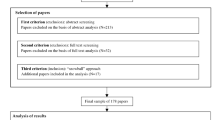
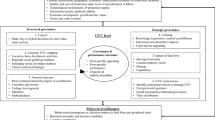
Abstract
Remanufacturing is an essential close loop cycle of the circular economy, and it supports the effective transformation of linear into circular economy. Some factors are critical to adopt remanufacturing practices to move a step ahead in direction circular economy. Therefore, the main aim of the present research is to explore and evaluate these critical success factors (CSFs) of the remanufacturing practices adoption to shift towards circular economy. Initially, thirteen CSFs of adoption of remanufacturing practices are identified using two-step process of literature survey and expert’s opinion. These finalised CSFs are contextually modelled using the Interpretive Structural Modelling (ISM). Further, MICMAC analysis is performed to categorise these CSFs according to their driving and dependence power. Results of present study reveals that the most significant CSFs are ‘subsidies and tax reduction’, ‘top management involvement’ and ‘financial support for technological research’. These CSFs are required more attention to adopt remanufacturing practices to shift towards circular economy. The findings of this research might help the management and policy planner to formulate the strategies for effective adoption of remanufacturing practices in their organisation.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Govindan K, Hasanagic M (2018) A systematic review on drivers, barriers, and practices towards circular economy: a supply chain perspective. Int J Prod Res 56(1-2):278–311. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2017.1402141
Ghisellini P, Cialani C, Ulgiati S (2016) A review on circular economy: the expected transition to a balanced interplay of environmental and economic systems. J Clean Prod 114:11–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.09.007
Haleem A, Khan S, Luthra S, Varshney H, Alam M, Khan M (2021) Supplier evaluation in the context of circular economy: A forward step for resilient business and environment concern. Bus Strateg Environ 30(4):2119–2146. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2736
Okorie O, Obi M, Russell J, Charnley F, Salonitis K (2021) A triple bottom line examination of product cannibalisation and remanufacturing: A review and research agenda. Sustain Prod Consum 27:958–974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.02.013
Franklin-Johnson E, Figge F, Canning L (2016) Resource duration as a managerial indicator for circular economy performance. J Clean Prod 133:589–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.023
MacArthur E (2015) Towards a Circular Economy: Business Rationale for an Accelerated Transition. https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/assets/downloads/TCE_Ellen-MacArthur-Foundation_9-Dec-2015.pdf. Accessed 25 Oct 2019
Alamerew Y, Brissaud D (2019) Correction to: circular economy assessment tool for end-of-life product recovery strategies. J Remanuf 9(3):187–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13243-019-00069-4
Xia X, Govindan K, Zhu Q (2015) Analyzing internal barriers for automotive parts remanufacturers in China using grey-DEMATEL approach. J Clean Prod 87:811–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.09.044
Pamminger R, Glaser S, Wimmer W (2021) Modelling of different circular end-of-use scenarios for smartphones. Int J Life Cycle Assess 26(3):470–482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11367-021-01869-2
Wei S, Tang O, Sundin E (2015) Core (product) acquisition management for remanufacturing: a review. J Remanuf 5(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13243-015-0014-7
Li Y, Kannan D, Garg K, Gupta S, Gandhi K, Jha P (2018) Business orientation policy and process analysis evaluation for establishing third party providers of reverse logistics services. J Clean Prod 182:1033–1047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.241
Su B, Heshmati A, Geng Y, Yu X (2013) A review of the circular economy in China: moving from rhetoric to implementation. J Clean Prod 42:215–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.11.020
Geng Y, Zhu Q, Doberstein B, Fujita T (2009) Implementing China’s circular economy concept at the regional level: A review of progress in Dalian, China. Waste Manag 29(2):996–1002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2008.06.036
Lewandowski M (2016) Designing the business models for circular economy—towards the conceptual framework. Sustainability 8(1):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8010043
Khan S, Haleem A (2020) Strategies to implement circular economy practices: A fuzzy DEMATEL approach. J Ind Integr Manag 05(02):253–269. https://doi.org/10.1142/s2424862220500050
Mangla S, Luthra S, Mishra N, Singh A, Rana N, Dora M, Dwivedi Y (2018) Barriers to effective circular supply chain management in a developing country context. Prod Plan Control 29(6):551–569. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2018.1449265
