor tissues.
Conclusion
In summary, these results indicate that miR-125-5p can inhibit thyroid cancer cell growth, migration and invasion through the ERK/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng SP et al (2011) Leptin enhances migration of human papillary thyroid cancer cells through the PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Oncol Rep 26:1265–1271
Feng X, Wang Z, Fillmore R, Xi Y (2014) MiR-200, a new star miRNA in human cancer. Cancer Lett 344:166–173
Fenton MS et al (2010) Sunitinib inhibits MEK/ERK and SAPK/JNK pathways and increases sodium/iodide symporter expression in papillary thyroid cancer. Thyroid 20:965–974
Fu J et al (2013) Metallothionein 1G functions as a tumor suppressor in thyroid cancer through modulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. BMC Cancer 13:462
Furet P et al (2013) Discovery of NVP-BYL719 a potent and selective phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase alpha inhibitor selected for clinical evaluation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23:3741–3748
Greco F et al (2019) The potential role of microRNAs as biomarkers in benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol Focus 5:497–507
Guo F, Hou X, Sun Q (2018) MicroRNA-9-5p functions as a tumor suppressor in papillary thyroid cancer via targeting BRAF. Oncol Lett 16:6815–6821
He B, Yin B, Wang B, Xia Z, Chen C, Tang J (2012) MicroRNAs in esophageal cancer (review). Mol Med Rep 6:459–465
Inoue Y et al (2014) Associations of single nucleotide polymorphisms in precursor-microRNA (miR)-125a and the expression of mature miR-125a with the development and prognosis of autoimmune thyroid diseases. Clin Exp Immunol 178:229–235
Jiang YW, Chen LA (2012) microRNAs as tumor inhibitors, oncogenes, biomarkers for drug efficacy and outcome predictors in lung cancer (review). Mol Med Rep 5:890–894
Jin D, Fang Y, Li Z, Chen Z, Xiang J (2015) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitionassociated microRNAs in colorectal cancer and drug-targeted therapies (review). Oncol Rep 33:515–525
Kong J et al (2016) miR-125/Pokemon auto-circuit contributes to the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol 37:511–519
Kumarasamy C, Devi A, Jayaraj R (2018) Prognostic value of microRNAs in head and neck cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis protocol. Syst Rev 7:150
Kumazaki M et al (2013) Anti-cancer effects of naturally occurring compounds through modulation of signal transduction and miRNA expression in human colon cancer cells. J Nutr Biochem 24:1849–1858
Kunej T et al (2011) Epigenetic regulation of microRNAs in cancer: an integrated review of literature. Mutat Res 717:77–84
Lee HM, Kim TS, Jo EK (2016) MiR-146 and miR-125 in the regulation of innate immunity and inflammation. BMB Rep 49:311–318
Leonardi GC et al (2012) microRNAs and thyroid cancer: biological and clinical significance (review). Int J Mol Med 30:991–999
Li C, Zamore PD (2018) Preparation of antisense oligonucleotides to inhibit miRNA function. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2018:2
Li P, Dong M, Wang Z (2019) Downregulation of TSPAN13 by miR-369-3p inhibits cell proliferation in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC). Bosn J Basic Med Sci 19:146–154
Liu AF, Wang JX, Li FL, Chen YJ (2017) Research progress on miR-125 family in malignant hematologic diseases-review. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 25:1842–1846
Liu F et al (2018) miR-214 regulates papillary thyroid carcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting PSMD10. Int J Mol Med 42:3027–3036
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Ma J et al (2017) HOTAIR regulates HK2 expression by binding endogenous miR-125 and miR-143 in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression. Oncotarget 8:86410–86422
Markovic I et al (2018) Multifocality as independent prognostic factor in papillary thyroid cancer—a multivariate analysis. J BUON 23:1049–1054
Milosevic Z et al (2014) Targeting RAS-MAPK-ERK and PI3K-AKT-mTOR signal transduction pathways to chemosensitize anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. Transl Res 164:411–423
Orlandella FM, Di Maro G, Ugolini C, Basolo F, Salvatore G (2016) TWIST1/miR-584/TUSC2 pathway induces resistance to apoptosis in thyroid cancer cells. Oncotarget 7:70575–70588
Portela RA et al (2015) Unusual sites of metastasis of papillary thyroid cancer: case series and review of the literature. Ear Nose Throat J 94:E43–E47
