Abstract
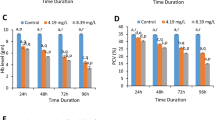
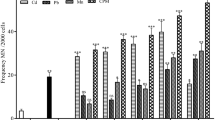
Tannery industries are globally situated. The genotoxic effect was analyzed in erythrocytes of a freshwater fish, Labeo rohita exposed to tannery industry effluent using micronucleus test. Micronucleus test is simple, rapid and reliable method used in laboratory for monitoring genotoxic damage. The 96 h LC50 value was calculated by using Finney method and it came out to be 7.07 %. Fishes were exposed to three sub-lethal concentrations (3.53, 1.76 and 0.88 % of 96 h LC50 value) for 24, 48, 72 and 96 h. Presence of one micronucleus was predominant than two and three to five micronuclei in erythrocytes of fishes exposed to effluent. Concentration 3.53 % proved to be highly toxic and 0.88 % can act as a safe disposal concentration. The results showed concentration and time dependent response. Thus, results revealed that discharge of tannery effluent caused clastogenic effects in fish erythrocytes. This may lead to stock depletion of fishes and aquatic organisms living in rivers. Similar clastogenic effects may also occur in human population living around rivers using contaminated water and consuming contaminated fishes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anubumani S, Mohankumar MN. Nuclear and cytoplasmic abnormalities in the fish Catla catla (Hamilton) exposed to chemicals and ionizing radiation. Res J Environ Sci. 2011;5:867–77.
Ayllon F, Suciu R, Gephard S, Juanes F, Garcia-Vazquez E. Conventional armament wastes induce micronuclei in wild brown trout Salmo trutta. Mutat Res. 2000;470:169–76.
Ayoola SO, Bassey BO, Alimba CG, Ajani EK. Textile effluent induced genotoxic effect and oxidative stress in Clarias gariepius. Pak J Biol Sci. 2012;15:804–12.
Bosnic M, Buljan J, Daniels RP. Pollutants in Tannery effluents. United Nations Industrial Development Organization. 2000. https://www.unido.org/fileadmin/import/userfiles/puffk/l_pollutants.pdf. Accessed 16 April 2015.
Cavas T, Ergene-Gozukara S. Induction of micronuclei and nuclear abnormalities in Oreochromis niloticus following exposure to petroleum refinery and chromium processing plant effluents. Aquat Toxicol. 2005;74:264–71.
Crott JW, Mashiyama SD, Ames BC, Fenech M. The effect of folic acid deficiency and MTHFR C677T polymorphism on chromosome damage in human lymphocytes in vitro. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2001;10:1089–96.
Central Pollution Control Board. Ministry of Environment and Forests. Environment Protection Rules. 2010. http://www.cpcb.nic.in/Industry-Specific-Standards/Effluents/418.pdf. Accessed 15 June 2015.
Ergene S, Cavas T, Celik A, Koleli N, Kaya F, Karahan A. Monitoring of nuclear abnormalities in peripheral erythrocytes of three fish species from the Goksu Delta (Turkey): genotoxic damage in relation to water pollution. Ecotoxicol. 2007;16:385–91.
Fenech M, Holland N, Chang WP, Zeiger E, Bonnasi S. The human micronucleus project an international collaborative study on the use of micronucleus technique for measuring DNA damages in humans. Mutat Res. 1999;428:271–83.
Finney DJ. Probit analysis. 3rd ed. London: Cambridge University Press; 1971.
Gravato C, Santos MA. Juvenile sea bass liver biotransformation and erythrocytic genotoxic responses to pulp mill contaminants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2002;53:104–16.
Jaya Choudary, Abha, Anand MJ. Cytogenetic effect of chromium trioxide in an air breathing teleost Channa punctatus. Int J Pharm Bio Sci. 2012;2:246–53.
Kirschbaum AA, Seriani R, Pereira CDS, Assuncao A, Abessa DMS, Rotundo MM, et al. Cytotoxicity biomarkers in fat snook Centropomus parallelus fromCananeia and Sao Vicente estuaries, Brazil. Genet Mol Biol. 2009;32:151–4.
Manna GK, Biswas S. Micronucleus test (MNT) in four species of fishes treated with bacterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Natl Acad Sci Lett. 1986;9:189–91.
Manna G, Sadhukhan A. Use of cells of gill and kidney of tilapia fish in micronucleus test. Curr Sci. 1986;55:498–501.
Matsumoto ST, Mantovani MS, Malaguttii MIA, Dias AL, Fonseca IC, Marin-Morales MA. Genotoxicity and mutagenicity of water contaminated with tannery effluents, as evaluated by the micronucleus test and comet assay using the fish, Oreochromis niloticus and chromosome aberrations in onion root-tips. Genet Mol Biol. 2006;29:148–58.
Mount DR, Hockett JR. Use of toxicity identification evaluation methods to characterize, identify and confirm hexavalent chromium toxicity in an industrial effluent. Water Res. 2000;34:1379–85.
Poongothai K, Shayin S, Usharani MV. Induction of micronuclei in fish by polluted waterand heavy metals. Cytobios. 1996;86:17–22.
Praveen N, Shadab GGHA. Cytogenetic evaluation of cadmium chloride on Channa Punctatus. J Environ Biol. 2012;33:663–6.
Praveena M, Sailaja MC, Rao KJ. Clatogenic effects induced due to chromium intoxication in a freshwater fish, Labeo rohita (Hamilton). Int J Adv Sci Tech Res. 2014;4:647–56.
Saleh KAJ. The intensity of pollutant genotoxicity in Lake Uluabat. Int J Biotechnol Biochem. 2010;6:625–31.
Shimizu N, Itoh N, Utiyama H, Wahl GM. Selective entrapment of extrachromosomally amplified DNA by nuclear budding and micronucleation during S phase. J Cell Biol. 1998;140:1307–20.
Sreenivasan RS, Moorthy PK. Biochemical stress of chromium in tannery effluents on the freshwater fish, Tilapia mossambicus (Pisces). Int J Biol Med Res. 2011;2:616–20.
Steenken S. Purine basis, nucleosides and nucleotides: aqueous solution redox chemistry and transformation reactions of their radical cations and e− and OH adducts. Chem Rev. 1989;89:503–20.
Von Sonntag C. The chemical basis of radiation biology. New York: Taylor and Francis; 1987.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank the Department of Zoology and Environmental Sciences, Punjabi University, Patiala for extending help and support in the form of infrastructure to carry out the research work smoothly.
Author’s contributions
Diana Handa carried out all the work of collection of effluent, fishes and experimental part with the help of Rohit Kalotra (Co-author), Gurinder Kaur Walia and Dr. Harbhajan Kaur have been involved in drafting the manuscript for its content.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walia, G.K., Handa, D., Kaur, H. et al. Ecotoxicological studies on fish, Labeo rohita exposed to tannery industry effluent by using micronucleus test. Nucleus 58, 111–116 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-015-0140-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-015-0140-5