Mestre A, Cooper T (2017) Circular product design. A multiple loops life cycle design approach for the circular economy. Des J 20(sup1):S1620–S1635. https://doi.org/10.1080/14606925.2017.1352686
Singhal D, Tripathy S, Jena S (2019) Acceptance of remanufactured products in the circular economy: an empirical study in India. Manag Decis 57(4):953–970
Fofou R, Jiang Z, Wang Y (2021) A review on the lifecycle strategies enhancing remanufacturing. Appl Sci 11(13):5937
Fedotkina O, Gorbashko E, Vatolkina N (2019) Circular economy in Russia: drivers and barriers for waste management development. Sustainability 11(20):5837. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205837
Zhang A, Venkatesh V, Liu Y, Wan M, Qu T, Huisingh D (2019) Barriers to smart waste management for a circular economy in China. J Clean Prod 240:118198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118198
Khan S, Haleem A (2021) Investigation of circular economy practices in the context of emerging economies: a CoCoSo approach. Int J Sustain Eng 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1080/19397038.2020.1871442
Hazen B, Mollenkopf D, Wang Y (2016) Remanufacturing for the circular economy: an examination of consumer switching behavior. Bus Strateg Environ 26(4):451–464
Khan S, Maqbool A, Haleem A, Khan M (2020) Analyzing critical success factors for a successful transition towards circular economy through DANP approach. Manag Environ Qual: Int J 31(3):505–529. https://doi.org/10.1108/meq-09-2019-0191
Matsumoto M, Chinen K, Jamaludin K, Yusoff B (2020) Barriers for remanufacturing business in Southeast Asia: the role of governments in circular economy. Sustain Prod Life Cycle Eng Manag:151–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6779-7_11
Shao J, Huang S, Lemus-Aguilar I, Ünal E (2019) Circular business models generation for automobile remanufacturing industry in China. J Manuf Technol Manag 31(3):542–571. https://doi.org/10.1108/jmtm-02-2019-0076
Haleem A, Sushil Q, M. A., & Kumar, S. (2012) Analysis of critical success factors of world class manufacturing practices: an application of interpretative structural modelling and interpretive ranking process. Prod Plan Control 23(10-11):722–734. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2011.642134
Khan S, Haleem A, Khan M, Abidi M, Al-Ahmari A (2018a) Implementing traceability Systems in Specific Supply Chain Management (SCM) through critical success factors (CSFs). Sustainability 10(2):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10010204
Sharma V, Garg S, Sharma P (2016) Identification of major drivers and roadblocks for remanufacturing in India. J Clean Prod 112:1882–1892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.11.082
Zhang T, Chu J, Wang X, Liu X, Cui P (2011) Development pattern and enhancing system of automotive components remanufacturing industry in China. Resour Conserv Recycl 55(6):613–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2010.09.015
Haleem A, Khan S, Pundir H, Jain A, Upadhyay P, Khan M (2020) Investigating barriers toward the implementation of circular economy: A fuzzy CRITIC approach. J Ind Integr Manag 06(01):107–139. https://doi.org/10.1142/s2424862220500177
Vasanthakumar C, Vinodh S, Ramesh K (2016a) Application of interpretive structural modelling for analysis of factors influencing lean remanufacturing practices. Int J Prod Res 54(24):7439–7452. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2016.1192300
Mukherjee K, Mondal S (2009) Analysis of issues relating to remanufacturing technology – a case of an Indian company. Tech Anal Strat Manag 21(5):639–652. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537320902969174
Ansari Z, Kant R, Shankar R (2019) Prioritizing the performance outcomes due to adoption of critical success factors of supply chain remanufacturing. J Clean Prod 212:779–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.038
Subramoniam R, Huisingh D, Chinnam R, Subramoniam S (2013) Remanufacturing decision-making framework (RDMF): research validation using the analytical hierarchical process. J Clean Prod 40:212–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.09.004
Xu B, Shi P, Liu B, Zhou X (2012) Engineering management problems of remanufacturing industry. China Surf Eng 25(6):107–111
Gaspari L, Colucci L, Butzer S, Colledani M, Steinhilper R (2017) Modularization in material flow simulation for managing production releases in remanufacturing. J Remanuf 7(2-3):139–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13243-017-0037-3
Xu B (2010) Remanufacture engineering and its development in China. China Surf Eng 23:1–6 (in Chinese)
Kumar A, Dixit G (2018) An analysis of barriers affecting the implementation of e-waste management practices in India: A novel ISM-DEMATEL approach. Sustain Prod Consum 14:36–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2018.01.002
