Abstract
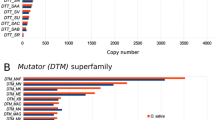
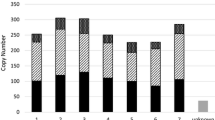
Sequence comparisons of ammonium transporter 1–2 genes (OsAMT1-2) in different rice accessions revealed a MITE insertion in the upstream region of the gene. The 391-bp MITE, classified as a Mutator superfamily member and named Imcrop, included terminal inverted repeat (TIR) and 9-bp target site duplication (TSD) sequences. We identified 151 Imcrop elements dispersed on 12 chromosomes of the japonica reference genome. Of these, 12.6% were found in genic regions and 33.1% were located within 1.5 kb of annotated rice genes. We constructed comparative insertion maps with 111 and 102 intact Imcrop elements in the japonica and indica reference genomes, respectively. The Imcrop elements showed relatively even distribution across all chromosomes although their frequency was higher on chromosomes 1, 3, and 4 in both genomes. Seventy seven Imcrop elements were detected in both subspecies, whereas 34 and 25 insertions were found only in the japonica or indica genome, respectively. We compared insertion polymorphisms of 19 Imcrop elements found inside genes in 48 Korean rice cultivars, consisting of 42 japonica and six Tongil-types (indica-japonica cross). Thirteen insertions were common to all cultivars indicating these elements were present before indica-japonica divergence. The six other elements showed insertion polymorphisms among accessions, showing their recent insertion history or no critical positive effect of their insertion on the rice genome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bureau TE and Wessler SR (1992) Tourist — a large family of small inverted repeat elements frequently associated with maize genes. Plant Cell 4:1283–1294.
Casacuberta JM and Santiago N (2003) Plant LTR-retrotransposons and MITEs: Control of transposition and impact on the evolution of plant genes and genomes. Gene 311:1–11.
El Amrani A, Marie L, Ainouche A, Nicolas J, and Couee I (2002) Genome-wide distribution and potential regulatory functions of AtATE, a novel family of miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Genet. Genomics 267:459–471.
Feschotte C, Jiang N, and Wessler SR (2002) Plant transposable elements: Where genetics meets genomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 3:329–341.
Feschotte C, Swamy L, and Wessler SR (2003) Genome-wide analysis of mariner-like transposable elements in rice reveals complex relationships with Stowaway miniature inverted repeat transposable elements (MITEs). Genetics 163:747–758.
Gonzalez J and Petrov D (2009) MITEs — the ultimate parasites. Science 325:1352–1353.
Guillet-Claude C, Birolleau-Touchard C, Manicacci D, Rogowsky PM, Rigau J, Murigneux A, Martinant JP, and Barriere Y (2004) Nucleotide diversity of the ZmPox3 maize peroxidase gene: Relationships between a MITE insertion in exon 2 and variation in forage maize digestibility. BMC Genet. 5:19.
Huang J, Zhang K, Shen Y, Huang Z, Li M, Tang D, Gu M, and Cheng Z (2009) Identification of a high frequency transposon induced by tissue culture, nDaiZ, a member of the hAT family in rice. Genomics 93:274–281.
IRGSP (2005) The map-based sequence of the rice genome. Nature 436:793–800.
Jiang N, Bao ZR, Zhang XY, Hirochika H, Eddy SR, McCouch SR, and Wessler SR (2003) An active DNA transposon family in rice. Nature 421:163–167.
Jiang N, Feschotte C, Zhang XY, and Wessler SR (2004) Using rice to understand the origin and amplification of miniature inverted repeat transposable elements (MITEs). Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 7:115–119.
Juretic N, Bureau TE, and Bruskiewich RM (2004) Transposable element annotation of the rice genome. Bioinformatics 20:155–160.
Kapitonov VV and Jurka J (2007) Helitrons on a roll: Eukaryotic rolling-circle transposons. Trends Genet. 23:521–529.
Kapitonov VV and Jurka J (2006) Self-synthesizing DNA transposons in eukaryotes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:4540–4545.
Karki S, Tsukiyama T, Okumoto Y, Rizal G, Naito K, Teraishi M, Nakazaki T, and Tanisaka T (2009) Analysis of distribution and proliferation of mPing family transposons in a wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Breeding Sci. 59:297–307.
Kikuchi K, Terauchi K, Wada M, and Hirano HY (2003) The plant MITE mPing is mobilized in anther culture. Nature 421:167–170.
Kimura S, Oyanagi M, Fukuda T, Ohno Y, Hongo C, Itoh Y, Koda T, and Ozeki Y (2008) Role of miniature inverted repeat trans posable elements inserted into the promoter region of a carrot phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene and its gene expression. Plant Biotech. 25:473–481.
