Abstract
Background
Whether obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is causally associated with an increased risk of cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) remains controversial. We conducted a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) study to clarify the causal relationship between OSA and CSVD risk.
Methods
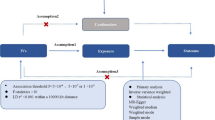
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with OSA at the genome-wide significance level (P < 5 × 10− 8) in the FinnGen consortium were selected as instrumental variables. Summary-level data for white matter hyperintensities (WMHs), lacunar infarctions (LIs), cerebral microbleeds (CMBs), fractional anisotropy (FA), and mean diffusivity (MD) were obtained from three meta-analyses of genome-wide association studies (GWASs). The random-effects inverse-variance weighted (IVW) method was selected for the major analysis. Weighted-median, MR-Egger, MR pleiotropy residual sum and outlier (MR-PRESSO), and leave-one-out analysis methods were implemented for the sensitivity analyses.
Results
Genetically predicted OSA was not associated with LIs (odds ratio [OR] = 1.10, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.86–1.40), WMHs (OR = 0.94, 95% CI = 0.83–1.07), FA (OR = 1.33, 95% CI = 0.75–2.33), MD (OR = 0.93, 95% CI = 0.58–1.47), CMBs (OR = 1.29, 95% CI = 0.86–1.94), mixed CMBs (OR = 1.17, 95% CI = 0.63–2.17), and lobar CMBs (OR = 1.15, 95% CI = 0.75–1.76) in IVW method. The results of the sensitivity analyses were generally consistent with the major analyses.
Conclusions
This MR study does not support causal associations between OSA and the risk of CSVD in individuals of European ancestry. These findings need to be further validated in randomized controlled trials, larger cohort studies, and MR studies based on larger GWASs.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Summary-level data for lacunar stroke are publicly available (PMID: 33773637, https://cd.hugeamp.org/); Summary-level data for white matter hyperintensities, fractional anisotropy, and mean diffusivity are publicly available (PMID: 32358547, https://cd.hugeamp.org/); Summary-level data for cerebral microbleeds are publicly available (PMID: 32913026, https://cd.hugeamp.org/); FinnGen consortium data are available through application (https://r8.finngen.fi/).
References
Akoudad S, Wolters FJ, Viswanathan A et al (2016) Association of Cerebral Microbleeds with Cognitive decline and Dementia. JAMA Neurol 73:934–943
Alvarez-Sabín J, Romero O, Delgado P et al (2018) Obstructive sleep apnea and silent cerebral infarction in hypertensive individuals. J Sleep Res 27:232–239
Birnefeld J, Wåhlin A, Eklund A et al (2020) Cerebral arterial pulsatility is associated with features of small vessel disease in patients with acute stroke and TIA: a 4D flow MRI study. J Neurol 267:721–730
Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Burgess S (2015) Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol 44:512–525
Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Haycock PC et al (2016) Consistent estimation in mendelian randomization with some Invalid Instruments using a weighted median estimator. Genet Epidemiol 40:304–314
Burgess S, Thompson SG (2015) Mendelian randomization: methods for using genetic variants in causal estimation. CRC Press
Burgess S, Davies NM, Thompson SG (2016) Bias due to participant overlap in two-sample mendelian randomization. Genet Epidemiol 40:597–608
Burgess S, Bowden J, Fall T et al (2017) Sensitivity analyses for robust causal inference from mendelian randomization analyses with multiple genetic variants. Epidemiology 28:30–42
Cai M, Jacob MA, van Loenen MR et al (2022) Determinants and temporal Dynamics of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: 14-Year Follow-Up. Stroke 53:2789–2798
Castronovo V, Scifo P, Castellano A et al (2014) White matter integrity in obstructive sleep apnea before and after treatment. Sleep 37:1465–1475
Chen HL, Lu CH, Lin HC et al (2015) White matter damage and systemic inflammation in obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 38:361–370
Chen X, Wang J, Shan Y et al (2019) Cerebral small vessel disease: neuroimaging markers and clinical implication. J Neurol 266:2347–2362
Cho ER, Kim H, Seo HS et al (2013) Obstructive sleep apnea as a risk factor for silent cerebral infarction. J Sleep Res 22:452–458
Choi KM, Thomas RJ, Yoon DW et al (2016) Interaction between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and shortened telomere length on Brain White Matter Abnormality. Sleep 39:1639–1645
Croall ID, Tozer DJ, Moynihan B et al (2018) Effect of Standard vs intensive blood pressure control on cerebral blood Flow in Small Vessel Disease: the PRESERVE Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol 75:720–727
De Silva TM, Faraci FM (2020) Contributions of aging to Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Annu Rev Physiol 82:275–295
Del Brutto OH, Mera RM, Zambrano M et al (2017) Relationship between obstructive sleep apnea and neuroimaging signatures of cerebral small vessel disease in community-dwelling older adults. The Atahualpa Project Sleep Med 37:10–12