San-Francisco A, Sopelana N, Fernandez J, Otegi J, Minguez R (2020) Analysis about the incorporation of remanufacturing concept into life cycle assessment theories. J Remanuf 10(2):127–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13243-019-00078-3
Gao L (2012) Three drag of remanufacturing industry. Chinese National Conditions and Strength, p 13 (in Chinese)
Kapetanopoulou P, Tagaras G (2011) Drivers and obstacles of product recovery activities in the Greek industry. Int J Oper Prod Manag 31(2):148–166. https://doi.org/10.1108/01443571111104746
Warfield J (1974) Developing interconnection matrices in structural modeling. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern SMC-4(1):81–87. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsmc.1974.5408524
Sushil (2012) Interpreting the interpretive structural model. Glob J Flex Syst Manag 13(2):87–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40171-012-0008-3
Sushil (2016) How to check correctness of total interpretive structural models? Ann Oper Res 270(1-2):473–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-016-2312-3
Ansari M, Kharb R, Luthra S, Shimmi S, Chatterji S (2013) Analysis of barriers to implement solar power installations in India using interpretive structural modeling technique. Renew Sust Energ Rev 27:163–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.07.002
Shuaib M, Khan U, Haleem A (2016) Modelling knowledge sharing factors and understanding its linkage to competitiveness. Int J Glob Bus Compet 11(1):23–36
Mannan B, Khurana S, Haleem A (2016) Modeling of critical factors for integrating sustainability with innovation for Indian small- and medium-scale manufacturing enterprises: an ISM and MICMAC approach. Cogent Bus Manag 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2016.1140318
Sushil (2017) Multi-criteria valuation of flexibility initiatives using integrated TISM – IRP with a big data framework. Prod Plan Control 28(11-12):999–1010. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2017.1336794
Mukherjee K, Mondal S, Chakraborty K (2017) Impact of various issues on extending the useful life of a product through product recovery options. J Remanuf 7(1):77–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13243-017-0034-6
Haleem A, Imran Khan M, Khan S, Hafaz Ngah A (2018) Assessing barriers to adopting and implementing halal practices in logistics operations. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng 404:012012. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/404/1/012012
Duperrin JC, Godet M (1973) Methode de hierarchisation des elements d’un systeme. Rapport Economique du CEA. Paris, pp. 45–51
Khan S, Fatma N, Khan MI, Haleem A (2022) Modelling of barriers towards the adoption of strategic entrepreneurship: an Indian context. In: Contextual Strategic Entrepreneurship (pp 35–55). Springer, Cham
Khan M, Khan S, Haleem A (2019) Using integrated weighted IRP-fuzzy TISM approach towards evaluation of initiatives to harmonise halal standards. Benchmarking: Int J 26(2):434–451. https://doi.org/10.1108/bij-04-2018-0086
Qureshi M, Kumar D, Kumar P (2008) An integrated model to identify and classify the key criteria and their role in the assessment of 3PL services providers. Asia Pac J Mark Logist 20(2):227–249. https://doi.org/10.1108/13555850810864579
Tseng M, Bui T, Lim M (2021) Resource utilization model for sustainable solid waste management in Vietnam: A crisis response hierarchical structure. Resour Conserv Recycl 171:105632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105632
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix 1
Appendix 1
Expert’s Profile | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
S No | Designation/position | Experience (in Year) | Education | Expertise Area |
1 | Professor | 32 | PhD | Circular Economy, Industry 4.0, and supply chain management |
2 | Academia | 12 | PhD | Sustainable supply chain |
3 | Associate Professor | 13 | PhD | Circular Supply chain management, |
4 | Supply Chain Manager | 14 | B. Tech | Supply chain management |
5 | Procurement Manager | 15 | M. Tech | Supply chain management |
6 | Industrial Consultant | 20 | PhD | Industrial Engineering |
7 | Manufacturing Consultant | 20 | PhD | Production Engineering |
8 | Operations Head | 12 | M. Tech | Mechanical Engineering |
9 | Quality Control Manager | 13 | PhD | Quality Management |
10 | Operations Manager | 15 | M. Tech | Production Management |
11 | Design Engineer | 14 | M. Tech | Production Engineering |
12 | Warehouse Manager | 20 | MBA | Logistics Management |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, S., Haleem, A. & Fatma, N. Effective adoption of remanufacturing practices: a step towards circular economy. Jnl Remanufactur 12, 167–185 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13243-021-00109-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13243-021-00109-y