Abstract
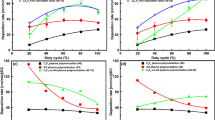
The surface free energy of three polymeric substrates, PMMA (poly(methyl methacrylate)), PS (polystyrene) and PC (polycarbonate), subjected to a RF O2 plasma treatment and washing with water was studied with the aim of fabricating surface micro-systems using a LbL technique. More uniform hysteresis of the deionized(DI) water contact angle after the plasma treatment followed by washing with water was observed on the PS surface compared to that on the PMMA and PC surfaces. XPS showed that washing with water may alter the plasma generated functionality, which readily forms oxygen containing groups, such as C=O and O-C=O. The surface free energy measured by the acid-base method showed that the Lewis base components on PS were less affected than those on PMMA and PC, due to the weak solvent effect of the former. During the LbL coating of the polyelectrolyte, the solvent effect was less likely to occur on PS, which exhibited better electrostatic bonding of the positive and negative polyelectrolytes (PEL). The fluorescence intensity was similar to the above findings, which may help determine the best substrate for surface micro-patterning using the LbL technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q. G. Tan, J. Ji, M. A. Barbosa, C. Fonseca, and J. C. Shen, Biomaterials, 24, 4699 (2003).
Y. H. Wang, C. X. Guo, Y. W. Chen, C.W. Hu, and W. H. Yu, J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 264, 176 (2003).
G. Decher, Science, 277, 1232 (1997).
A. R. Esker, C. Mengel, and G. Wegner, Science, 280, 892 (1998).
A. Michna, Z. Adamczyk, and M. Zembala, Colloid Surface A, 302, 467 (2007).
A. Asthana, Y. Asthana, I. K. Sung, and D. P. Kim, Lab Chip, 6, 1200 (2006).
H. W. Shim, J. H. Lee, T. S. Hwang, Y. W. Rhee, Y. M. Bae, J. S. Choi, J. Y. Han, and C. S. Lee, Biosens. Bioelectron., 22, 3188 (2007).
F. L. Yap and Y. Zhang, Bionsens. Bioelectron., 22, 775 (2007).
J. A. Jaber and J. B. Schlenoff, Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci., 11, 324 (2006).
D. Falconnet, G. Csucs, H. M. Grandin, and M. Textor, Biomaterials, 27, 3044 (2006).
Y. Zhao, S. Tang, S.-W. Myung, N. Lu, and H.-S. Choi, Polymer Testing, 25, 327 (2006).
B. V. Derjaguin and L. Landau, Acta Physicochim. URSS, 14, 633 (1941)
E. J. Verway and J. T. G. Overbeek, Theory of the Stability of Lyophobic Colloids, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1948.
J. H. Lee, H. W. Shim, H. S. Choi, Y. A. Son, and C. S. Lee, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 69, 1581 (2008).
L. H. Lee, Langmuir, 12, 1681 (1996).
B. Bouali, F. Ganachaud, J. P. Chape, C. Pichot, and P. Lanteri, J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 208, 81 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Tang, S., Choi, HK. et al. Effect of plasma-treated polymer substrates on fabricating surface microsystems through LbL coating. Macromol. Res. 18, 413–420 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-010-0506-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-010-0506-0