Abstract
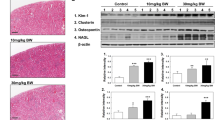
We investigated the proteins showing differential expression in response to TiO2 nanoparticles in mouse kidney using a proteomic approach to better understand the molecular mechanism by which TiO2 nanoparticles-induced nephrotoxicity at the protein level. More than 1,100 protein spots in mouse kidney were detected by the two-dimensional gel eletrophoresis and comparative analysis revealed that the expression of 11 proteins were changed by more than 2 fold in response to TiO2 nanoparticles. Of these, 10 were up-regulated and 1 was down-regulated upon treatment with TiO2 nanoparticles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park, E. J. et al. Oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in cultured BEAS-2B cells. Toxicol Lett 180:222–229 (2008).
Johnston, H. J. et al. Identification of the mechanisms that drive the toxicity of TiO2 particulates: the contribution of physicochemical characteristics. Part Fibre Toxicol 6:33 (2009).
Park, E. J., Yoon, J. H., Choi, K. H., Yi, J. H. & Park, K. S. Induction of chronic inflammation in mice treated with titanium dioxide nanoparticles by intratracheal instillation. Toxicology 260:37–46 (2009).
Kiss, B. et al. Investigation of micronized titanium dioxide penetration in human skin xenografts and its effect on cellular functions of human skin-derived cells. Exp Dermatol 17:659–667 (2008).
Bhattacharya, K. et al. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and DNA-adduct formation but not DNA-breakage in human lung cells. Part Fibre Toxicol 6:17 (2009).
Chen, H. W. et al. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce emphysema-like lung injury in mice. FASEB J 20:2393–2395 (2006).
Liu, H. et al. Biochemical toxicity of nano-anatase TiO2 particles in mice. Biol Trace Elem Res 129:170–180 (2009).
Baggs, R. B., Ferin, J. & Oberdörster, G. Regression of pulmonary lesions produced by inhaled titanium dioxide in rats. Vet Pathol 34:592–597 (1997).
Chen, J., Dong, X., Zhao, J. & Tang, G. In vivo acute toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles to mice after intraperitioneal injection. J Appl Toxicol 29:330–337 (2009).
Xiao, G. G., Wang, M., Li, N., Loo, J. A. & Nel, A. E. Use of proteomics to demonstrate a hierarchical oxidative stress response to diesel exhaust particle chemicals in a macrophage cell line. J Biol Chem 278:50781–50790 (2003).
Blackford, J. A. Jr., Jones, W., Dey, R. D. & Castranova, V. Comparison of inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression and lung inflammation following intratracheal instillation of silica, coal, carbonyl iron, or titanium dioxide in rats. J Toxicol Environ Health 51:203–218 (1997).
Burrows, F., Zhang, H. & Kamal, A. Hsp90 activation and cell cycle regulation. Cell Cycle 3:1530–1536 (2004).
Taiyab, A., Sreedhar, A. S. & Rao, Ch. M. Hsp90 inhibitors, GA and 17AAG, lead to ER stress-induced apoptosis in rat histiocytoma. Biochem Pharmacol 78:142–152 (2009).
Lee, H. N. et al. Reduced formation of advanced glycation endproducts via interactions between glutathione peroxidas 3 and dihydroxyacetone kinase 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 389:177–180 (2009).
Molin, M., Pilon, M. & Blomberg, A. Dihydroxyacetone-induced death is accompanied by advanced glycation endproduct formation in selected proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Caenorhabditis elegans. Proteomics 7:3764–3774 (2007).
Uchida, K. et al. Protein modification by a Maillard reaction intermediate methylglyoxal. Immunochemical detection of fluorescent 5-methylimidazolone derivatives in vivo. FEBS Lett 410:313–318 (1997).
Elsea, S. H. et al. Haploinsufficiency of cytosolic serine hydroxymethyltransferase in the Smith-Magenis syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 57:1342–1350 (1995).
Scheer, J. B., Mackey, A. D. & Gregory J. F. 3rd. Activities of hepatic cytosolic and mitochondrial forms of serine hydroxymethyltransferase and hepatic glycine concentration are affected by vitamin B-6 intake in rats. J Nutr 135:233–238 (2005).
Hawwa, R., Larsen, S. D., Ratia, K. & Mesecar, A. D. Structure-based and random mutagenesis approaches increase the organophosphate-degrading activity of a phosphotriesterase homologue from Deinococcus radiodurans. J Mol Biol 393:36–57 (2009).
Madeira, C., Freitas, M. E., Vargas-Lopes, C., Wolosker, H. & Panizzutti, R. Increased brain D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) activity in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 101:76–83 (2008).
D’Aniello, A. et al. Biological role of D-amino acid oxidase and D-aspartate oxidase. Effects of D-amino acids. J Biol Chem 268:26941–26949 (1993).
Tommerup, N. & Leffers, H. Assignment of the human genes encoding 14,3-3 Eta (YWHAH) to 22q12, 14-3-3 zeta (YWHAZ) to 2p25.1-p25.2, and 14-3-3 beta (YWHAB) to 20q13.1 by in situ hybridization. Genomics 33:149–150 (1996).
Garcia-Guzman, M., Dolfi, F., Russello, M. & Vuori, K. Cell adhesion regulates the interaction between the docking protein p130 (Cas) and the 14-3-3 proteins. J Biol Chem 274:5762–5768 (1999).
Bhakoo, K. K., Craig, T. J. & Styles, P. Developmental and regional distribution of aspartoacylase in rat brain tissue. J Neurochem 79:211–220 (2001).
Delorme, A. C., Danan, J. L. & Mathieu, H. Biochemical evidence for the presence of two vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding proteins in mouse kidney. J Biol Chem 258:1878–1884 (1983).
Durkin, J. P., Brewer, L. M. & MacManus, J. P. Occurrence of the tumor-specific, calcium-binding protein, oncomodulin, in virally transformed normal rat kidney cells. Cancer Res 43:5390–5394 (1983).
Vamanu, C. I. et al. Induction of cell death by TiO2 nanoparticles: studies on a human monoblastoid cell line. Toxicol In Vitro 22:1689–1696 (2008).
Park, S. K., Lee, C. W. & Lee, M. Y. Inhibitory effect of ore minerals on the allergic inflammation in mouse. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 51:269–275 (2008).
Kim, J. J. & Lee, M. Y. Differential expression of cytosolic and nuclear proteins during s-nitrosoglutathione-induced cell death. Biochip J 3:326–332 (2009).
Yamashita, R., Fujiwara, Y., Yuan, X., Yasuda, K. & Kaburagi, Y. 2-D LC-MS/MS analysis of secreted proteins from HepG2 cells: Combination with various sample preparation methods before in-solution trypsin digestion. J Electrophoresis 49:1–4 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, YM., Park, SK., Rhee, SK. et al. Proteomic profiling of the differentially expressed proteins by TiO2 nanoparticles in mouse kidney. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 6, 414–420 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-010-0055-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-010-0055-9