Abstract
Background
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most commonly diagnosed malignant tumor and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. As a novel non-coding RNA, LINC00657 was firstly identified as an oncogenic role in breast cancer. However, few research focus on the effect of LINC00657 on the progression of HCC.
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of LINC00657 on HCC tissues and cells, and further explore the potential mechanism.
Methods
We first measured the expression of LINC00657 in HCC tissues and cell lines using qRT-PCR. Next we established LINC00657 knockdown in HCC cells. CCK-8 assay, cell invasion assay, flow cytometry analysis, qRT-PCR and western blotting were applied to assess the role of LINC00657 knockdown in the biological behavior of HCC cells. The bioinformatics analysis and the rescue experiment were devoted to the underlying mechanism.
Results
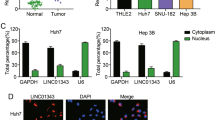
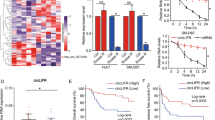
LINC00657 was remarkably overexpressed in HCC tissues and cell lines, associated with poor prognosis. LINC00657 knockdown repressed cell proliferation and invasion, promoted cell apoptosis of HCC cell lines. The bioinformatics analysis showed LINC00657 sponged miR-424 as a ceRNA. Besides, PD-L1 mimic rescued the suppression of si-LINC00657 in the biological behavior of HCC cells.
Conclusion
In a word, we observed LINC00657 regulated PD-L1 expression by sponging miR-424, thus affecting the developments of hepatocellular carcinoma. These findings LINC00657 may provide new evidence for therapeutic application in hepatocellular carcinoma.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424
Chen S, Wang RX, Liu Y, Yang WT, Shao ZM (2017) PD-L1 expression of the residual tumor serves as a prognostic marker in local advanced breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Int J Cancer 140:1384–1395
Chu L, Yu L, Liu J, Song S, Yang H, Han F, Liu F, Hu Y (2019) Long intergenic non-coding LINC00657 regulates tumorigenesis of glioblastoma by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-190a-3p. Aging (Albany NY) 11:1456–1470
Fang Y, Liang X, Xu J, Cai X (2018) miR-424 targets AKT3 and PSAT1 and has a tumor-suppressive role in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag Res 10:6537–6547
Feng RM, Zong YN, Cao SM, Xu RH (2019) Current cancer situation in China: good or bad news from the 2018 Global Cancer Statistics? Cancer Commun (Lond) 39:22
Gutschner T, Diederichs S (2012) The hallmarks of cancer: a long non-coding RNA point of view. RNA Biol 9:703–719
He L, Hannon GJ (2004) MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 5:522–531
Jin C, Li M, Ouyang Y, Tan Z, Jiang Y (2017) MiR-424 functions as a tumor suppressor in glioma cells and is down-regulated by DNA methylation. J Neurooncol 133:247–255
Koirala P, Roth ME, Gill J, Piperdi S, Chinai JM, Geller DS, Hoang BH, Park A, Fremed MA, Zang X et al (2016) Immune infiltration and PD-L1 expression in the tumor microenvironment are prognostic in osteosarcoma. Sci Rep 6:30093
Kung JT, Colognori D, Lee JT (2013) Long noncoding RNAs: past, present, and future. Genetics 193:651–669
Lei Y, Wang YH, Wang XF, Bai J (2018) LINC00657 promotes the development of colon cancer by activating PI3K/AKT pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:6315–6323
Munn DH, Bronte V (2016) Immune suppressive mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment. Curr Opin Immunol 39:1–6
Peng W, Fan H (2016) Long noncoding RNA CCHE1 indicates a poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes carcinogenesis via activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 83:450–455
Ponting CP, Oliver PL, Reik W (2009) Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 136:629–641
Rafiee A, Riazi-Rad F, Havaskary M, Nuri F (2018) Long noncoding RNAs: regulation, function and cancer. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev 34:153–180
Sia D, Villanueva A, Friedman SL, Llovet JM (2017) Liver cancer cell of origin, molecular class, and effects on patient prognosis. Gastroenterology 152:745–761
Sun W, Yang Y, Xu C, Guo J (2017) Regulatory mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs on gene expression in cancers. Cancer Genet 216–217:105–110
Tatli Dogan H, Kiran M, Bilgin B, Kilicarslan A, Sendur MAN, Yalcin B, Ardicoglu A, Atmaca AF, Gumuskaya B (2018) Prognostic significance of the programmed death ligand 1 expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and correlation with the tumor microenvironment and hypoxia-inducible factor expression. Diagn Pathol 13:60
Tay Y, Rinn J, Pandolfi PP (2014) The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 505:344–352
Tovoli F, Negrini G, Benevento F, Faggiano C, Goio E, Granito A (2018) Systemic treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma: challenges and future perspectives. Hepat Oncol 5:HEP01
Wang YG, Wang T, Shi M, Zhai B (2019) Long noncoding RNA EPB41L4A-AS2 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma development by sponging miR-301a-5p and targeting FOXL1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:153
Wu X, Ruan Y, Jiang H, Xu C (2017) MicroRNA-424 inhibits cell migration, invasion, and epithelial mesenchymal transition by downregulating doublecortin-like kinase 1 in ovarian clear cell carcinoma. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 85:66–74
Yu WB, Rao A, Vu V, Xu L, Rao JY, Wu JX (2017) Management of centrally located hepatocellular carcinoma: update 2016. World J Hepatol 9:627–634
Zhang R, Niu Z, Pei H, Peng Z (2020) Long noncoding RNA LINC00657 induced by SP1 contributes to the non-small cell lung cancer progression through targeting miR-26b-5p/COMMD8 axis. J Cell Physiol 235:3340–3349
Zhao X, Liu Y, Yu S (2017) Long noncoding RNA AWPPH promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through YBX1 and serves as a prognostic biomarker. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1863:1805–1816
Zhu RX, Seto WK, Lai CL, Yuen MF (2016) Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Asia-Pacific Region. Gut Liver 10:332–339
Acknowledgement
In compliance with the ethics committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, all patients provided written consent for the use of their tissues in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TT designed experiments; XLC, GPZ and TL performed experiments; CGZ and LB analyzed the data; JMZ wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Xinling Cao, Guanping Zhang, Tao Li, Chengming Zhou, Lei Bai, Jinming Zhao and Turgunjan Tursun declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, X., Zhang, G., Li, T. et al. LINC00657 knockdown suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by sponging miR-424 to regulate PD-L1 expression. Genes Genom 42, 1361–1368 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-020-01001-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-020-01001-y