Rong Y, Zhou M, Cui X, Li W, Chen W (2018) MiRNA-regulated changes in extracellular matrix protein levels associated with a severe decline in lung function induced by silica dust. J Occup Environ Med 60:316–321
Saini S, Tulla K, Maker AV, Burman KD, Prabhakar BS (2018) Therapeutic advances in anaplastic thyroid cancer: a current perspective. Mol Cancer 17:154
Salim H et al (2013) miRNA-214 is related to invasiveness of human non-small cell lung cancer and directly regulates alpha protein kinase 2 expression. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 52:895–911
Shaham L, Binder V, Gefen N, Borkhardt A, Izraeli S (2012) MiR-125 in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Leukemia 26:2011–2018
Shi XB et al (2007) An androgen-regulated miRNA suppresses Bak1 expression and induces androgen-independent growth of prostate cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19983–19988
Suh B et al (2019) Increased cardiovascular risk in thyroid cancer patients taking levothyroxine: a nationwide cohort study in Korea. Eur J Endocrinol 180:11–20
Svoronos AA et al (2016) OncomiR or tumor suppressor? The duplicity of MicroRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res 76:3666–3670
Thomson JM et al (2006) Extensive post-transcriptional regulation of microRNAs and its implications for cancer. Genes Dev 20:2202–2207
Toteda G et al (2017) High doses of hydroxytyrosol induce apoptosis in papillary and follicular thyroid cancer cells. J Endocrinol Invest 40:153–162
Trindade-da-Silva CA et al (2016) 15-Deoxy-Delta(12,14)-prostaglandin J2 induces apoptosis and upregulates SOCS3 in human thyroid cancer cells. PPAR Res 2016:4106297
Tuncer M et al (2014) Metastasis of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer into the thyroid gland: a literature review accompanied by a rare case. Korean J Urol 55:222–225
Valenti MT, Dalle Carbonare L, Mottes M (2018) Role of microRNAs in progenitor cell commitment and osteogenic differentiation in health and disease (review). Int J Mol Med 41:2441–2449
Won JK et al (2012) The crossregulation between ERK and PI3K signaling pathways determines the tumoricidal efficacy of MEK inhibitor. J Mol Cell Biol 4:153–163
Xu J et al (2015) PIG3 plays an oncogenic role in papillary thyroid cancer by activating the PI3K/AKT/PTEN pathway. Oncol Rep 34:1424–1430
Yang J et al (2015) Unusual synchronous skeletal muscle and lung metastasis in papillary thyroid cancer: a case report and review of the literature. Oncol Lett 9:727–730
Yu CY et al (2018) A systematic review and meta-analysis of subsequent malignant neoplasm risk after radioactive iodine treatment of thyroid cancer. Thyroid 28(1662):1673
Zhang Y et al (2009) Clinicopathological significance of microRNA-21 and miR-125 expression in colorectal cancer. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi 12:623–626
Zhang K, Zhang Y, Liu C, Xiong Y, Zhang J (2014) MicroRNAs in the diagnosis and prognosis of breast cancer and their therapeutic potential (review). Int J Oncol 45:950–958
Zhang Y et al (2018) Comparison of miRNA evolution and function in plants and animals. Microrna 7:4–10
Zhu L et al (2016) Thyroid hormone receptor beta1 suppresses proliferation and migration by inhibiting PI3K/Akt signaling in human colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Rep 36:1419–1426
Zhu T et al (2017) A pilot study of circulating microRNA-125b as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer 27:3–10
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RW is responsible for the guarantor of integrity of the entire study, study concepts & design, definition of intellectual content, literature research, experimental studies, data acquisition & analysis, statistical analysis, manuscript preparation & review; CW is responsible for the study concepts & design, experimental studies, data analysis, statistical analysis, manuscript review; XJM and LW are responsible for the clinical studies, data acquisition. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
Rong Wang, Chen Wang, Xian-Jie Meng and Li Wei declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The study was approved by The Third Affiliated Hospital of Medical College of Shihezi University, China (No. 20-198).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Wang, C., Meng, XJ. et al. miR-125-5p inhibits thyroid cancer growth and metastasis by suppressing the ERK/PI3K/AKT signal pathway. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-021-00175-0
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-021-00175-0