Edwards BA, Wellman A, Sands SA et al (2014) Obstructive sleep apnea in older adults is a distinctly different physiological phenotype. Sleep 37:1227–1236
Gottlieb DJ, Punjabi NM (2020) Diagnosis and management of obstructive sleep apnea: a review. JAMA 323:1389–1400
Kepplinger J, Barlinn K, Boehme AK et al (2014) Association of sleep apnea with clinically silent microvascular brain tissue changes in acute cerebral ischemia. J Neurol 261:343–349
Knol MJ, Lu D, Traylor M et al (2020) Association of common genetic variants with brain microbleeds: a genome-wide association study. Neurology 95:e3331–e3343
Koo DL, Kim JY, Lim JS et al (2017) Cerebral microbleeds on MRI in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. J Clin Sleep Med 13:65–72
Kumar R, Chavez AS, Macey PM et al (2012) Altered global and regional brain mean diffusivity in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. J Neurosci Res 90:2043–2052
Lee WJ, Jung KH, Nam HW et al (2021) Effect of obstructive sleep apnea on cerebrovascular compliance and cerebral small vessel disease. PLoS ONE 16:e0259469
Li HQ, Feng YW, Yang YX et al (2022) Causal relations between Exposome and Stroke: a mendelian randomization study. J Stroke 24:236–244
Liu X, Lam DC, Mak HK et al (2022) Associations of sleep apnea risk and oxygen desaturation indices with cerebral small vessel disease burden in patients with stroke. Front Neurol 13:956208
Lutsey PL, Norby FL, Gottesman RF et al (2016) Sleep apnea, sleep duration and brain MRI markers of cerebral vascular disease and Alzheimer’s Disease: the atherosclerosis risk in Communities Study (ARIC). PLoS ONE 11:e0158758
Macey PM, Kumar R, Woo MA et al (2008) Brain structural changes in obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 31:967–977
Macey PM, Kumar R, Yan-Go FL et al (2012) Sex differences in white matter alterations accompanying obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 35:1603–1613
Nasrallah IM, Pajewski NM, Auchus AP et al (2019) Association of Intensive vs Standard blood pressure control with cerebral White Matter Lesions. JAMA 322:524–534
Pasi M, van Uden IW, Tuladhar AM et al (2016) White Matter Microstructural damage on Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: clinical consequences. Stroke 47:1679–1684
Persyn E, Hanscombe KB, Howson JMM et al (2020) Genome-wide association study of MRI markers of cerebral small vessel disease in 42,310 participants. Nat Commun 11:2175
Petrea RE, O’Donnell A, Beiser AS et al (2020) Mid to Late Life Hypertension Trends and Cerebral Small Vessel Disease in the Framingham Heart Study. Hypertension 76:707–714
Schammel NC, VandeWater T, Self S et al (2022) Obstructive sleep apnea and white matter hyperintensities: correlation or causation? Brain Imaging Behav 16:1671–1683
Song TJ, Park JH, Choi KH et al (2017) Moderate-to-severe obstructive sleep apnea is associated with cerebral small vessel disease. Sleep Med 30:36–42
Taylor-Bateman V, Gill D, Georgakis M et al (2021) Cardiovascular Risk factors and MRI markers of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: a mendelian randomization study. Neurology
Traylor M, Persyn E, Tomppo L et al (2021) Genetic basis of lacunar stroke: a pooled analysis of individual patient data and genome-wide association studies. Lancet Neurol 20:351–361
van Middelaar T, Argillander TE, Schreuder F et al (2018) Effect of Antihypertensive Medication on Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Stroke 49:1531–1533
Verbanck M, Chen CY, Neale B et al (2018) Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet 50:693–698
Yamashiro K, Tanaka R, Tanaka Y et al (2014) Visceral fat accumulation is associated with cerebral small vessel disease. Eur J Neurol 21:667–673
Young T, Peppard PE, Gottlieb DJ (2002) Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: a population health perspective. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165:1217–1239
Zacharias HU, Weihs A, Habes M et al (2021) Association between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Brain White Matter Hyperintensities in a Population-Based cohort in Germany. JAMA Netw Open 4:e2128225
Zhang DD, Cao Y, Mu JY et al (2022) Inflammatory biomarkers and cerebral small vessel disease: a community-based cohort study. Stroke Vasc Neurol 7:302–309
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge all participants and investigators for sharing genome-wide association studies (GWASs) summary-level data.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BW, FL, and GYS contributed to the study conception and design. BW, FL, and SW contributed to data acquisition and analysis. BW drafted the manuscript. BW and SW have revised the manuscript. All authors approved the current version of the manuscript for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, B., Liu, F., Sun, G. et al. Correlation between obstructive sleep apnea and cerebral small vessel disease: a mendelian randomization study. Genes Genom 45, 1179–1186 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-023-01402-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-023-01402-9