Kohany O, Gentles AJ, Hankus L, and Jurka J (2006) Annotation, submission and screening of repetitive elements in Repbase: RepbaseSubmitter and Censor. BMC Bioinformatics 7:474.
Kuang HH, Padmanabhan C, Li F, Kamei A, Bhaskar PB, Shu OY, Jiang JM, Buell CR, and Baker B (2009) Identification of miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements (MITEs) and biogenesis of their siRNAs in the Solanaceae: New functional implications for MITEs. Genome Res. 19:42–56.
Kwon SJ, Kim DH, Lim MH, Long Y, Meng JL, Lim KB, Kim JA, Kim JS, Jin M, Kim HI, et al. (2007) Terminal repeat retrotransposon in miniature (TRIM) as DNA markers in Brassica relatives. Mol. Genet. Genomics 278:361–370.
Lisch D and Jiang N (2009) Muataor and MULE transposons. Maize Handbook 2:277–306.
Lyons M, Cardle L, Rostoks N, Waugh R, and Flavell A (2008) Isolation, analysis and marker utility of novel miniature inverted repeat transposable elements from the barley genome. Mol. Genet. Genomics 280:275–285.
Murray MG and Thopson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular-weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 8:4321–4325.
McClintock B (1951) Chromosome organization and genic expression. Cold Spring Harbour Sym. Quant. Biol. 16:13–47.
Moon S, Jung KH, Lee D, Jiang WZ, Koh HJ, Heu MH, Lee DS, Suh HS, and An G (2006) Identification of active transposon dTok, a member of the hAT family, in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 47:1473–1483.
Nakazaki T, Okumoto Y, Horibata A, Yamahira S, Teraishi M, Nishida H, Inoue H, and Tanisaka T (2003) Mobilization of a transposon in the rice genome. Nature 421:170–172.
Oki N, Yano K, Okumoto Y, Tsukiyama T, Teraishi M, and Tanisaka T (2008) A genome-wide view of miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements (MITEs) in rice, Oryza sativa ssp. japonica. Genes Genet. Syst. 83:321–329.
Ouyang S and Buell CR (2004) The TIGR Plant Repeat Databases: a collective resource for the identification of repetitive sequences in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:D360–3.
Santiago N, Herraiz C, Goni JR, Messeguer X, and Casacuberta JM (2002) Genome-wide analysis of the Emigrant family of MITEs of Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Biol. Evol. 19:2285–2293.
Turcotte K, Srinivasan S, and Bureau T (2001) Survey of transposable elements from rice genomic sequences. Plant J. 25:169–179.
Wessler SR, Bureau TE, and White SE (1995) LTR-retrotransposons and MITEs: important players in the evolution of plant genomes. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 5:814–821.
Wicker T, Sabot F, Hua-Van A, Bennetzen JL, Capy P, Chalhoub B, Flavell A, Leroy P, Morgante M, Panaud O, et al. (2007) A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements. Nat. Rev. Genet. 8:973–982.
Yang G and Hall TC (2003) MDM-1 and MDM-2: Two Mutator-derived MITE families in rice. J. Mol. Evol. 56:255–264.
Yang G, Lee YH, Jiang YM, Shi XY, Kertbundit S, and Hall TC (2005) A two-edged role for the transposable element Kiddo in the rice ubiquitin2 promoter. Plant Cell 17:1559–1568.
Yang G, Nagel DH, Feschotte C, Hancock CN, and Wessler SR (2009) Tuned for transposition: Molecular determinants underlying the hyperactivity of a Stowaway MITE. Science 325:1391–1394.
Yang TJ, Kwon SJ, Choi BS, Kim JS, Jin M, Lim KB, Park JY, Kim JA, Lim MH, Kim HI, et al. (2007) Characterization of terminal-repeat retrotransposon in miniature (TRIM) in Brassica relatives. Theor. Appl. Genet. 114:627–636.
Yu J, Hu S, Wang J, Wong GK, Li S, Liu B, Deng Y, Dai L, Zhou Y, Zhang X, et al. (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica). Science 296:79–92.
Zhang XY, Jiang N, Feschotte C, and Wessler SR (2004) PIF- and Pong-like transposable elements: Distribution, evolution and relationship with Tourist-like miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements. Genetics 166:971–986.
Zuker M. (2003) Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 31(13):3406–3415.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mo, YJ., Kim, KY., Shin, WC. et al. Characterization of Imcrop, a Mutator-like MITE family in the rice genome. Genes Genom 34, 189–198 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-011-0193-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-011-0193-z